How To Write A Summary In English

Welcome to the wonderful world of summarizing! Whether you’re a tourist trying to quickly understand a museum guide, an expat catching up on local news, or simply someone prepping for a short stay and wanting to absorb key information fast, mastering the art of summary writing is an invaluable skill. Don't worry, it's easier than you think! This guide will break down the process into simple, manageable steps, so you can confidently create clear and concise summaries in English.
What Exactly Is a Summary?
Before diving in, let's clarify what we mean by "summary." A summary is a shortened version of a text that captures its main points and key ideas. It's like the essence of the original piece, distilled into a more compact and easily digestible form. Think of it as providing a brief overview or a "sneak peek" into the full text. Crucially, a good summary remains objective, meaning it doesn't include your personal opinions, interpretations, or embellishments. You're simply relaying the author's ideas in a shorter format. We want to provide just the facts!
Why is summarizing important for travelers and expats?
Imagine you're visiting a historical site with tons of informational placards. Reading every single one in detail could take hours! A quick summary of each will allow you to absorb the core facts more efficiently and move on to the next interesting exhibit. Similarly, if you're trying to navigate a new country's political landscape through local news, you don't necessarily need to read every in-depth article. Summaries help you stay informed without getting bogged down in the details. Also, if you're learning the language, summarization can be a great method for solidifying new vocabulary and grammatical structures you encounter in text.
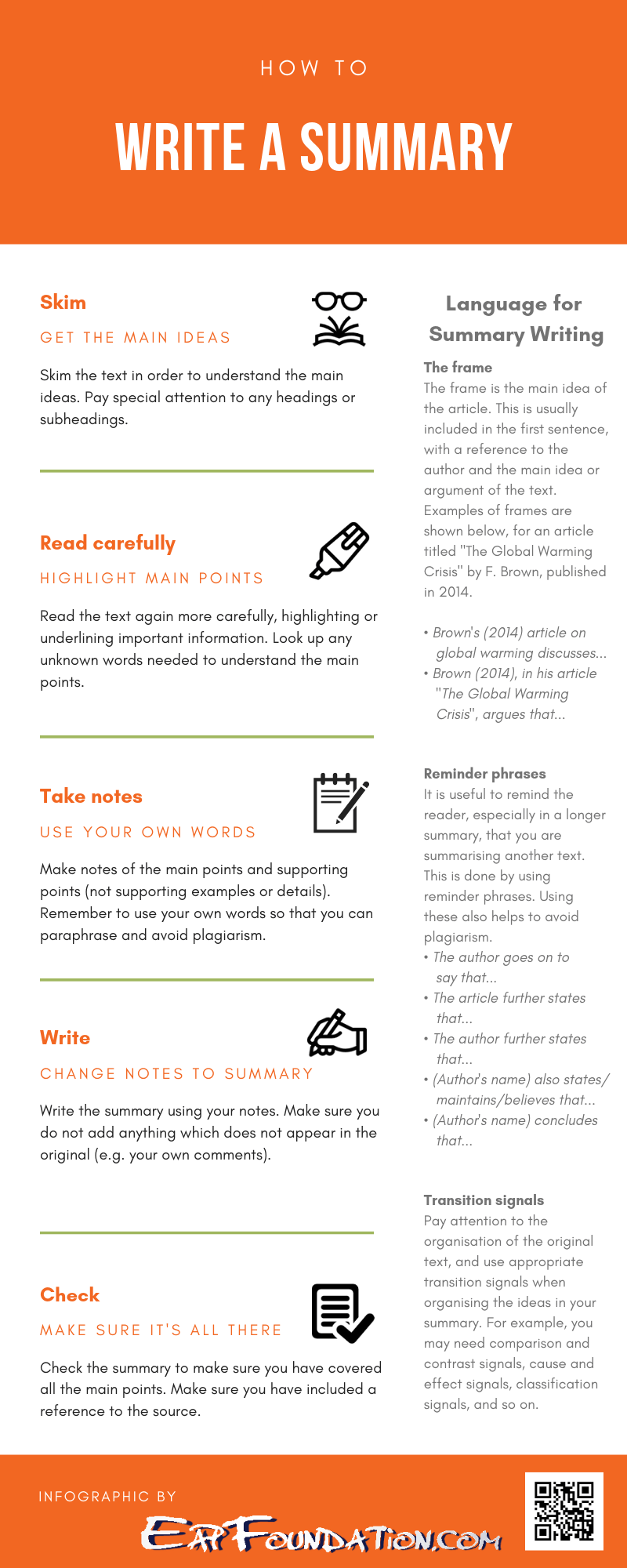
The Step-by-Step Guide to Summary Writing
Here's a simple, step-by-step approach to writing effective summaries:
Step 1: Thoroughly Read and Understand the Original Text
This is the most crucial step. You can't summarize something you don't understand! Read the text carefully, paying attention to the main ideas, supporting arguments, and key facts. Don't be afraid to read it more than once. Highlight or underline important points as you go. If there are unfamiliar words, look them up in a dictionary or online.
Pro-tip for Tourists: Many museums and historical sites offer audio guides or written materials in multiple languages. If available, use the English version alongside your native language version to help you grasp the nuances of the text more easily. Sometimes, direct translations can miss subtle cultural or historical references.
Step 2: Identify the Main Idea (or Thesis Statement)
Every good text has a central point or argument. This is often stated explicitly in a thesis statement (usually found in the introduction or conclusion), but sometimes it's implied throughout the text. Identifying the main idea is key to crafting an accurate summary. Ask yourself: "What is the author trying to convey?" or "What is the central argument being presented?"
Pro-tip for Expats: Pay attention to the context in which the text was written. What are the current social, political, or economic issues that might be influencing the author's perspective? Understanding the context will help you identify the main idea more accurately.
Step 3: Identify the Key Supporting Points
Once you've identified the main idea, look for the supporting points that the author uses to back it up. These are the reasons, examples, evidence, or arguments that are used to justify or explain the main idea. Just like you identified the main idea, highlight or underline each of the key supporting points.
Pro-tip for Short-Stay Visitors: Focus on identifying the most relevant information for your specific needs. For example, if you're only interested in the history of a particular neighborhood, focus on summarizing the parts of the text that relate to that topic.
Step 4: Write Your First Draft
Now it's time to put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard)! Start by writing a brief sentence or two that states the main idea of the text. Then, use your notes on the key supporting points to build out the rest of the summary. Remember to keep your summary concise and objective.
Here are some tips for writing your first draft:
- Use your own words: Avoid simply copying and pasting phrases from the original text. Paraphrase the information in your own language.
- Focus on the essentials: Include only the most important information. Omit minor details, examples, or anecdotes.
- Be objective: Don't include your personal opinions, interpretations, or judgments. Simply report the author's ideas accurately.
- Maintain the original order: Generally, it's best to present the information in the same order as it appears in the original text. This helps to maintain the flow of the argument.
- Use transitional words and phrases: Use words like "therefore," "however," "in addition," "furthermore," and "as a result" to connect your ideas and create a smooth, coherent summary.
Example:
Original Text (Excerpt): "The city's new transportation plan aims to reduce traffic congestion by investing in public transportation and promoting cycling. Specifically, the plan proposes expanding the subway system, increasing the frequency of bus routes, and building new bike lanes throughout the city. The plan is expected to significantly improve air quality and reduce commute times for residents."
Summary: "The city's transportation plan seeks to alleviate traffic by enhancing public transit and encouraging cycling through subway expansion, increased bus frequency, and new bike lanes. The anticipated results include improved air quality and shorter commute times."
Step 5: Revise and Edit Your Summary
Once you've written your first draft, take some time to revise and edit it. Read it carefully to make sure it's accurate, concise, and clear. Check for any grammatical errors or typos. Make sure your summary accurately reflects the main ideas and supporting points of the original text.
Here are some things to look for during the revision process:
- Accuracy: Does your summary accurately reflect the main ideas and supporting points of the original text?
- Conciseness: Is your summary as short as possible without omitting any important information?
- Clarity: Is your summary easy to understand? Are your sentences clear and concise?
- Objectivity: Have you avoided including your personal opinions or interpretations?
- Grammar and spelling: Are there any grammatical errors or typos in your summary?
Pro-tip: Ask a friend or colleague to read your summary and give you feedback. A fresh pair of eyes can often spot errors or areas for improvement that you might have missed.
Tips for Different Types of Texts
The specific approach to summarizing may vary slightly depending on the type of text you're working with. Here are some tips for summarizing different types of texts:
Summarizing News Articles
When summarizing news articles, focus on the who, what, where, when, why, and how of the story. Identify the main event, the key people involved, the location, the time frame, the reasons behind the event, and the way it unfolded.
Summarizing Academic Articles
When summarizing academic articles, focus on the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. Identify the problem the author is trying to solve, the approach they took to solve it, the findings of their research, and the implications of those findings.
Summarizing Literary Texts
When summarizing literary texts (such as novels or short stories), focus on the plot, characters, setting, and theme. Identify the main events of the story, the key characters and their relationships, the location and time period of the story, and the underlying message or meaning of the story.
Practice Makes Perfect!
Like any skill, summary writing takes practice. The more you practice, the better you'll become at identifying the main ideas and key supporting points of a text, and at writing concise and accurate summaries. Try summarizing articles, blog posts, news stories, or even movie plots. The best way to learn is by doing!
Pro-tip for Tourists and Expats: Look for opportunities to practice your summary writing skills in real-world situations. For example, after reading a local newspaper article, try summarizing it for a friend who doesn't speak the language. Or, after visiting a museum, try writing a brief summary of what you learned for your travel journal.
By following these steps and practicing regularly, you'll be well on your way to mastering the art of summary writing. Good luck, and happy summarizing!