Belehrung Nach 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz Vorlage
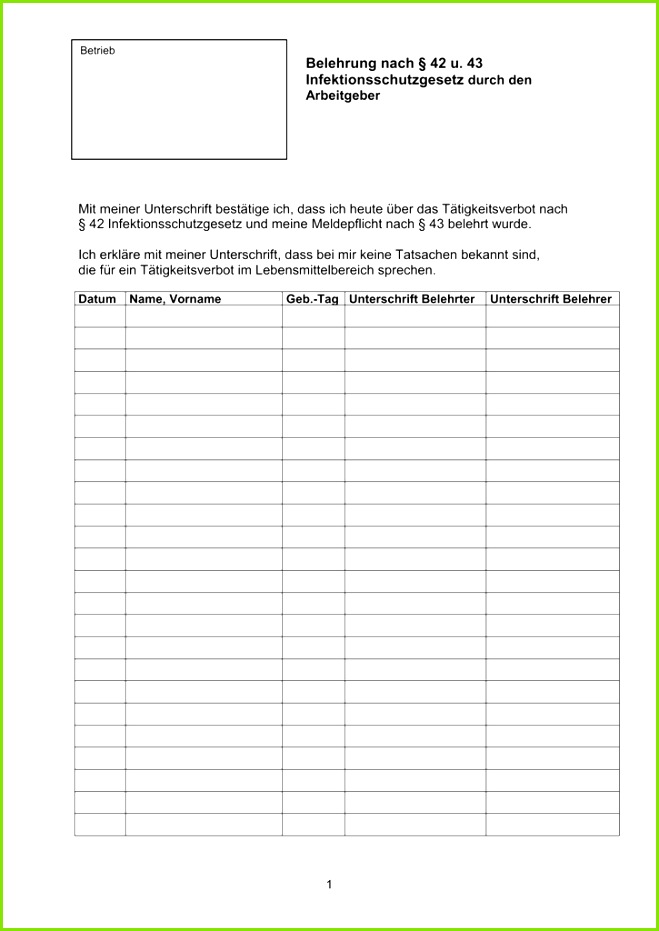
The "Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz" (Instruction according to § 43 Infection Protection Act) is a mandatory health instruction in Germany for individuals working in the food industry. This article provides a comprehensive overview of what this instruction entails, who needs it, its purpose, the process of obtaining it, and its validity.
What is the Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz?
The "Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz" is a legally required instruction on hygiene and infection prevention, based on § 43 of the German Infektionsschutzgesetz (IfSG – Infection Protection Act). Its primary aim is to prevent the spread of infectious diseases through food.
This instruction covers essential aspects of food hygiene, personal hygiene, and relevant legal regulations. It emphasizes the importance of identifying symptoms of certain infectious diseases and taking appropriate action to prevent contamination of food.
Who Needs this Instruction?
Anyone who works in direct contact with food, or with utensils that come into contact with food, needs this instruction before starting their employment. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Restaurant staff (cooks, waiters/waitresses, kitchen helpers)
- Employees in food processing plants (e.g., meat processing, bakeries)
- Staff in canteens and cafeterias
- Food vendors (e.g., market stalls, food trucks)
- Personnel involved in food transportation and storage
- Childcare workers preparing food for children
Essentially, if your job involves handling, preparing, serving, or selling food, you are legally required to undergo this instruction.
What Does the Instruction Cover?
The Belehrung covers a range of topics, including:
Infectious Diseases
The instruction will cover common infectious diseases that can be transmitted through food, such as:
- Salmonellosis (Salmonella infection)
- Shigellosis (Shigella infection)
- Campylobacteriosis (Campylobacter infection)
- Escherichia coli infections (EHEC)
- Norovirus infections
- Hepatitis A and E
You will learn about the symptoms of these diseases and how they can be transmitted through contaminated food.
Hygiene Practices
The Belehrung emphasizes the importance of proper hygiene practices, including:
- Handwashing: Proper handwashing techniques are thoroughly explained, including when and how to wash your hands effectively. This is a crucial aspect of preventing the spread of pathogens.
- Personal Hygiene: Maintaining good personal hygiene, such as showering regularly, wearing clean clothing, and keeping fingernails short and clean, is also addressed.
- Food Handling: Safe food handling practices, such as preventing cross-contamination, storing food at appropriate temperatures, and cooking food thoroughly, are covered in detail.
- Workplace Hygiene: Maintaining a clean and hygienic work environment, including regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces and equipment, is also emphasized.
Legal Responsibilities
The instruction also covers your legal responsibilities as a food handler, including:
- Reporting any symptoms of infectious diseases to your employer immediately.
- Adhering to all hygiene regulations and guidelines.
- Cooperating with health authorities in the event of an outbreak.
How to Obtain the Belehrung
There are several ways to obtain the Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz:
- Local Health Department (Gesundheitsamt): The most common way is to attend a training session at your local health department (Gesundheitsamt). These sessions are often offered in multiple languages and are usually free of charge. Contact your local Gesundheitsamt to find out about upcoming dates and registration procedures.
- Online Courses: Many online providers offer certified Belehrung courses. These courses are often more convenient as they can be completed at your own pace and on your own schedule. However, ensure that the online course is officially recognized by the German authorities.
- Employer-Provided Training: Some employers, particularly larger companies, may offer the Belehrung training in-house.
Regardless of the method you choose, you will typically receive a certificate upon completion of the instruction. This certificate serves as proof that you have undergone the required training and are aware of your responsibilities regarding food hygiene.
What to Expect During the Instruction
The instruction session typically involves a presentation or lecture followed by a short quiz or test to assess your understanding of the material. The duration of the instruction varies depending on the provider, but it usually lasts between one and two hours.
You will be provided with informational materials, such as handouts or brochures, that summarize the key points covered during the instruction. It is important to pay attention during the instruction and ask any questions you may have to ensure that you fully understand the content.
Important: Bring your ID (passport or similar) as proof of identity.
Validity of the Belehrung
The initial Belehrung is valid indefinitely. However, it is your responsibility to ensure that your knowledge of food hygiene and infection prevention remains up-to-date. Employers are also required to provide regular refresher training to their employees.
While the law doesn't specify a mandatory re-training interval, best practice dictates that refresher courses should be attended regularly. Many employers recommend (and sometimes require) a refresher course every one to two years. This is especially important as regulations and best practices in food hygiene can change over time.
Keep your certificate safe, as you may need to present it to your employer or to health authorities upon request.
Cost of the Belehrung
The cost of the Belehrung varies depending on the provider. Attending a session at the local Gesundheitsamt is often free of charge. Online courses typically cost between €20 and €50. Employer-provided training is usually free for employees.
Consequences of Not Having the Belehrung
Working in the food industry without the required Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz is a violation of German law. Both the employee and the employer can face penalties, including fines. In severe cases, the business may even be temporarily shut down.
More importantly, working without proper knowledge of food hygiene and infection prevention can put the health of consumers at risk. By undergoing the Belehrung, you are contributing to the safety and well-being of the community.
Where to Find More Information
You can find more information about the Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz on the following websites:
- Your local Gesundheitsamt website.
- The website of the Robert Koch-Institut (RKI), the German federal government's central institution for disease control and prevention.
- The website of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (Bundesministerium für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft, BMEL).
By taking the time to understand the requirements of the Belehrung nach § 43 Infektionsschutzgesetz and undergoing the necessary training, you can ensure that you are complying with German law and contributing to the safety of the food supply.
This information is intended for general guidance only and does not constitute legal advice. Always consult with the relevant authorities or a qualified professional for specific advice related to your situation.