Als Wenn Oder Als Ob

Understanding the nuances of conjunctions like als, wenn, oder, and als ob is crucial for mastering German grammar and expressing yourself accurately. These words, while seemingly simple, introduce different types of clauses and convey distinct meanings related to time, comparison, alternatives, and hypothetical situations. This article provides a comprehensive guide to using these conjunctions correctly.
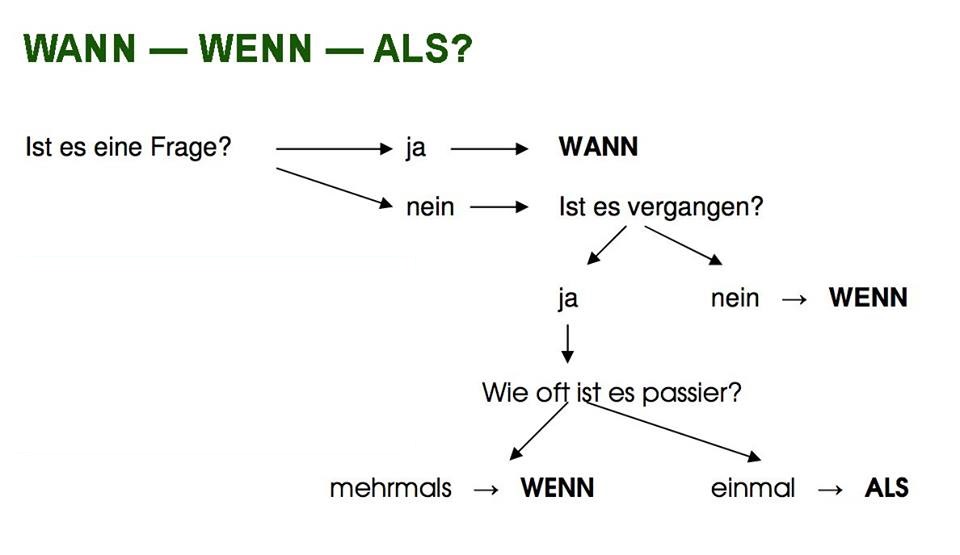
Als: Comparisons in the Past
The word als is primarily used for comparisons when referring to a past event or a statement that is generally untrue in the present. It translates to "than" in English when making a comparison.
Usage and Examples:
- Unequal Comparisons in the Past: Als is used when comparing two things that are not equal, specifically when the action or state being compared is in the past.
- With Negative Statements in the Present: Als can also be used when the statement being compared to is demonstrably false.
Ich war jünger, als ich dachte. (I was younger than I thought.)
Das Essen war besser, als ich erwartet hatte. (The food was better than I had expected.)
Er ist nicht so reich, als er vorgibt. (He is not as rich as he pretends to be.)
Important Considerations:
- Avoid with Equal Comparisons: Do not use als when the things being compared are equal. Instead, use so…wie.
Falsch: Er ist so groß als sein Bruder. Richtig: Er ist so groß wie sein Bruder. (He is as tall as his brother.)
- Case after als: The case of the noun or pronoun following als depends on the grammatical function within the clause. Often, the nominative case is used for simple comparisons.
Er ist älter als ich. (He is older than I.) (ich is in the nominative case.)
Wenn: Conditional and Repeated Actions
Wenn introduces conditional clauses ("if") and describes repeated actions or general truths. It is one of the most versatile conjunctions in German.
Usage and Examples:
- Conditional Clauses: Wenn is used to express conditions. It translates to "if" in English. The clause introduced by wenn describes the condition, and the main clause describes the consequence.
Wenn ich Zeit habe, gehe ich ins Kino. (If I have time, I will go to the cinema.)
Wenn es regnet, bleiben wir zu Hause. (If it rains, we will stay at home.)
- Repeated Actions: Wenn can also describe actions that occur repeatedly or habitually.
Wenn ich müde bin, trinke ich Kaffee. (When I am tired, I drink coffee.)
Wenn die Sonne scheint, gehe ich spazieren. (When the sun shines, I go for a walk.)
- General Truths: Wenn can introduce statements that are generally true.
Wenn man lernt, verbessert man sich. (When one studies, one improves.)
Word Order with Wenn Clauses:
Wenn introduces a subordinate clause. This means the verb in the wenn clause goes to the end of the clause. When the wenn clause comes before the main clause, there is a verb-subject inversion in the main clause.
Wenn ich Zeit habe, gehe ich ins Kino. (verb at the end of the wenn clause)
Wenn ich Zeit habe, gehe ich ins Kino. (verb-subject inversion in the main clause)
Ich gehe ins Kino, wenn ich Zeit habe. (No inversion if the wenn clause follows the main clause)
Oder: Expressing Alternatives
Oder simply means "or" and is used to present alternatives or choices.
Usage and Examples:
- Presenting Alternatives: Oder connects two or more possibilities.
Möchtest du Kaffee oder Tee? (Would you like coffee or tea?)
Wir können ins Kino gehen oder zu Hause bleiben. (We can go to the cinema or stay at home.)
- Offering Corrections or Clarifications: Oder can also be used to offer a correction or clarification.
Das ist der Dom, oder? (That's the cathedral, isn't it?) (A tag question)
Er ist Lehrer, oder besser gesagt, war Lehrer. (He is a teacher, or rather, he used to be a teacher.)
Word Order with Oder:
Oder does not affect the word order of the clauses it connects. Each clause maintains its standard word order.
Als Ob: Hypothetical Situations and Comparisons
Als ob is used to express hypothetical situations or comparisons that are not necessarily true. It translates to "as if" or "as though" in English.
Usage and Examples:
- Hypothetical Situations: Als ob introduces a clause that describes a situation that is contrary to fact or unlikely to be true. The verb in the als ob clause is always in the subjunctive II (Konjunktiv II) form.
Er tut so, als ob er alles wüsste. (He acts as if he knew everything.) (He doesn't actually know everything.)
Sie sah aus, als ob sie geweint hätte. (She looked as if she had been crying.) (She may or may not have been crying.)
- Expressing Doubt or Disbelief: Als ob can also express doubt or disbelief about a statement.
Als ob das wahr wäre! (As if that were true!) (I don't believe that's true.)
Grammatical Structure with Als Ob:
The als ob clause requires the use of the subjunctive II. If the subjunctive II form is the same as the past tense form (Präteritum), then the auxiliary verb würde + infinitive is used to avoid ambiguity. For example:
- Er tat, als ob er krank wäre. (He acted as if he were sick.) (wäre is the subjunctive II form of sein)
- Er tat, als ob er das Buch gelesen hätte. (He acted as if he had read the book.) (gelesen hätte is the subjunctive II perfect form of lesen, which is preferred over *las*)
- Er tat, als ob er kommen würde. (He acted as if he would come.) (Using würde because the Präteritum form of kommen is *kam*, which is identical to the indicative.)
Note that sometimes, the subjunctive I (Konjunktiv I) is used for als ob clauses, although it's less common.
Summary Table
To further clarify the usage, here's a summary table:
| Conjunction | Meaning | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Als | Than | Unequal comparisons in the past; negative statements in the present. | Ich war kleiner als mein Bruder. (I was shorter than my brother.) |
| Wenn | If/When | Conditional clauses, repeated actions, general truths. | Wenn es regnet, bleibe ich zu Hause. (If it rains, I stay at home.) |
| Oder | Or | Expressing alternatives or choices. | Möchtest du Kaffee oder Tee? (Would you like coffee or tea?) |
| Als ob | As if/As though | Hypothetical situations and comparisons, expressing doubt. | Er tut so, als ob er alles wüsste. (He acts as if he knew everything.) |
Mastering these conjunctions will significantly improve your German fluency and allow you to express more complex ideas with accuracy. Practice using them in various contexts to solidify your understanding. Good luck!