Direkte Demokratie Vor Und Nachteile Tabelle
Willkommen! You've probably heard about Switzerland, land of stunning landscapes, delicious chocolate, and… direct democracy. It's a concept woven into the very fabric of Swiss life, and it’s more than just a political system; it’s a way of life. As you explore Switzerland, you'll encounter it everywhere, from ballot boxes in train stations to lively discussions in local cafes. Understanding direct democracy will not only enrich your travel experience but also give you a deeper insight into what makes Switzerland so unique.
What Exactly is Direct Democracy?
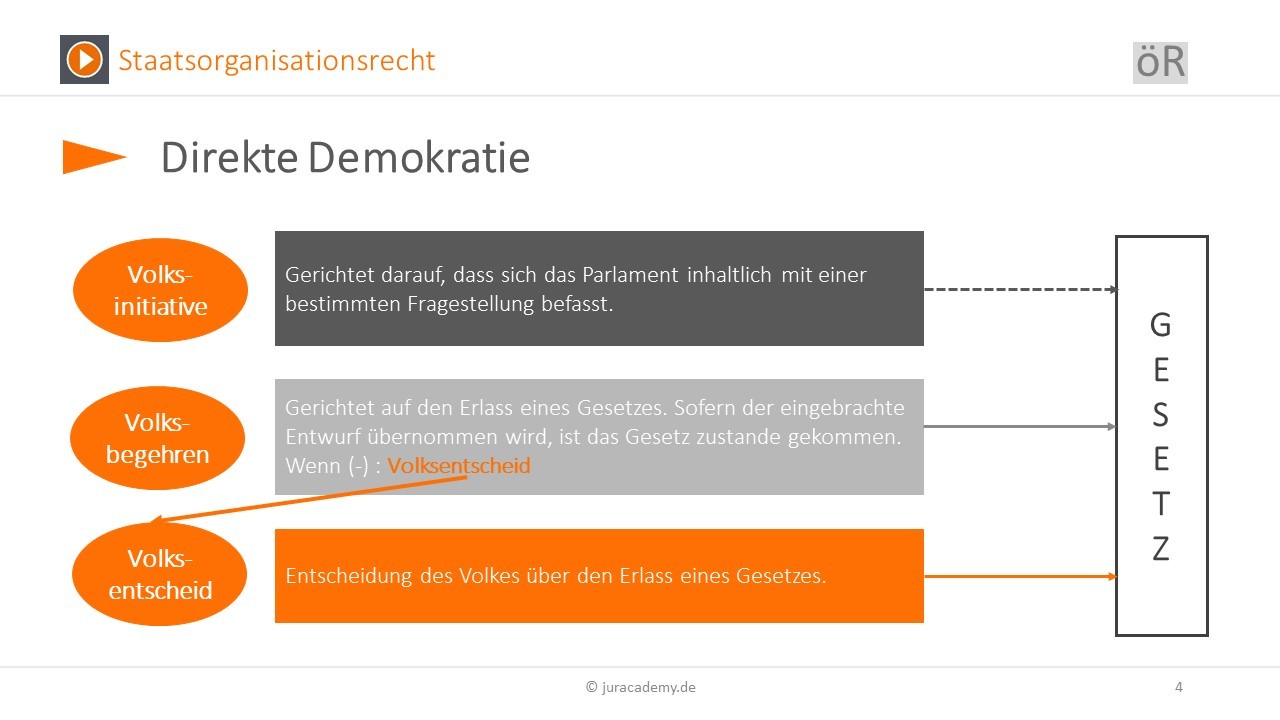
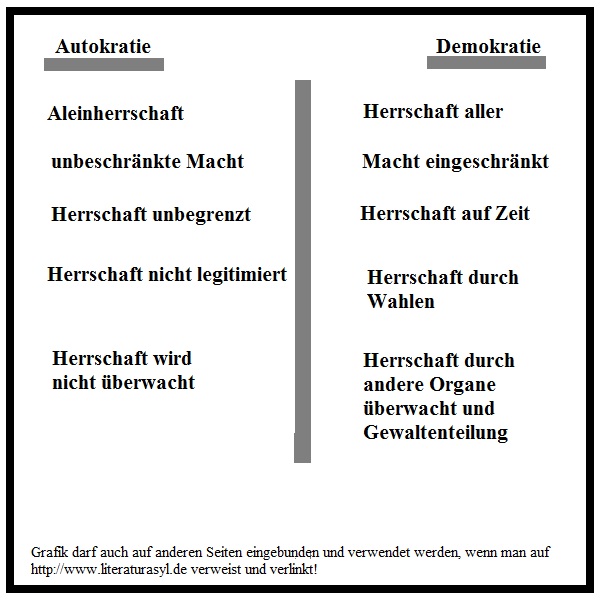
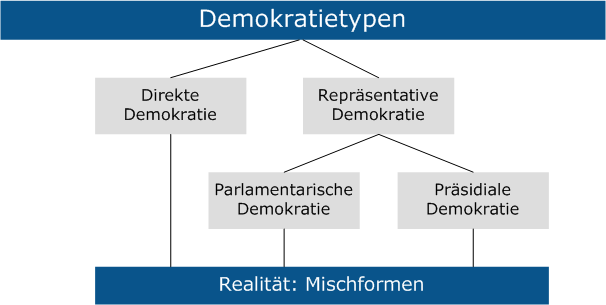
Unlike representative democracies where elected officials make decisions on behalf of the people, direct democracy empowers citizens to directly participate in the decision-making process. Think of it as a town hall meeting on a national scale, but with modern technology to make it accessible to everyone. In Switzerland, this happens primarily through popular initiatives and referendums.
A popular initiative allows citizens to propose changes to the constitution. If enough signatures (usually around 100,000) are collected, the proposal is put to a national vote. This gives citizens the power to set the agenda and bring important issues to the forefront.
A referendum, on the other hand, allows citizens to vote on laws passed by parliament. There are two main types: a mandatory referendum, which is required for constitutional amendments or joining international organizations, and an optional referendum, which can be triggered if enough citizens (usually around 50,000) request a vote on a specific law. This ensures that the government remains accountable to the people and that no major decision is made without their consent.
Direct Democracy in Action: A Quick History
The roots of direct democracy in Switzerland go back centuries to the Landsgemeinden, open-air assemblies where citizens directly made decisions in cantons like Appenzell Innerrhoden and Glarus. While these traditional assemblies still exist in a few cantons, the modern system of direct democracy was gradually developed throughout the 19th century, solidifying Switzerland's unique political identity.
Today, Switzerland boasts one of the most developed direct democratic systems in the world. It's a constantly evolving process, with ongoing debates about how to improve participation and ensure that all voices are heard. From environmental protection to social welfare, direct democracy has shaped Switzerland's policies and values in profound ways.
The Good and the Not-So-Good: A Balanced View
Direct democracy, like any political system, has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both sides of the coin is crucial to appreciating its complexities.
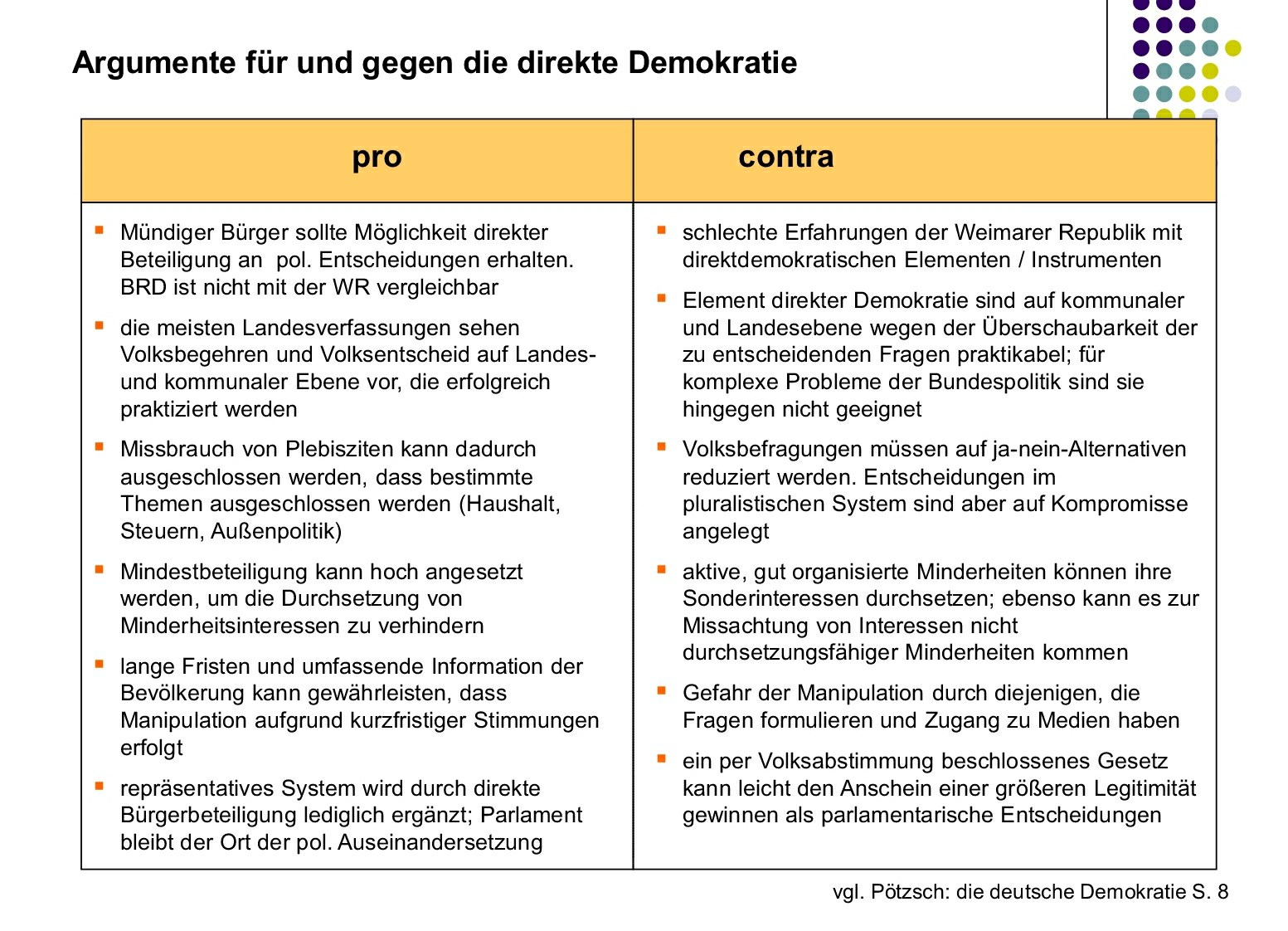
Pros and Cons of Direct Democracy: A Table
Here's a table summarizing the main advantages and disadvantages of direct democracy:
| Advantages (Vorteile) | Disadvantages (Nachteile) |
|---|---|
Increased Citizen Participation: Empowers citizens to actively participate in decision-making, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility. |
Tyranny of the Majority: Decisions may not always protect the rights of minorities, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes. |
Greater Government Accountability: Keeps the government in check by allowing citizens to overturn unpopular laws and propose new ones. |
Complexity and Information Overload: Citizens need to be well-informed about complex issues, which can be time-consuming and challenging. |
Enhanced Political Stability: Fosters consensus and reduces the risk of radical political shifts. |
Slow Decision-Making Process: Referendums and initiatives can take time, leading to delays in implementing important policies. |
Increased Legitimacy of Laws: Laws passed through direct democracy are generally perceived as more legitimate and enjoy greater public support. |
Voter Apathy: Despite opportunities for participation, some citizens may choose not to engage, leading to lower turnout rates. |
Education and Awareness: Forces citizens to educate themselves on important issues, leading to a more informed electorate. |
Influence of Special Interests: Well-funded interest groups may be able to sway public opinion through advertising and lobbying. |
Reduced Corruption: Makes it more difficult for corrupt officials to abuse their power, as citizens have the power to hold them accountable. |
Potential for Instability if Misused: Can be exploited by extremist groups to push divisive or harmful agendas. |
Stronger Social Cohesion: Promotes dialogue and compromise, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility. |
Framing Effects and Manipulation: The way issues are framed can significantly influence voter behavior, potentially leading to biased outcomes. |
Digging Deeper: Understanding the Nuances
Let's explore some of these points in more detail:
* Increased Citizen Participation vs. Voter Apathy: While direct democracy offers opportunities for greater participation, it doesn't guarantee it. Voter turnout can vary significantly depending on the issue at stake. Factors like the complexity of the issue, the level of public awareness, and the perceived importance of the outcome can all influence participation rates. * Greater Government Accountability vs. Slow Decision-Making: The referendum process can certainly slow things down, as laws are subject to popular vote. However, proponents argue that this delay is a worthwhile trade-off for ensuring that laws reflect the will of the people and are not rushed through without proper consideration. * Tyranny of the Majority vs. Stronger Social Cohesion: Finding a balance between protecting minority rights and respecting the will of the majority is a constant challenge in any democracy. Switzerland addresses this through various mechanisms, including constitutional safeguards, independent courts, and a culture of compromise and consensus-building. * Complexity and Information Overload vs. Education and Awareness: Direct democracy demands that citizens be well-informed. The Swiss government and various organizations provide information about upcoming votes, but it's ultimately up to each individual to engage with the issues and make their own informed decision. This can be challenging in an era of information overload and misinformation. * Influence of Special Interests: Just like in any political system, special interests can exert influence in direct democracy. However, the transparency of the Swiss system and the ability of citizens to directly challenge decisions can help to mitigate this influence.Experiencing Direct Democracy Firsthand
As a visitor to Switzerland, you can witness direct democracy in action in several ways:
* Observe a Landsgemeinde: If you happen to be in Appenzell Innerrhoden or Glarus during the Landsgemeinde season (usually in late April or early May), consider attending one of these open-air assemblies. It's a unique and historic experience that offers a glimpse into the origins of direct democracy. * Read the Newspapers: Swiss newspapers provide extensive coverage of political debates and upcoming votes. Even if you don't speak German, French, Italian, or Romansh fluently, you can still get a sense of the key issues and arguments by reading the headlines and looking at the visuals. * Talk to Locals: Engage in conversations with Swiss citizens about political issues. You'll likely find that they are passionate about their country and its system of governance, and they'll be happy to share their perspectives with you. * Check Out Government Websites: The Swiss government provides information about upcoming votes and initiatives on its website. While much of the content is in the national languages, you may find some information available in English as well.Direct Democracy: More Than Just a System
Ultimately, direct democracy in Switzerland is more than just a political system; it's a cultural value. It reflects a deep-seated belief in the importance of citizen participation, government accountability, and consensus-building. As you explore Switzerland, take the time to learn more about this unique aspect of Swiss life. It will undoubtedly enhance your understanding of the country and its people, leaving you with a richer and more meaningful travel experience. The concept of actively participating in decision-making and shaping your community's future is deeply ingrained in the Swiss psyche. It’s a fascinating system that encourages active citizenship and ensures that the government truly represents the will of the people. Enjoy your exploration of Switzerland – and its unique political landscape!