Orientierungsplan Für Bildung Und Erziehung
Willkommen! Planning a trip to Germany, especially with children, or even considering a longer stay? Then understanding the German education system, particularly the Orientierungsplan für Bildung und Erziehung (Orientation Plan for Education and Upbringing), can be incredibly helpful. While it primarily targets early childhood education, its principles and goals resonate throughout the entire system and understanding them can offer valuable insight into German culture and values.
Was ist der Orientierungsplan? (What is the Orientation Plan?)
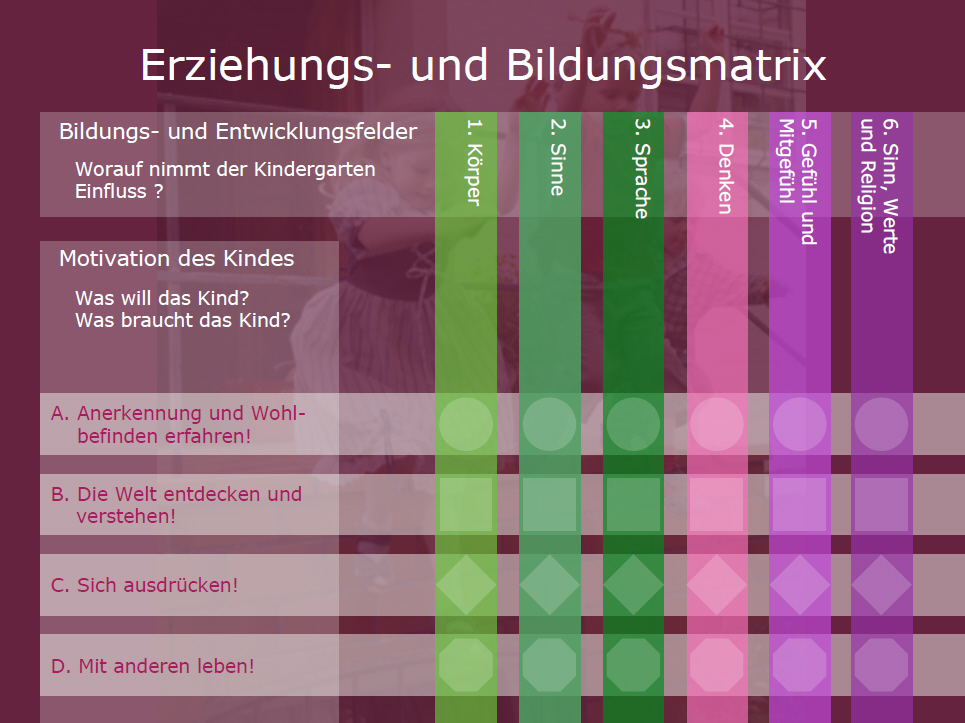
The Orientierungsplan, often shortened to simply "Orientierungsplan," is a framework document that outlines the goals and content of early childhood education (Frühkindliche Bildung) in various German states (Bundesländer). Think of it as a roadmap for educators working with children typically aged 0 to 6, before they enter primary school (Grundschule). It's not a strict curriculum, but rather a guideline emphasizing holistic development and individual needs. Importantly, each Bundesland has its own version of the Orientierungsplan, adapted to its specific context and priorities. This means there are slight variations between, for example, the Orientierungsplan in Baden-Württemberg and the one in Bavaria. However, the underlying principles remain broadly consistent.
Why is it important to know about the Orientierungsplan?
Even for short-term visitors or expats, understanding the core principles of the Orientierungsplan can be beneficial in several ways:
- Choosing childcare: If you need to utilize German childcare facilities, such as Kitas (Kindergärten), even temporarily, knowing the Orientierungsplan's principles will help you assess the quality and philosophy of the institution. You'll be better equipped to ask informed questions and ensure your child's needs are met.
- Understanding child-rearing approaches: The Orientierungsplan reflects deeply ingrained cultural values regarding child development and education. Observing how children are treated and educated in Germany, guided by these principles, can provide valuable insights into German society.
- Engaging with German families: Understanding the educational philosophy prevalent in Germany can facilitate meaningful conversations with local families and build stronger connections.
- Respecting cultural norms: Awareness of the Orientierungsplan demonstrates respect for German educational standards and a willingness to understand their approach to raising children.
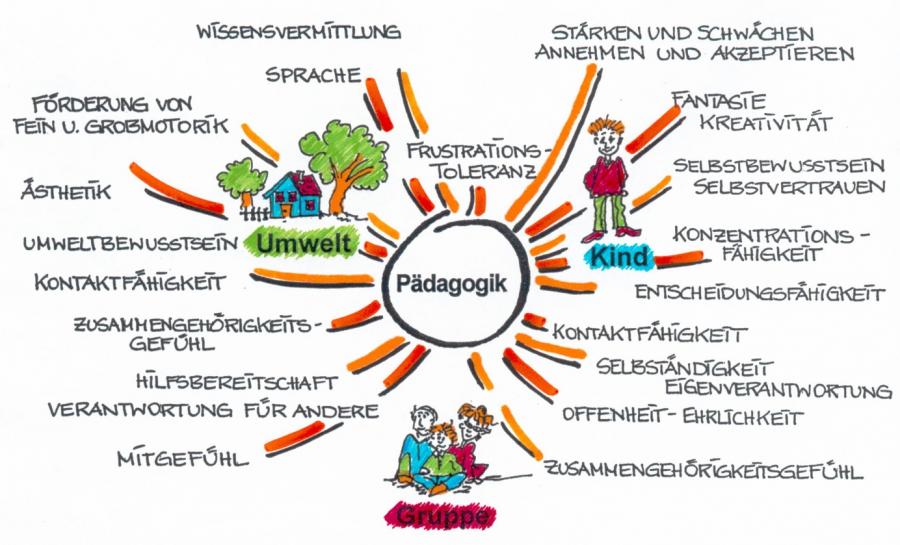
Die Kernbereiche des Orientierungsplans (The Core Areas of the Orientation Plan)
While the specific categories may differ slightly between states, the Orientierungsplan generally focuses on the following key areas of development:
- Sprache und Kommunikation (Language and Communication): This emphasizes the importance of developing children's language skills, both verbal and non-verbal. This includes vocabulary acquisition, grammar, storytelling, active listening, and the ability to express themselves effectively. Bilingualism and multilingualism are often actively encouraged.
- Soziale und emotionale Entwicklung (Social and Emotional Development): This area focuses on fostering children's self-esteem, empathy, and ability to form positive relationships. It includes learning to manage emotions, resolve conflicts peacefully, and cooperate with others. Building a strong sense of self is a key goal.
- Kognitive Entwicklung (Cognitive Development): This encompasses the development of thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and creativity. It includes exploring the world through observation, experimentation, and critical thinking. Play-based learning is central to this area.
- Motorische Entwicklung (Motor Development): This focuses on developing children's gross and fine motor skills through physical activity, movement games, and creative expression. It includes activities like running, jumping, climbing, drawing, and building. Outdoor play is considered crucial for motor development and overall well-being.
- Kreativität und ästhetische Bildung (Creativity and Aesthetic Education): This encourages children to explore their creative potential through art, music, drama, and other forms of artistic expression. It includes developing an appreciation for beauty and the ability to express themselves in imaginative ways. The process is often valued more than the end product.
- Werte und Normen (Values and Norms): This area focuses on instilling a sense of values, ethics, and social responsibility in children. It includes learning about fairness, respect, tolerance, and the importance of contributing to the community. Democratic principles are often introduced at an early age.
- Mathematische Bildung (Mathematical Education): Early mathematical concepts are introduced through play and everyday activities. This includes developing an understanding of numbers, shapes, patterns, and spatial relationships. Manipulatives and hands-on activities are commonly used.
- Naturwissenschaftliche und technische Bildung (Science and Technology Education): Children are encouraged to explore the natural world through observation, experimentation, and inquiry. This includes learning about plants, animals, weather, and basic scientific principles. Encouraging curiosity is key to scientific exploration.
Wie wird der Orientierungsplan umgesetzt? (How is the Orientation Plan Implemented?)
The Orientierungsplan is implemented through a variety of methods, primarily through play-based learning. This means that children learn through engaging in activities that are fun, stimulating, and tailored to their individual interests and developmental levels. Educators act as facilitators, creating a supportive and stimulating environment where children can explore, experiment, and discover.
Here are some key aspects of its implementation:
- Observation and Documentation: Educators carefully observe each child's development and document their progress. This information is used to plan activities that are tailored to their individual needs and interests.
- Partnerschaftliche Zusammenarbeit mit Eltern (Partnership with Parents): Collaboration between educators and parents is considered essential for children's success. Regular communication and involvement of parents in the educational process are highly valued. Parent-teacher conferences are common.
- Reflexion und Evaluation (Reflection and Evaluation): Educators regularly reflect on their practices and evaluate the effectiveness of their programs. This ensures that the Orientierungsplan is being implemented effectively and that children are making progress towards their goals.
- Inklusion (Inclusion): The Orientierungsplan emphasizes the importance of creating an inclusive environment where all children, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, can participate and thrive.
- Emphasis on Selbständigkeit (Independence): Fostering independence and self-reliance is a key goal. Children are encouraged to take initiative, make choices, and solve problems on their own.
Beispiele in der Praxis (Examples in Practice)
Let's look at some concrete examples of how the Orientierungsplan might be implemented in a Kita:
- Sprachentwicklung: Educators might read stories aloud, sing songs, and engage in conversations with children to develop their language skills. They might also provide opportunities for children to create their own stories through drawing, writing, or dramatic play.
- Soziale Entwicklung: Educators might facilitate group activities that encourage children to cooperate, share, and resolve conflicts peacefully. They might also provide opportunities for children to practice empathy by discussing different emotions and perspectives.
- Kognitive Entwicklung: Educators might provide puzzles, building blocks, and other materials that encourage children to think critically and solve problems. They might also take children on field trips to museums, parks, or other places of interest to stimulate their curiosity and learning.
- Motorische Entwicklung: Educators might provide opportunities for children to run, jump, climb, and play outdoors. They might also provide materials for drawing, painting, and sculpting to develop their fine motor skills.
Die Bedeutung des Spiels (The Importance of Play)
It's crucial to reiterate the central role of play in the implementation of the Orientierungsplan. Play is not seen as simply a recreational activity, but as a vital tool for learning and development. Through play, children explore the world, experiment with new ideas, develop social skills, and build self-confidence. Educators carefully curate the play environment to provide opportunities for children to learn and grow in all areas of development.
Whether you are visiting Germany for a short time or planning a longer stay, understanding the Orientierungsplan für Bildung und Erziehung can provide valuable insights into the country's educational philosophy and cultural values. It offers a glimpse into how German society approaches the important task of nurturing and educating its youngest citizens. By appreciating these principles, you can better navigate the cultural landscape and create more meaningful experiences during your time in Germany.













/rebuy-akeneo/b/f/f/f/bfff42f12cb357e39792132efcb51ddfe4d1cc4a_frontcover_media_1397204.jpeg?t=1709061934)