Gründung Von Brd Und Ddr
Hallo und herzlich willkommen! Germany, a land steeped in history and culture, holds a unique story of division and reunification. This guide aims to unravel the complexities surrounding the founding of the Federal Republic of Germany (BRD) and the German Democratic Republic (DDR), offering insights for tourists, expats, and those planning a short stay. Understanding this pivotal period will undoubtedly enrich your experience of Germany.
The Aftermath of World War II: A Divided Germany
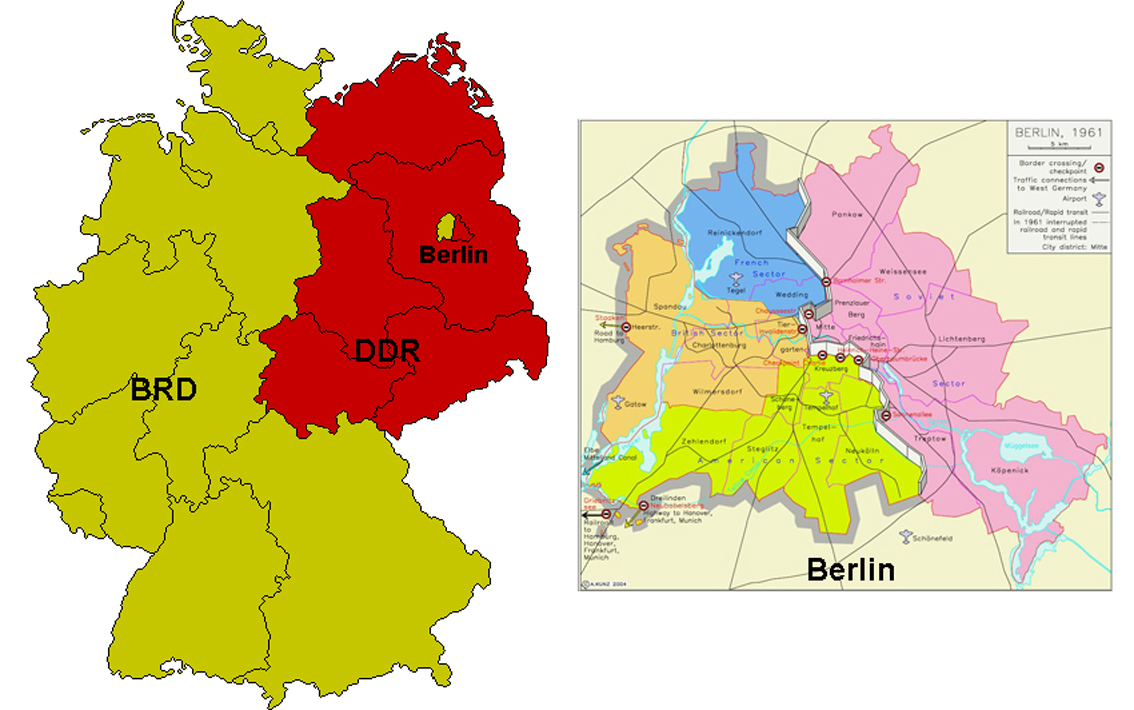
To truly grasp the founding of the BRD and DDR, we must first understand the context of post-World War II Germany. The unconditional surrender of Nazi Germany in May 1945 left the country in ruins, both physically and politically. The Allied powers – the United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union – assumed control of the country, dividing it into four occupation zones.
Each Allied power administered its respective zone, with Berlin, located entirely within the Soviet zone, also divided into four sectors. Initially, the Allied powers aimed to govern Germany collectively through the Allied Control Council. However, growing ideological differences between the Western Allies and the Soviet Union soon led to increasing tensions and a breakdown of cooperation.
The Yalta Conference and the Potsdam Conference in 1945 outlined the initial plans for the post-war order in Germany, focusing on demilitarization, denazification, democratization, and decartelization. However, disagreements over the implementation of these principles, particularly regarding economic reconstruction and the future political structure of Germany, widened the gap between the East and West.
The Seeds of Division: Diverging Ideologies
The diverging ideologies of the Allied powers played a crucial role in the eventual division of Germany. The Western Allies – the United States, Great Britain, and France – advocated for a democratic and capitalist Germany, integrated into the Western European economy. They supported the development of a market-based economy and the establishment of a parliamentary democracy.
In contrast, the Soviet Union aimed to create a socialist state in its occupation zone, aligned with the Soviet bloc. The Soviets promoted the nationalization of industries, the collectivization of agriculture, and the establishment of a communist government. They saw Germany as a crucial buffer zone against Western influence.
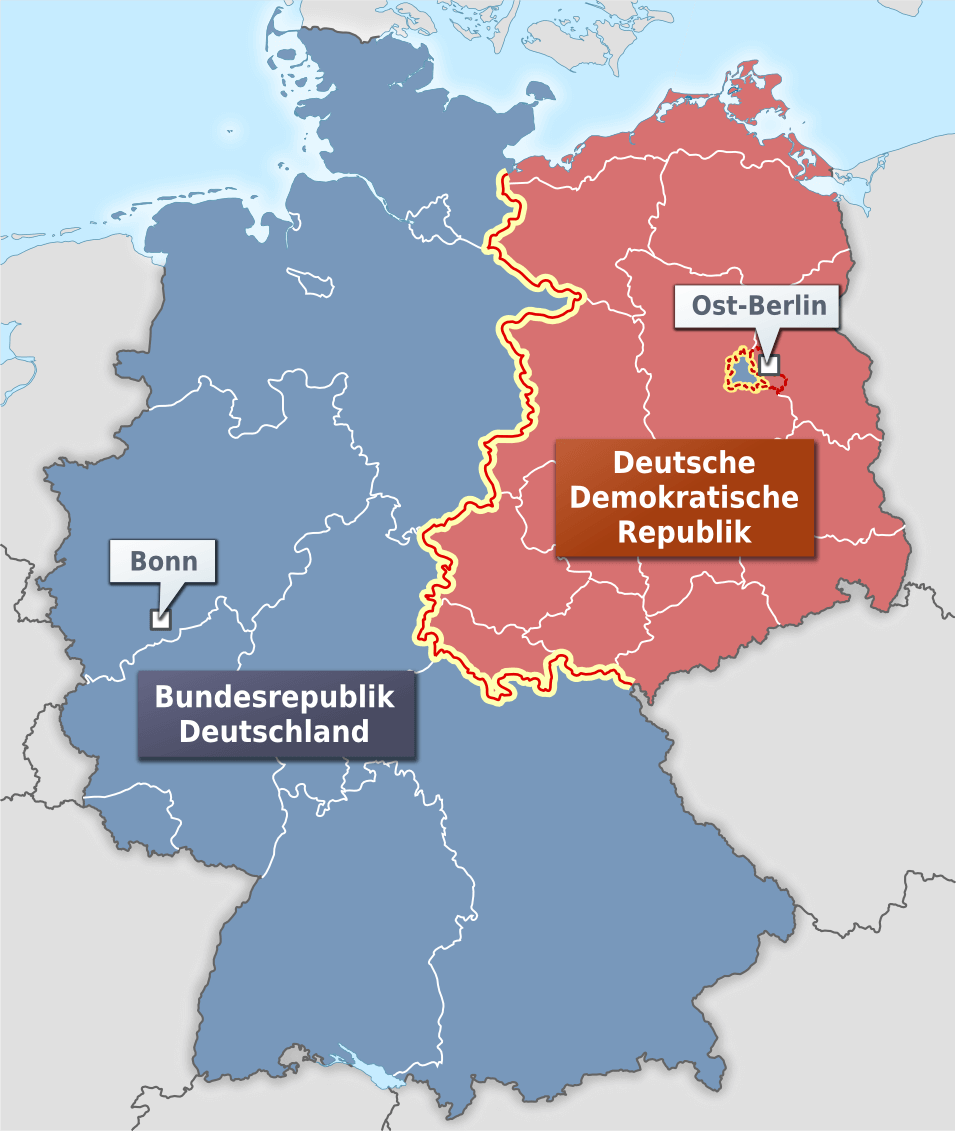
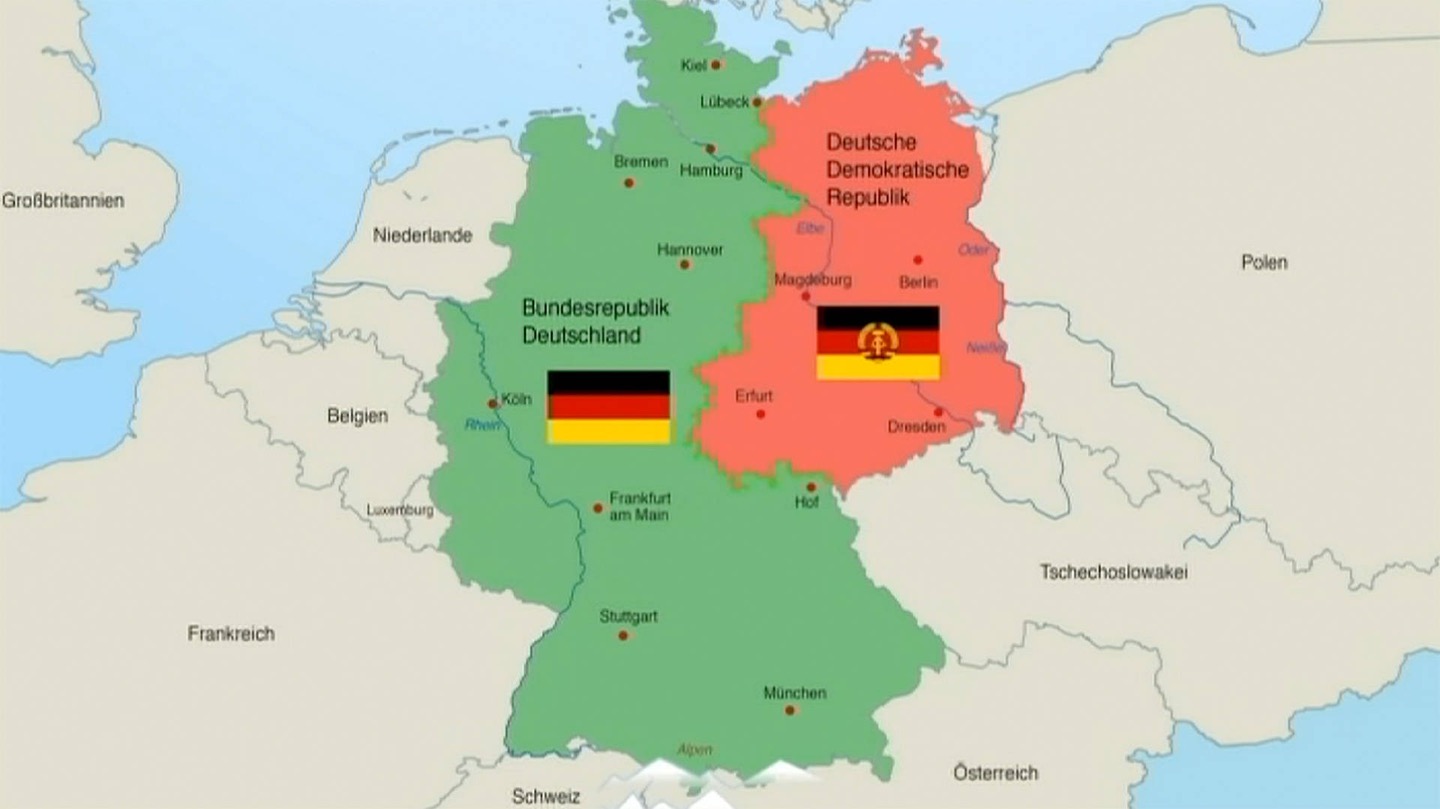
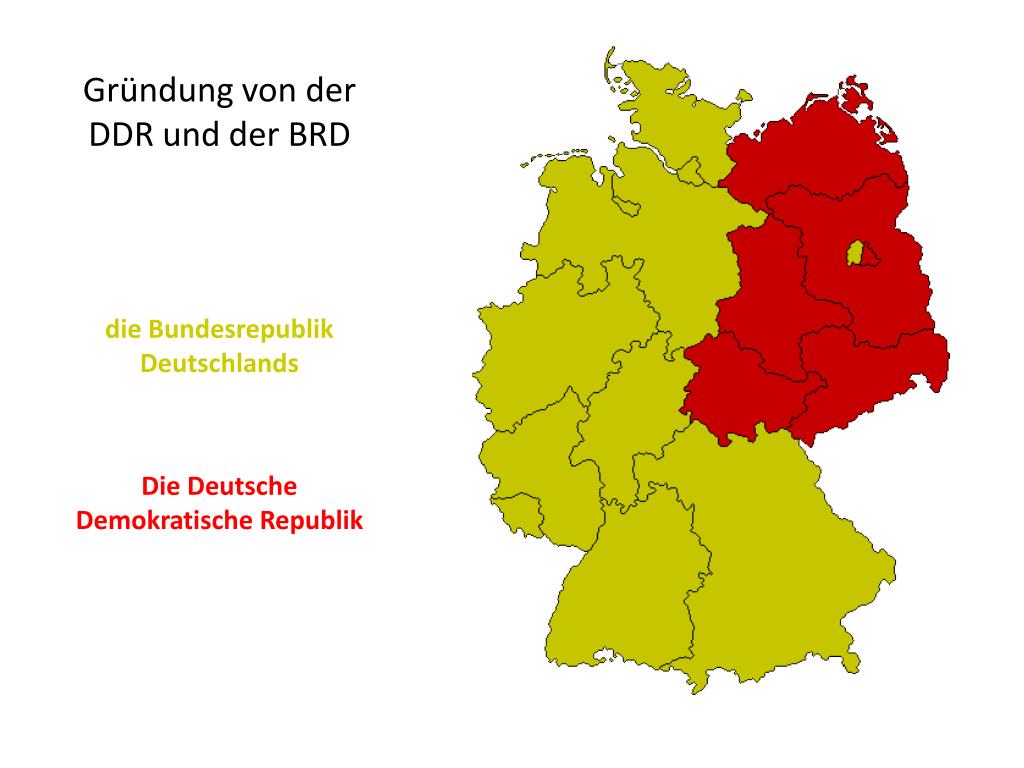
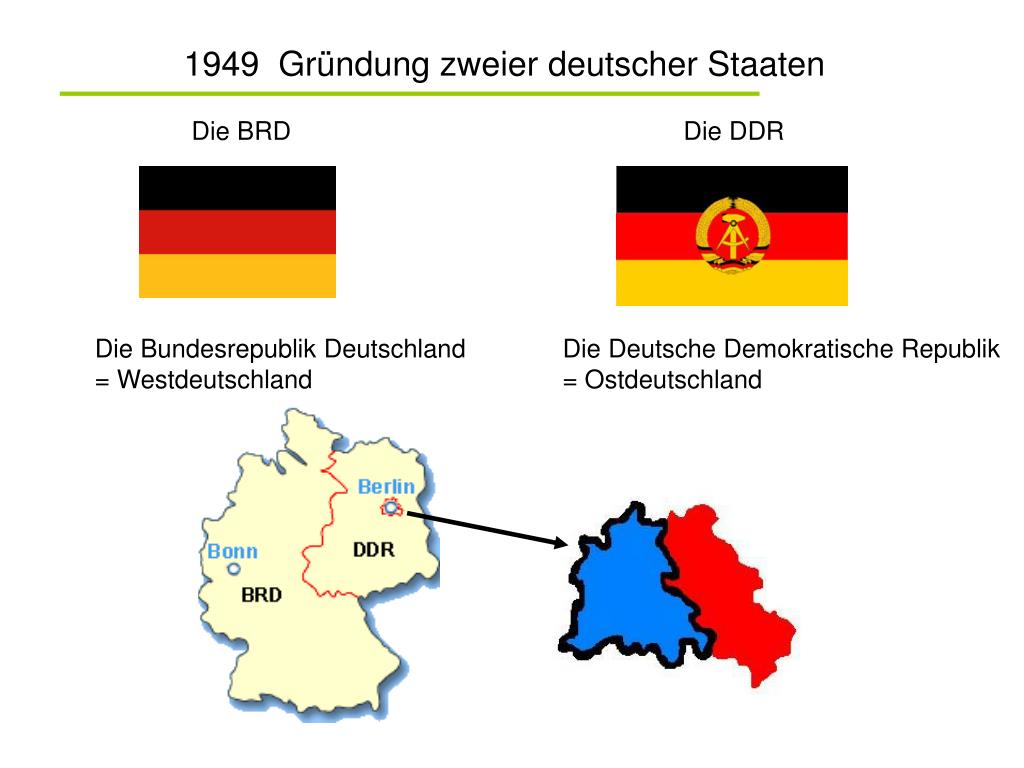
The Founding of the Federal Republic of Germany (BRD)
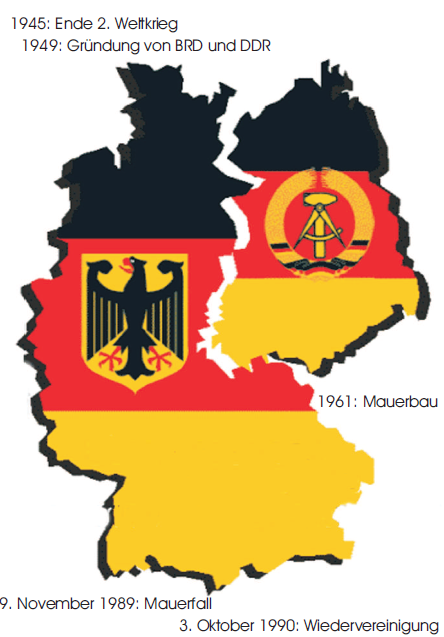
In 1949, the tensions between the Allied powers reached a breaking point. The Western Allies decided to proceed with the formation of a separate West German state. In April 1949, the "Basic Law" (Grundgesetz) was drafted and approved by the parliamentary council, composed of representatives from the Western occupation zones. This Basic Law served as the constitution of the new Federal Republic of Germany.
On May 23, 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany (BRD) was officially proclaimed in Bonn. Konrad Adenauer, a prominent member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), became the first Chancellor of West Germany. The BRD adopted a parliamentary democracy, with free elections and a multi-party system. It embraced a market economy and aligned itself with the Western powers, becoming a key member of NATO and the European Economic Community (EEC).
The BRD prioritized economic reconstruction and integration into the Western world. The "Wirtschaftswunder" (Economic Miracle) of the 1950s and 1960s saw West Germany experience rapid economic growth and prosperity, transforming it into a major economic power.
The Founding of the German Democratic Republic (DDR)
In response to the formation of the BRD, the Soviet Union established the German Democratic Republic (DDR) in its occupation zone. On October 7, 1949, the DDR was officially proclaimed in East Berlin. Wilhelm Pieck became the first President of the DDR, and Otto Grotewohl served as the first Prime Minister. The DDR adopted a socialist system, with the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) holding a dominant role in government and society.
The DDR was a one-party state, where political opposition was suppressed. The state controlled the economy, the media, and all aspects of public life. The Stasi (Staatssicherheit), the state security service, played a crucial role in maintaining control and suppressing dissent.
The DDR aimed to build a socialist society based on Marxist-Leninist principles. It nationalized industries, collectivized agriculture, and focused on industrial development. However, the DDR's economy struggled to compete with the West German economy, and living standards remained significantly lower.
The Berlin Wall: A Symbol of Division
The most visible symbol of the division of Germany was the Berlin Wall, erected by the DDR government in 1961. The Wall was built to prevent East Germans from fleeing to West Berlin and West Germany. It physically separated families, friends, and communities, and became a potent symbol of the Cold War.
The Berlin Wall not only divided Berlin but also represented the broader ideological and political divide between East and West. It served as a stark reminder of the restrictions on freedom and movement imposed by the DDR regime.
Experiencing the Legacy Today
Visiting Germany today offers a unique opportunity to explore the legacy of the division and reunification. In Berlin, you can visit remnants of the Berlin Wall, such as the East Side Gallery, and learn about the history of the Wall at the Berlin Wall Memorial. The Brandenburg Gate, once located in the no-man's land between East and West Berlin, now stands as a symbol of German unity.
You can also explore the former East German territories and experience the cultural differences that still exist between East and West Germany. Visiting museums and historical sites dedicated to the history of the DDR provides valuable insights into life under communist rule.
Understanding the founding of the BRD and DDR is essential for appreciating the complexities of German history and culture. It allows you to engage with the past and understand the challenges and triumphs of reunification. As you travel through Germany, take the time to reflect on the legacy of division and the importance of freedom and democracy.
Tips for Tourists and Expats:
- Learn about local history: Research the history of the region you are visiting, paying particular attention to the period of division.
- Visit historical sites and museums: Explore museums and historical sites dedicated to the history of the BRD and DDR.
- Talk to locals: Engage in conversations with locals to learn about their experiences and perspectives on the division and reunification.
- Be respectful of different viewpoints: Understand that different people may have different perspectives on the past.
- Reflect on the legacy of division: Consider the impact of the division on German society and the importance of freedom and democracy.
The history of the BRD and DDR is a crucial part of understanding modern Germany. By learning about this period, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the country's culture, its people, and its place in the world. We hope this guide has provided you with a valuable introduction to this important topic. Enjoy your trip to Germany!
Disclaimer: While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this guide, it is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a definitive historical account.
![Gründung Von Brd Und Ddr DDR und BRD • DDR und BRD im Vergleich · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/DDR_und_BRD_Karte-1024x576.jpg)







(25609718627BE4A35E2D829EDB185432).jpg)