Unterschied Freie Und Soziale Marktwirtschaft
Understanding the economic landscape of Germany is crucial for expats, newcomers, and anyone planning to live or work here. Two terms that frequently arise in discussions about the German economy are freie Marktwirtschaft (free market economy) and soziale Marktwirtschaft (social market economy). While often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts, with the latter forming the bedrock of Germany's economic system. This article will clearly outline the differences between these two economic models and explain why the soziale Marktwirtschaft is so important in Germany.
The Freie Marktwirtschaft (Free Market Economy)
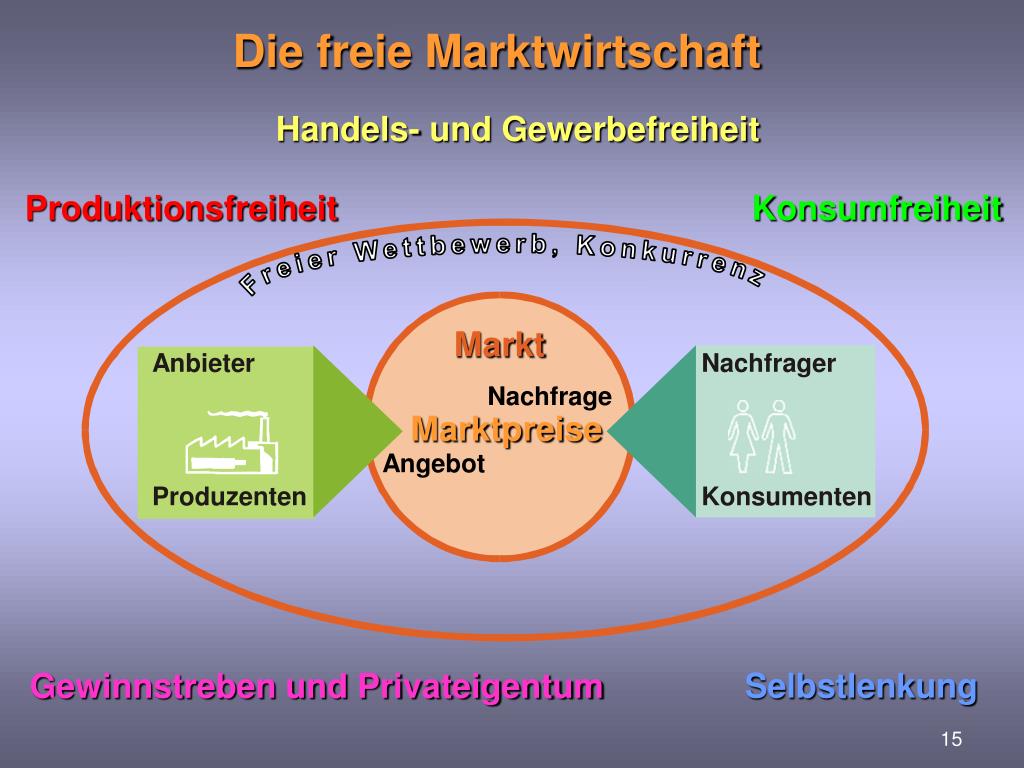
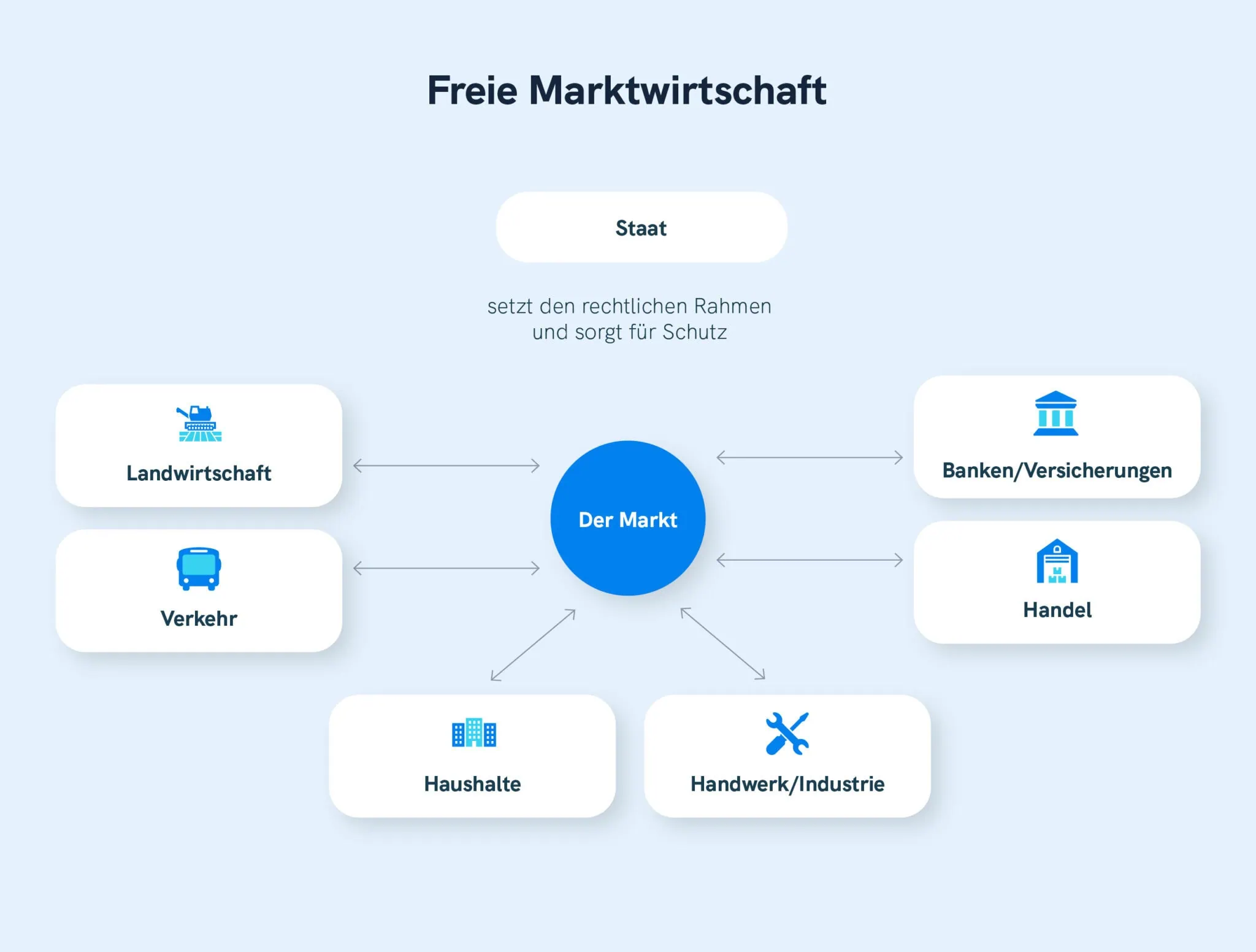
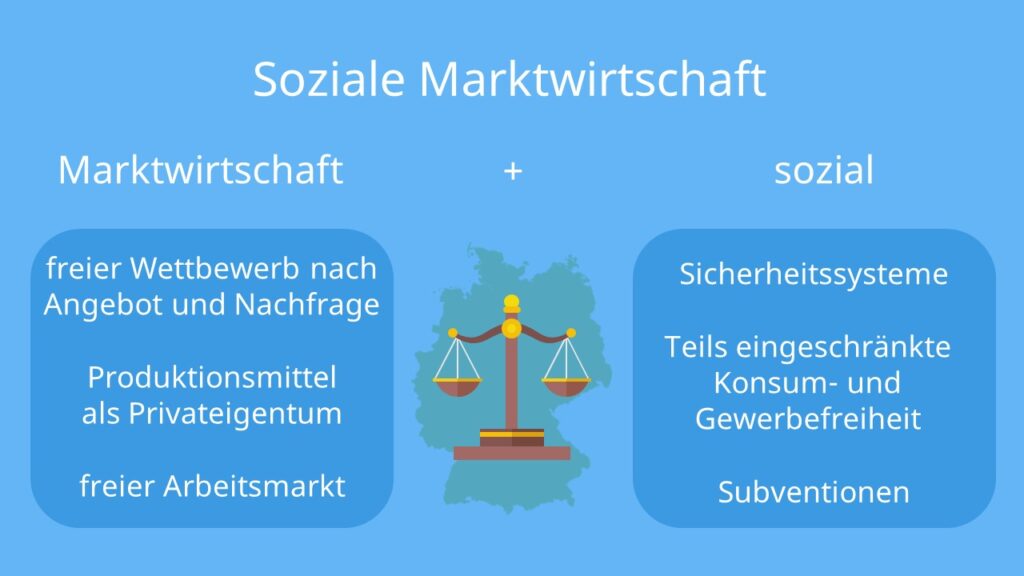
A freie Marktwirtschaft, or free market economy, is an economic system where the allocation of resources and the production of goods and services are primarily determined by the forces of supply and demand. In its purest form, a free market economy operates with minimal government intervention. Key characteristics include:
- Private Property: Individuals and businesses have the right to own property, including land, capital, and intellectual property.
- Free Enterprise: Businesses are free to operate without undue restrictions, choosing what to produce, how to produce it, and at what price to sell it.
- Competition: Many businesses compete with each other, driving innovation and efficiency. This competition keeps prices in check and offers consumers a wider range of choices.
- Price Mechanism: Prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand. High demand leads to higher prices, signaling to producers to increase production. Low demand leads to lower prices, signaling to producers to decrease production.
- Limited Government Intervention: The government's role is primarily limited to enforcing contracts, protecting property rights, and providing a legal framework for economic activity. There is generally little to no government involvement in setting prices, wages, or production levels.
Advocates of a free market economy argue that it leads to greater efficiency, innovation, and economic growth. The argument is that when businesses are free to pursue profit without excessive government interference, they are incentivized to develop new products, improve existing ones, and find more efficient ways to produce them. This, in turn, benefits consumers through lower prices and a wider variety of choices.
However, critics of the freie Marktwirtschaft point to potential drawbacks. These include:
- Inequality: Unfettered competition can lead to significant income and wealth inequality, as some individuals and businesses are more successful than others.
- Market Failures: The free market may fail to provide essential goods and services, such as public education, healthcare, and infrastructure, because there is no profit incentive to do so.
- Monopolies: Without regulation, dominant firms may exploit their market power to create monopolies, stifle competition, and raise prices.
- Externalities: The free market may not adequately account for externalities, such as pollution, which can harm the environment and public health.
- Economic Instability: The free market can be prone to boom-and-bust cycles, leading to economic instability and unemployment.
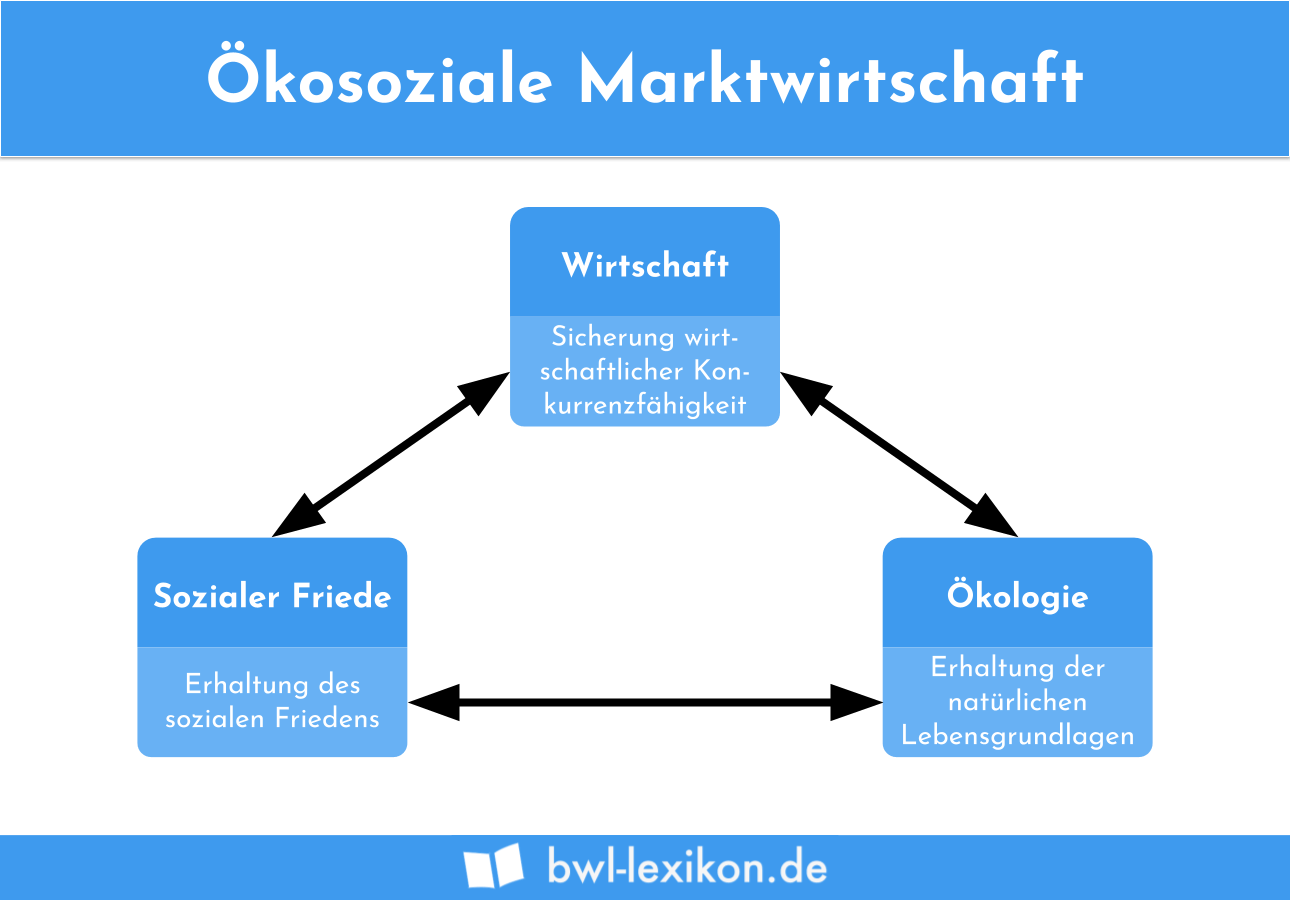
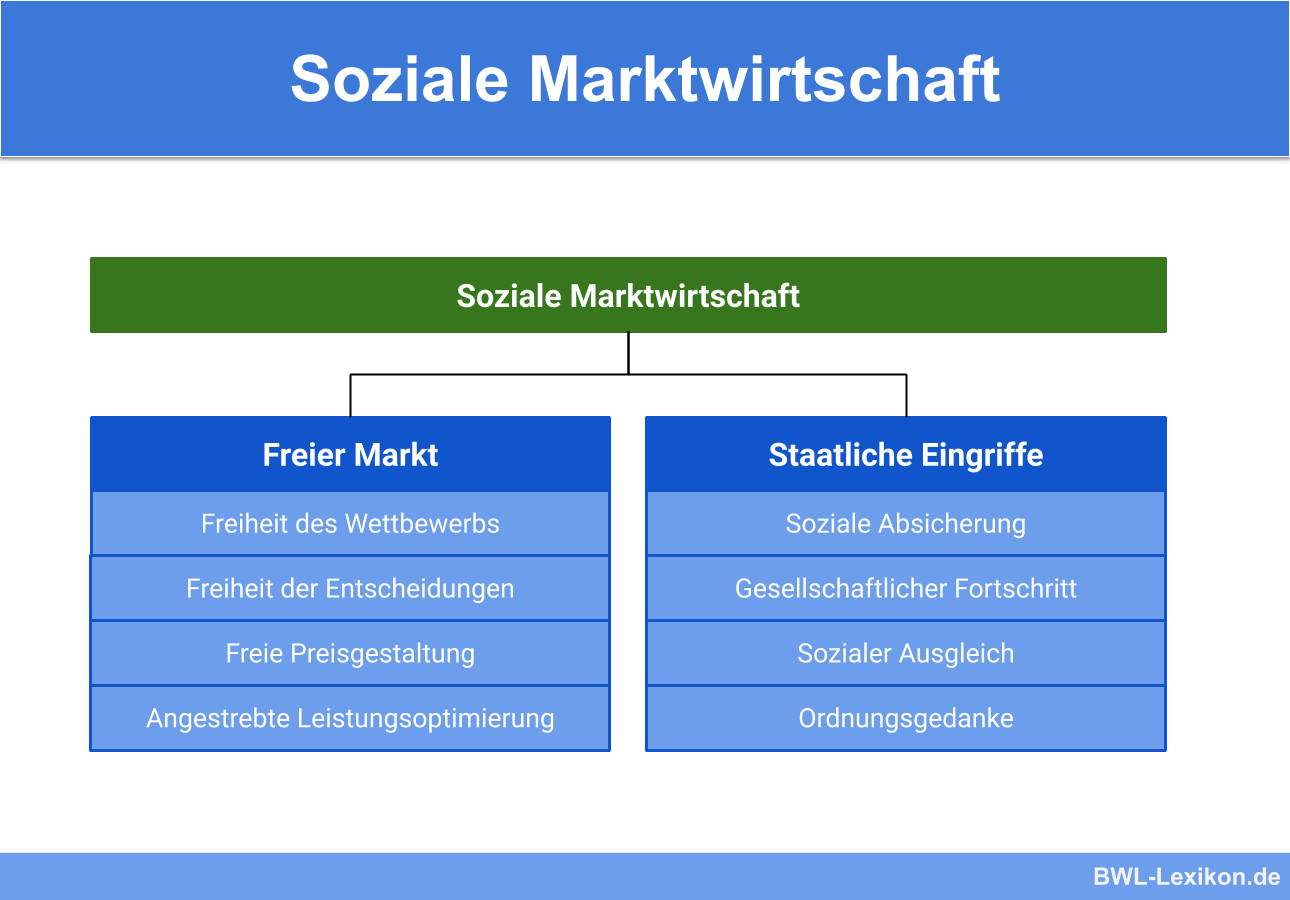
The Soziale Marktwirtschaft (Social Market Economy)
The soziale Marktwirtschaft, or social market economy, is a system that combines the principles of a free market economy with social policies aimed at mitigating its potential negative consequences. It seeks to harness the efficiency and dynamism of the free market while ensuring a degree of social justice and equity. This model was developed in post-World War II Germany by economists like Alfred Müller-Armack and Ludwig Erhard.
The key tenets of the soziale Marktwirtschaft include:
- Market Economy with Social Correctives: The system relies on free markets to allocate resources and generate wealth, but the government actively intervenes to address market failures and ensure social well-being.
- Strong Social Safety Net: A comprehensive social security system provides unemployment benefits, healthcare, pensions, and other forms of social assistance to protect individuals from economic hardship.
- Labor Rights and Collective Bargaining: Labor unions play a significant role in negotiating wages and working conditions, ensuring that workers receive fair compensation and treatment.
- Regulation and Antitrust Laws: The government regulates industries to prevent monopolies, protect consumers, and ensure fair competition. Strong antitrust laws prevent companies from dominating the market.
- Environmental Protection: Regulations are in place to protect the environment and mitigate the negative externalities of economic activity.
- Equal Opportunity: Policies are implemented to promote equal opportunity in education, employment, and other areas of life.
- Progressive Taxation: A progressive tax system is used to redistribute income and fund social programs. Those with higher incomes pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes.
The goal of the soziale Marktwirtschaft is to create a balance between economic freedom and social justice. It aims to foster economic growth and innovation while ensuring that the benefits of prosperity are shared more broadly across society. The government plays a crucial role in providing public goods and services, regulating markets, and maintaining a social safety net.
Examples of Social Policies in Germany
The soziale Marktwirtschaft is reflected in various social policies in Germany. Some examples include:
- Universal Healthcare: Germany has a universal healthcare system, ensuring that all citizens have access to quality medical care.
- Public Education: Education is free and accessible to all, regardless of income.
- Unemployment Benefits: Unemployed individuals receive unemployment benefits to help them meet their basic needs while they search for work.
- Pension System: A comprehensive pension system provides retirement income to elderly citizens.
- Rent Control: In some areas, rent control measures are in place to prevent landlords from charging excessively high rents.
- Co-determination (Mitbestimmung): Workers have the right to participate in the management of their companies, giving them a voice in important decisions.
Key Differences Summarized
Here's a table summarizing the key differences between a freie Marktwirtschaft and a soziale Marktwirtschaft:
| Feature | Freie Marktwirtschaft (Free Market Economy) | Soziale Marktwirtschaft (Social Market Economy) |
|---|---|---|
| Government Intervention | Minimal; limited to enforcing contracts and protecting property rights. | Significant; actively intervenes to address market failures and ensure social well-being. |
| Social Safety Net | Limited or non-existent. | Comprehensive; provides unemployment benefits, healthcare, pensions, and other forms of social assistance. |
| Labor Rights | Limited; workers have little power to negotiate wages and working conditions. | Strong; labor unions play a significant role in collective bargaining. |
| Regulation | Minimal; few regulations to protect consumers or the environment. | Extensive; regulations to prevent monopolies, protect consumers, and ensure environmental protection. |
| Income Inequality | Potentially high; significant disparities in income and wealth. | Lower; progressive taxation and social programs help to redistribute income. |
| Focus | Economic efficiency and growth. | Balance between economic efficiency, social justice, and environmental protection. |
Why the Soziale Marktwirtschaft Matters in Germany
The soziale Marktwirtschaft is central to understanding Germany's economic success and social stability. It has allowed Germany to achieve a high level of economic prosperity while maintaining a relatively egalitarian society. The system provides a safety net for those who are struggling, protects workers' rights, and ensures access to essential services such as healthcare and education.
For expats and newcomers, understanding the soziale Marktwirtschaft is essential for navigating the German labor market, accessing social services, and understanding the overall economic and social context of the country. It explains why taxes may be higher in Germany compared to other countries, but also why residents enjoy a high quality of life and a strong social safety net.
In conclusion, while the freie Marktwirtschaft emphasizes minimal government intervention and relies primarily on market forces, the soziale Marktwirtschaft seeks to strike a balance between economic freedom and social justice. Germany's commitment to the soziale Marktwirtschaft has been a key factor in its economic success and its reputation as a socially responsible and equitable society. Recognizing the distinctions between these two models provides valuable insight into the workings of the German economy and its underlying principles.


![Unterschied Freie Und Soziale Marktwirtschaft Wirtschaftsordnung • Definition & Beispiele · [mit Video]](https://blog.assets.studyflix.de/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/WP_Wirtschaftsordnung_freie-2-1024x576.jpg)