Petermann Und Petermann Beobachtungsbogen Pdf

Willkommen! Planning a trip, short stay, or even a more permanent move to Germany? Navigating a new culture can be exciting, but also a little daunting. This guide introduces you to something you might encounter, especially if you're traveling with or have children: the Petermann und Petermann Beobachtungsbogen. Don't worry, it's not as scary as the name sounds! Let's break it down and understand what it is, when you might see it, and how it's used.
What is the Petermann und Petermann Beobachtungsbogen?
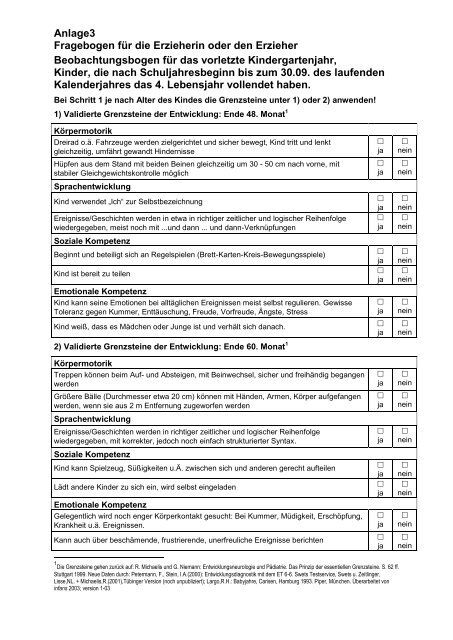
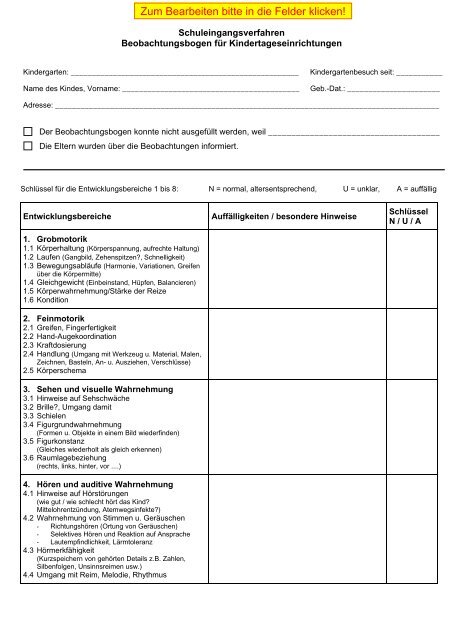
The Petermann und Petermann Beobachtungsbogen, often simply called the "Petermann Beobachtungsbogen," is a standardized observation checklist used in Germany (and other German-speaking countries) to assess the social and emotional development of children, particularly those aged 3 to 8 years old. It's a tool designed to help educators and caregivers identify potential strengths and areas where a child might need additional support.
Think of it as a comprehensive questionnaire that explores different aspects of a child's behavior, like their ability to interact with others, manage their emotions, and follow instructions. It's not a diagnostic tool, but rather a way to gather systematic information that can inform decisions about a child's care and education.
The "Petermann und Petermann" part refers to the authors of the questionnaire, Professor Franz Petermann and his wife, Professor Ulrike Petermann. They are well-known German psychologists specializing in child development and have developed several assessment tools used in educational settings.
Why is it used?
The Beobachtungsbogen helps to:
- Identify children who might benefit from early intervention programs. By systematically observing a child's behavior, educators can identify potential challenges before they become more significant problems.
- Inform individualized education plans (IEPs). If a child is struggling in certain areas, the Beobachtungsbogen can provide valuable information for developing a targeted plan to support their learning and development.
- Track a child's progress over time. The questionnaire can be administered periodically to monitor a child's development and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
- Facilitate communication between parents, educators, and other professionals. The Beobachtungsbogen provides a common language and framework for discussing a child's strengths and challenges.
When Might You Encounter It?
As a tourist or expat, you might encounter the Petermann Beobachtungsbogen in a few situations:
- Enrolling your child in a German Kindergarten (preschool) or Grundschule (primary school). Some institutions use it as part of their initial assessment process to get a better understanding of each child's individual needs.
- Seeking support services for your child. If you're concerned about your child's development and seeking professional help, the psychologist or therapist might use the Beobachtungsbogen as part of their assessment.
- Participating in certain research studies. If your child is participating in research related to child development, the Beobachtungsbogen might be used as a data collection tool.
It's important to note that not all Kindergartens or schools use this particular instrument. There are other similar tools available, and the choice of assessment method often depends on the institution's policies and the specific needs of the child.
What Does the Beobachtungsbogen Assess?
The questionnaire typically covers a wide range of behaviors and skills, often grouped into categories like:
- Social Behavior: How well the child interacts with peers and adults, their ability to cooperate, share, and resolve conflicts.
- Emotional Regulation: The child's ability to manage their emotions, their tendency to become easily frustrated or upset, and their overall emotional stability.
- Attention and Concentration: The child's ability to focus on tasks, their level of impulsivity, and their distractibility.
- Motor Skills: Both gross motor skills (running, jumping, climbing) and fine motor skills (drawing, writing, using utensils).
- Language Skills: The child's vocabulary, grammar, and ability to communicate effectively.
- Learning and Problem-Solving: The child's curiosity, their ability to solve simple problems, and their approach to new learning experiences.
The specific questions and format can vary depending on the version of the Beobachtungsbogen being used, but the general focus remains on assessing these key areas of development.
Understanding the Scoring and Interpretation
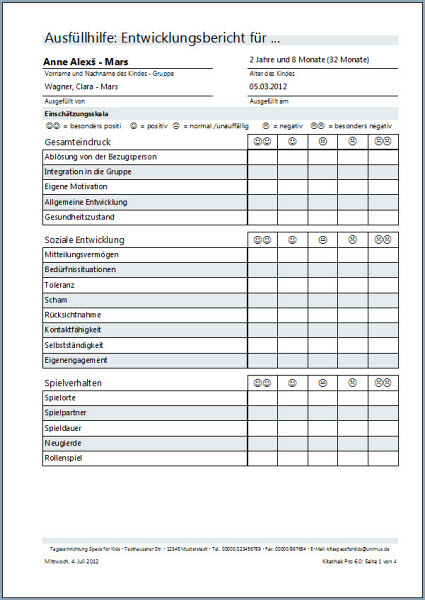
The Beobachtungsbogen is typically filled out by educators or caregivers who have had the opportunity to observe the child's behavior over a period of time. They rate each item on a scale, indicating the frequency or intensity of the observed behavior. For example, a question might ask, "Does the child share toys with others?" and the options might be "Never," "Sometimes," "Often," or "Always."
Once the questionnaire is completed, the responses are scored according to a standardized scoring system. The scores are then compared to normative data, which is based on the performance of a large sample of children of the same age. This allows professionals to determine whether a child's scores are within the typical range or whether they fall outside the norm.
It's crucial to understand that the results of the Beobachtungsbogen should be interpreted in conjunction with other information about the child, such as their medical history, family background, and observations from other sources. It's not a definitive diagnosis, but rather one piece of the puzzle.
What if Your Child is Assessed?
If your child is assessed using the Petermann Beobachtungsbogen, don't panic! It's simply a way for educators to get to know your child better and provide them with the best possible support.
Here are some tips for navigating the process:
- Ask questions. Don't hesitate to ask the educators or professionals why they are using the Beobachtungsbogen, what they hope to learn from it, and how the results will be used.
- Provide input. You are the expert on your child! Share your own observations and insights about their strengths and challenges.
- Request a copy of the results. You have the right to see the results of the assessment and discuss them with the professionals involved.
- Collaborate with the school or other professionals. Work together to develop a plan that addresses your child's individual needs.
- Remember it's just one data point. The Beobachtungsbogen is a valuable tool, but it's not the only factor to consider. Trust your instincts and advocate for your child's best interests.
Finding a Sample PDF (And Why You Might Not Need To)
You might be tempted to search for a "Petermann und Petermann Beobachtungsbogen PDF" online to see the questionnaire for yourself. While you might find some examples, it's important to understand that these forms are usually copyrighted and intended for use by trained professionals. Filling it out yourself without proper training and understanding of the scoring system would likely not be helpful and could even be misleading.
Furthermore, even if you find a PDF, it might not be the correct version being used by the school or professional you're working with. There are different versions of the Beobachtungsbogen, tailored to different age groups and specific purposes.
Instead of trying to administer the questionnaire yourself, focus on communicating openly and honestly with the educators or professionals involved. Your insights and observations are invaluable, and they will be the primary source of information used to understand your child.
The purpose of this guide is to inform and explain the tool and not endorse unlicensed or unqualified application.
Key Takeaways for Tourists, Expats, and Short-Term Visitors
- The Petermann und Petermann Beobachtungsbogen is a standardized observation checklist used in Germany to assess the social and emotional development of children.
- You might encounter it when enrolling your child in a German Kindergarten or school, or when seeking support services.
- It's used to identify children who might benefit from early intervention programs and to inform individualized education plans.
- Don't be afraid to ask questions and provide input if your child is assessed.
- Focus on collaborating with educators and professionals to support your child's development.
While understanding the Petermann Beobachtungsbogen can be helpful, especially if you plan on enrolling your child in the German education system, remember that your most important role is to be an advocate for your child and work collaboratively with educators to ensure their well-being and success. Enjoy your time in Germany!