John Rawls Theorie Der Gerechtigkeit

Willkommen! If you're exploring Germany – whether you're backpacking through vibrant cities, settling in as an expat, or just enjoying a short break – you might stumble across the name John Rawls. While he wasn't German (he was American!), his philosophical ideas, particularly his book "Eine Theorie der Gerechtigkeit" (A Theory of Justice), have profoundly influenced political thought here, and indeed, worldwide. Don't worry, you don't need a philosophy degree to understand why it's important! Think of it as understanding a key ingredient in the German approach to social fairness and justice.
Why Should You Care About Rawls on Your German Trip?
Okay, so why bother learning about a philosophical theory while you’re trying to decide between Currywurst and Döner? Because Rawls' ideas provide a fascinating lens through which to view German society. You’ll see echoes of his principles in social policies, discussions about inequality, and the overall sense of fairness that, while not perfect, is a defining characteristic of the country. Understanding Rawls can enrich your experience and give you a deeper appreciation for the values that shape German life.
The Big Idea: Justice as Fairness
Rawls' central argument is simple but powerful: Justice should be about fairness. But what *is* fairness? He tackled this question with a thought experiment called the "Originalposition" (original position) and the "Schleier des Nichtwissens" (veil of ignorance).
The Original Position and the Veil of Ignorance
Imagine a group of people tasked with creating a society's rules and laws *before* they know anything about their own position in that society. They don't know if they'll be rich or poor, male or female, healthy or disabled, intelligent or less so. They are behind the veil of ignorance.
Rawls argues that in this scenario, people would rationally choose principles of justice that are fair to *everyone*. Why? Because they wouldn’t want to risk ending up at the bottom of a system designed to benefit only a select few. Think about it: If you don't know whether you'll be born into privilege or disadvantage, you'll probably want to create a society that protects the vulnerable.
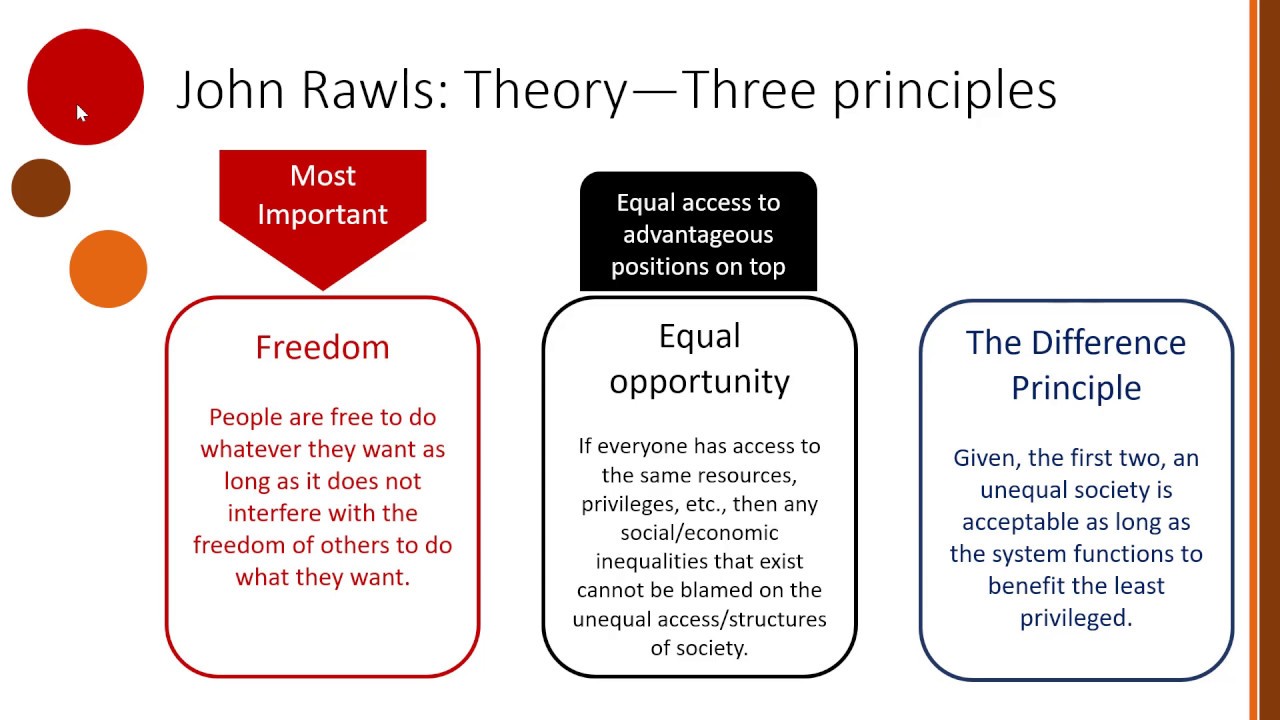
Two Key Principles of Justice
From behind the veil of ignorance, Rawls believes, people would agree on two fundamental principles:
- The Liberty Principle: Everyone should have an equal right to the most extensive total system of equal basic liberties compatible with a similar system of liberty for all. This means things like freedom of speech, freedom of conscience, the right to vote, and the right to a fair trial. These liberties can only be restricted to protect other liberties.
- The Difference Principle: Social and economic inequalities are to be arranged so that they are both:
- To the greatest benefit of the least advantaged.
- Attached to offices and positions open to all under conditions of fair equality of opportunity.
Let's break that down a bit.
The Liberty Principle prioritizes individual freedoms. It's the foundation of a just society, ensuring that everyone has basic rights and liberties that cannot be easily taken away.
The Difference Principle is more complex. It acknowledges that some inequality is inevitable (and even potentially beneficial – for example, incentivizing people to take on demanding jobs that contribute to society). However, it insists that any inequality must ultimately benefit the *least* well-off members of society. Think of progressive taxation or social welfare programs: these redistribute wealth to help those who are struggling. The second part, "attached to offices and positions open to all under conditions of fair equality of opportunity," emphasizes that everyone should have a fair chance to succeed, regardless of their background. This implies investment in education, healthcare, and other resources that level the playing field.
Rawls in the Real World: Examples in Germany
So, how does all this relate to Germany? You can see Rawlsian principles reflected in various aspects of German society:
- The Social Market Economy (Soziale Marktwirtschaft): Germany's economic system aims to balance economic freedom with social responsibility. It combines a free market with robust social safety nets, like unemployment benefits, universal healthcare, and affordable housing. This aligns with the Difference Principle by ensuring that even those who struggle economically are provided with a decent standard of living.
- Progressive Taxation: Germany has a progressive tax system, meaning that people with higher incomes pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes. This revenue is then used to fund social programs that benefit everyone, particularly those who are less fortunate. This is a direct application of the Difference Principle.
- Strong Labor Laws: German labor laws are designed to protect workers' rights, including fair wages, reasonable working hours, and job security. These laws help to ensure that workers are not exploited and have a fair chance to participate in the economy. This supports the idea of equality of opportunity.
- Universal Healthcare: Germany has a universal healthcare system that provides access to medical care for all citizens and legal residents, regardless of their income or social status. This is a fundamental aspect of ensuring a fair and just society, as it protects people from financial ruin due to illness.
- Education System: While debates continue about equity in the education system, Germany invests significantly in education and aims to provide equal opportunities for all children, regardless of their background. Public education is largely free, and there are programs in place to support students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Of course, Germany isn't a perfect Rawlsian utopia. There are ongoing debates about income inequality, social mobility, and the effectiveness of social programs. However, Rawls' ideas provide a framework for understanding the aspirations and values that underpin much of German social policy.
Criticisms and Considerations
It's important to note that Rawls' theory is not without its critics. Some argue that the veil of ignorance is an unrealistic thought experiment, and that people's values and biases would inevitably influence their choices, even behind the veil. Others argue that the Difference Principle is too demanding and could stifle economic growth. Libertarians, for example, often criticize the idea of redistributing wealth, arguing that it infringes on individual property rights.
Furthermore, some critics point out that Rawls' focus on justice within a single society neglects the issue of global justice. They argue that wealthy nations have a moral obligation to assist poorer nations, and that Rawls' theory doesn't adequately address this obligation. These are all important considerations when evaluating Rawls' work.
Beyond the Philosophy: Practical Takeaways for Your Trip
So, what can you actually *do* with this knowledge while you're in Germany? Here are a few ideas:
- Listen to Conversations: Pay attention to discussions about social and economic issues in the media or in everyday conversations. You'll often hear references to fairness, equality, and social responsibility – themes that are central to Rawls' philosophy.
- Observe Social Policies: Notice how social policies are implemented and how they affect people's lives. For example, consider the accessibility of public transportation for people with disabilities, or the support provided to refugees and asylum seekers.
- Visit Museums and Historical Sites: Many museums and historical sites in Germany address issues of social justice and equality. These can provide valuable insights into the country's history and the ongoing struggle for a more just society.
- Engage with Locals: Don't be afraid to ask Germans about their views on social issues. You might be surprised by the diversity of opinions and the passion with which people discuss these topics.
- Read Local News: Following local news outlets can provide a better understanding of ongoing social and political debates, allowing you to see how Rawlsian principles are being applied (or challenged) in real-time.
Conclusion: A Framework for Understanding
"Eine Theorie der Gerechtigkeit" is a complex and influential work. While you don't need to master every detail, understanding the core concepts – the original position, the veil of ignorance, and the two principles of justice – can provide a valuable framework for understanding German society and the values that shape its social policies. By engaging with these ideas, you can enrich your experience and gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of German life. Enjoy your trip!