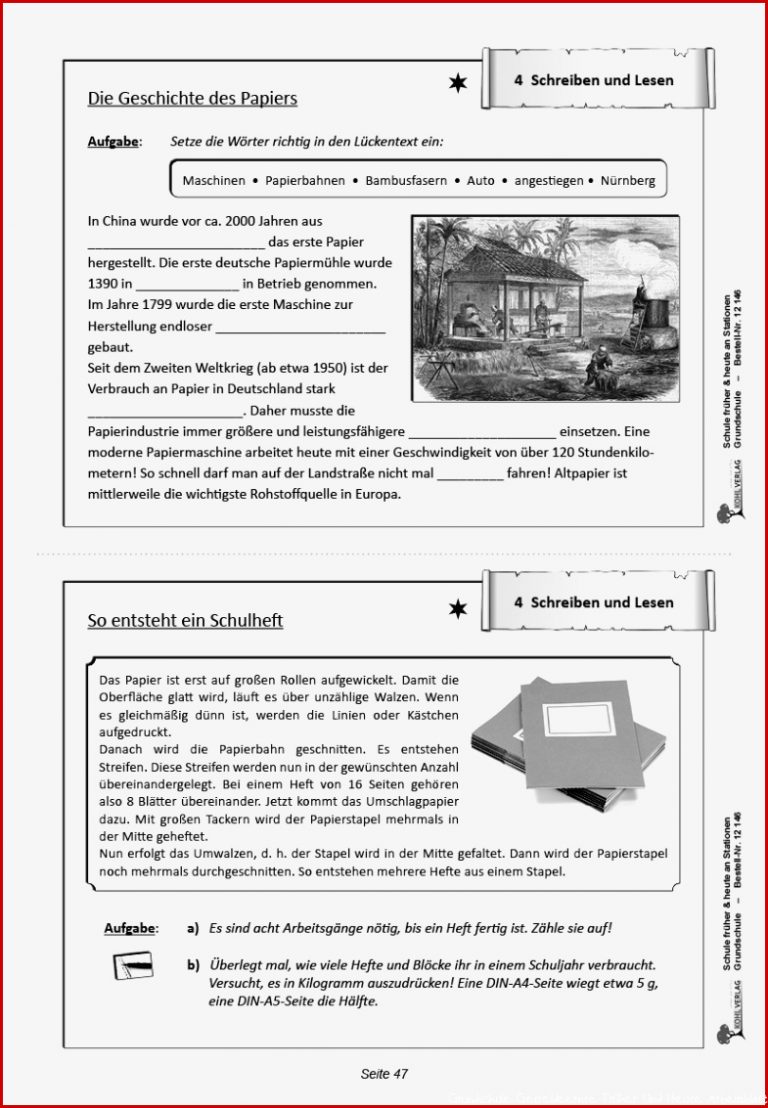
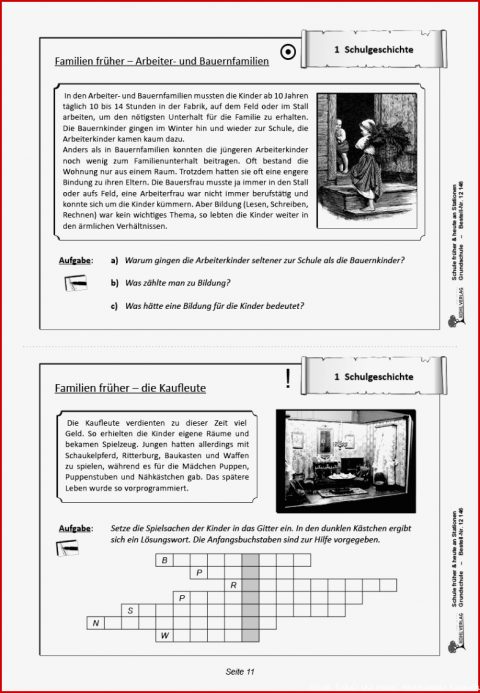
Schule Früher Und Heute Pdf

Herzlich willkommen! Are you curious about the evolution of education in Germany? Whether you're planning a trip, considering a move, or simply fascinated by German culture, understanding the schooling system, past and present, offers a unique insight into the country's values and priorities. Let's take a journey through time and explore the fascinating world of "Schule Früher Und Heute" (School Then and Now).
Schule Früher: A Glimpse into the Past
Imagine a time before computers, the internet, and even widespread access to books. German schools of the past, particularly before and during the 19th century, were vastly different from what you see today. Access to education was far from universal, heavily influenced by social class and religious affiliation. Let’s delve into some key aspects:
Education for the Elite
For the wealthy, education was often a privilege provided at home by private tutors. These tutors, often highly educated individuals, focused on classical subjects like Latin, Greek, history, and philosophy. The goal was to prepare young men for leadership roles in government, law, and the military. Young women from affluent families were typically educated in subjects considered appropriate for their social standing, such as music, art, and domestic skills.
Education for the Masses: Limited Opportunities
For the majority of the population, particularly in rural areas, formal schooling was rudimentary and often sporadic. Village schools, often one-room schoolhouses, were common. These schools, frequently run by the local pastor or a barely qualified teacher, provided basic instruction in reading, writing, and arithmetic. The emphasis was on religious instruction and preparing children for their future roles in agriculture or trades.
"Spare the rod and spoil the child" - a common saying reflecting the strict disciplinary methods employed in many historical German schools.
Discipline was harsh. Corporal punishment, including the use of the "Rohrstock" (cane), was common. Rote learning and memorization were emphasized over critical thinking. The curriculum was heavily dictated by the church and local authorities.
The Rise of the Prussian Education System
A pivotal moment in German education history was the development of the Prussian education system in the 18th and 19th centuries. Prussia, a powerful German state, recognized the importance of education for national unity and military strength. This system, although authoritarian in many ways, laid the foundation for a more structured and standardized approach to schooling.
Key features of the Prussian system included:
- Compulsory Education: Compulsory schooling was introduced, requiring children to attend school for a certain number of years.
- Teacher Training: The establishment of teacher training colleges to improve the quality of instruction.
- Standardized Curriculum: A standardized curriculum across schools, ensuring a consistent level of knowledge.
- Emphasis on Discipline and Obedience: A strong emphasis on discipline and obedience to authority.
While the Prussian system brought improvements, it also faced criticism for its rigid structure and emphasis on conformity. It served, however, as a model for other German states and influenced education systems worldwide.
Schule Heute: Education in Modern Germany
Fast forward to today, and the German education system has undergone significant transformations. While the influence of the Prussian model can still be seen in certain aspects, modern German schools are characterized by a greater emphasis on inclusivity, critical thinking, and preparing students for a rapidly changing world.
A Multi-Tiered System
The German education system is generally structured into four main levels:
- Grundschule (Primary School): From ages 6 to 10 (grades 1-4).
- Secondary Education I: This stage offers different school types based on academic ability and career aspirations. The main types are:
- Hauptschule: Focuses on vocational training and prepares students for apprenticeships.
- Realschule: Provides a more academic education than Hauptschule and prepares students for skilled trades or further vocational training.
- Gymnasium: The most academic track, preparing students for university studies.
- Gesamtschule: A comprehensive school that combines elements of the other three types, offering a more integrated learning environment.
- Secondary Education II: This stage includes vocational schools, upper secondary schools (Gymnasiale Oberstufe), and vocational colleges. Students can obtain the Abitur (university entrance qualification) at the Gymnasium or Gesamtschule.
- Tertiary Education (University): Offers a wide range of academic and professional programs.
Key Features of Modern German Schools
Here are some defining characteristics of the contemporary German education landscape:
- Compulsory Education: Compulsory schooling lasts for at least nine years, starting at age six.
- Free Education: Public education is generally free of charge, from primary school to university.
- Decentralization: Education is primarily the responsibility of the 16 federal states (Länder), leading to some variations in curriculum and school organization across the country.
- Emphasis on Vocational Training: Germany's dual system of vocational training, combining classroom instruction with on-the-job training in companies, is highly regarded worldwide.
- Inclusion: Efforts are underway to promote inclusion for students with disabilities, integrating them into mainstream schools whenever possible.
- Increasing Internationalization: German schools are increasingly incorporating international perspectives into their curriculum and encouraging student exchange programs.
Challenges and Debates
While the German education system has many strengths, it also faces challenges and ongoing debates:
- Social Inequality: Concerns remain about the impact of social background on educational attainment. Children from disadvantaged backgrounds may face barriers to accessing higher levels of education.
- Tracking: The early tracking of students into different school types (Hauptschule, Realschule, Gymnasium) is a subject of debate, with some arguing that it limits opportunities for late bloomers.
- Teacher Shortages: Like many countries, Germany faces a shortage of qualified teachers in certain subjects and regions.
- Digitalization: The integration of digital technologies into the classroom is an ongoing process, with schools working to equip themselves with the necessary infrastructure and resources.
What to Expect as a Tourist or Expat
If you're visiting Germany with children, or planning a longer stay, here are a few things to keep in mind:
- School Year: The school year typically starts in late August or early September, depending on the state.
- School Hours: School days usually run from morning until early afternoon, with variations depending on the school type and grade level.
- Extracurricular Activities: Many schools offer a variety of extracurricular activities, such as sports, music, and arts.
- Language Support: If your children don't speak German, they may be eligible for language support programs to help them integrate into the school system. Contact the local school authorities or the school directly for information.
- Private Schools: Private schools are available, but they typically charge tuition fees.
Understanding the German education system, both past and present, provides a fascinating window into the country's history, culture, and values. From the strict discipline of past centuries to the modern emphasis on inclusivity and critical thinking, "Schule Früher Und Heute" reflects the evolution of German society and its commitment to preparing future generations for the challenges and opportunities ahead. Enjoy exploring this important aspect of German life during your visit or stay!