Unterschied Soziale Und Freie Marktwirtschaft
Understanding the economic landscape of Germany requires differentiating between two key models: the soziale Marktwirtschaft (social market economy) and the freie Marktwirtschaft (free market economy). While both emphasize market forces, their approaches to social welfare and government intervention differ significantly.
Freie Marktwirtschaft: Pure Capitalism
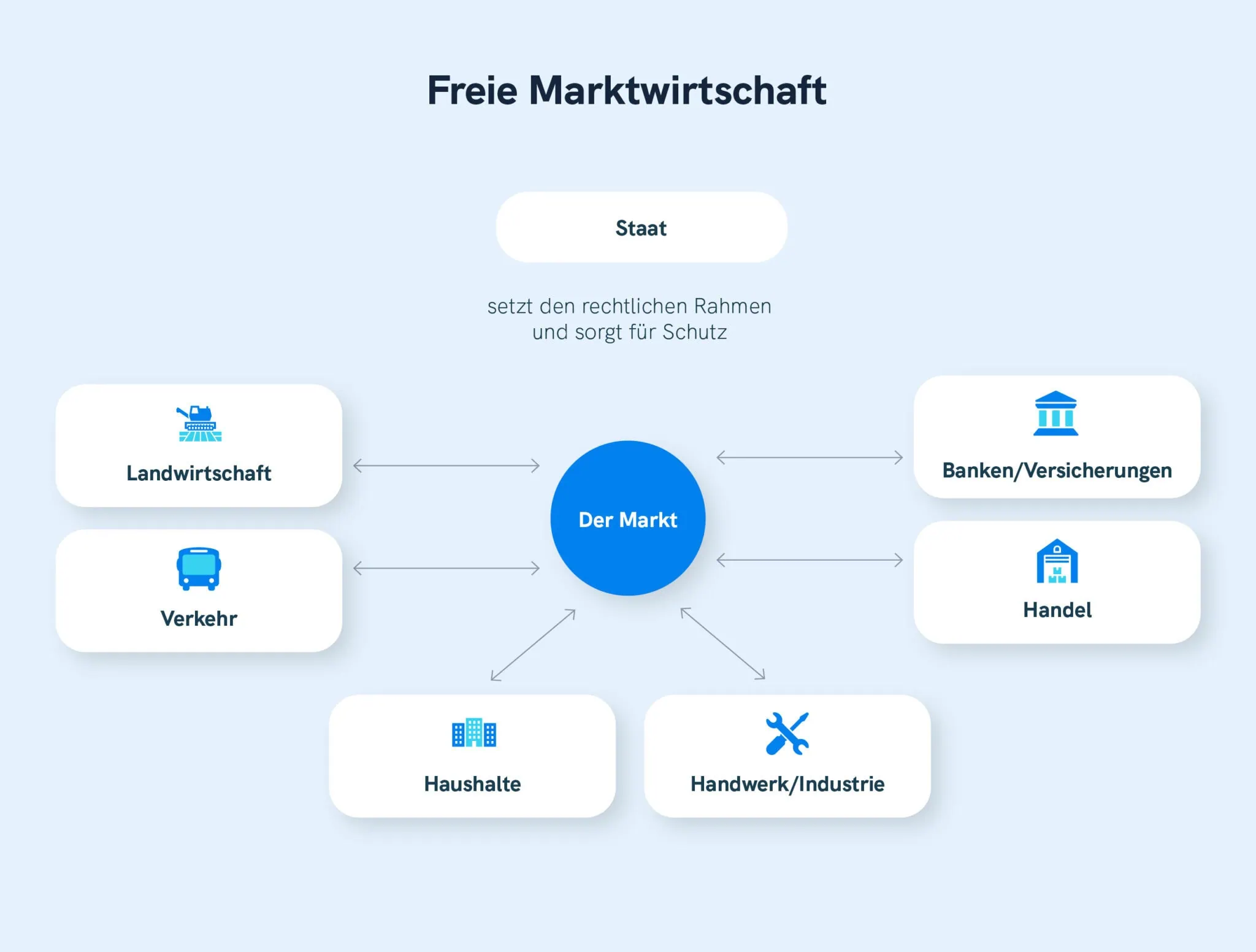
The freie Marktwirtschaft, often translated as a free market economy or laissez-faire capitalism, is based on the principles of minimal government intervention and maximum individual freedom. This model envisions a system where the market, driven by supply and demand, efficiently allocates resources. Key characteristics include:
- Private Property Rights: Individuals and businesses have the right to own and control property, including land, capital, and intellectual property.
- Free Competition: Businesses are free to compete with each other, leading to innovation, efficiency, and lower prices for consumers. No or very few barriers to entry exist.
- Price Mechanism: Prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand. The government does not control prices or wages.
- Profit Motive: Businesses are driven by the pursuit of profit. This incentivizes them to produce goods and services that consumers want.
- Limited Government Intervention: The government's role is limited to enforcing contracts, protecting property rights, and providing essential public goods, such as national defense.
In its purest form, a freie Marktwirtschaft prioritizes economic efficiency and individual liberty. Proponents argue that it fosters innovation, creates wealth, and provides consumers with a wide range of choices. However, critics point to potential downsides, including:
- Inequality: Without government intervention, wealth tends to concentrate in the hands of a few. This can lead to significant income and wealth disparities.
- Market Failures: The market may fail to provide essential goods and services, such as healthcare and education, to everyone.
- Exploitation: Businesses may exploit workers and consumers in their pursuit of profit.
- Environmental Degradation: The pursuit of profit may lead to environmental damage.
- Economic Instability: Free markets are prone to booms and busts, which can lead to unemployment and hardship.
Soziale Marktwirtschaft: A Balanced Approach
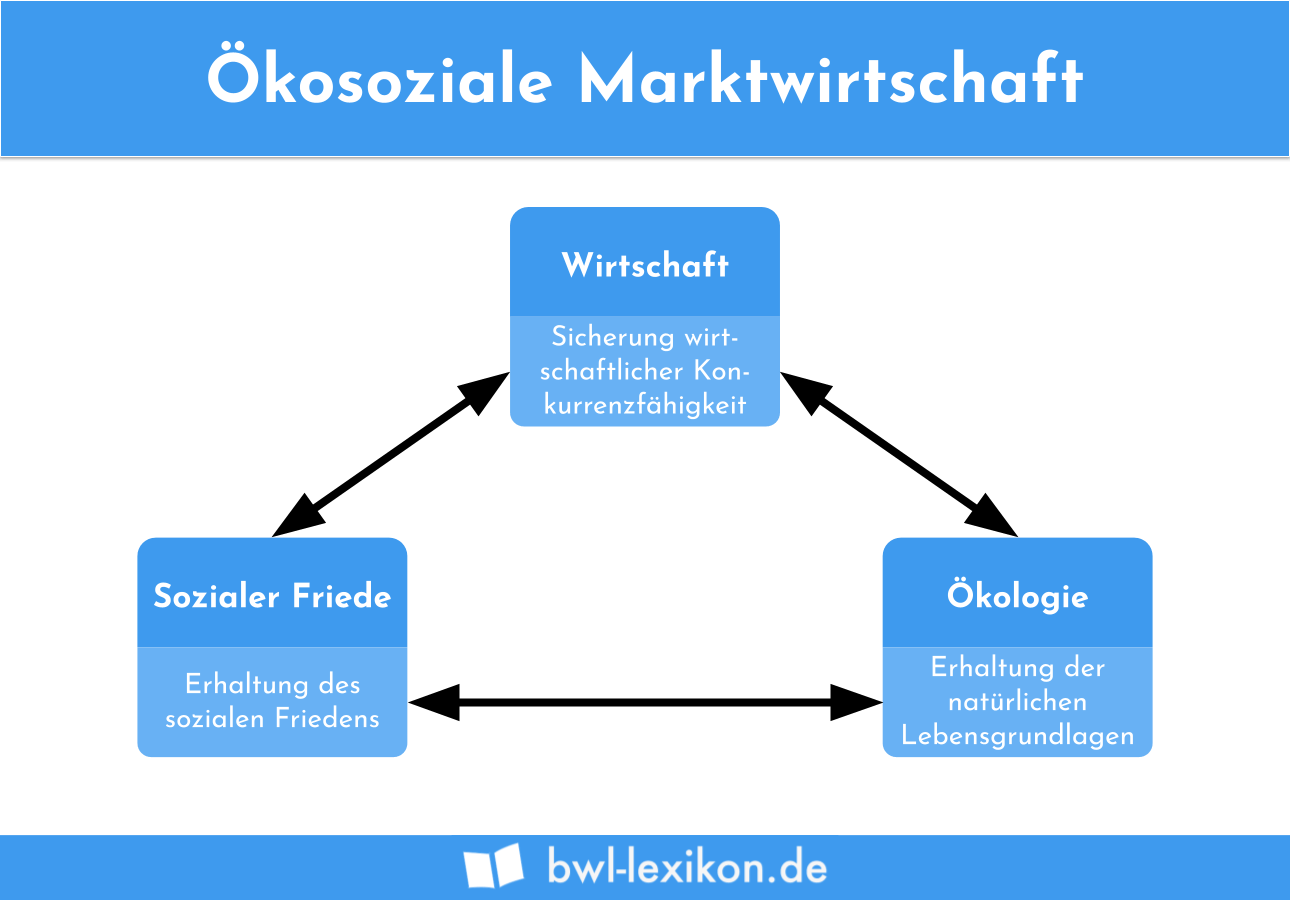
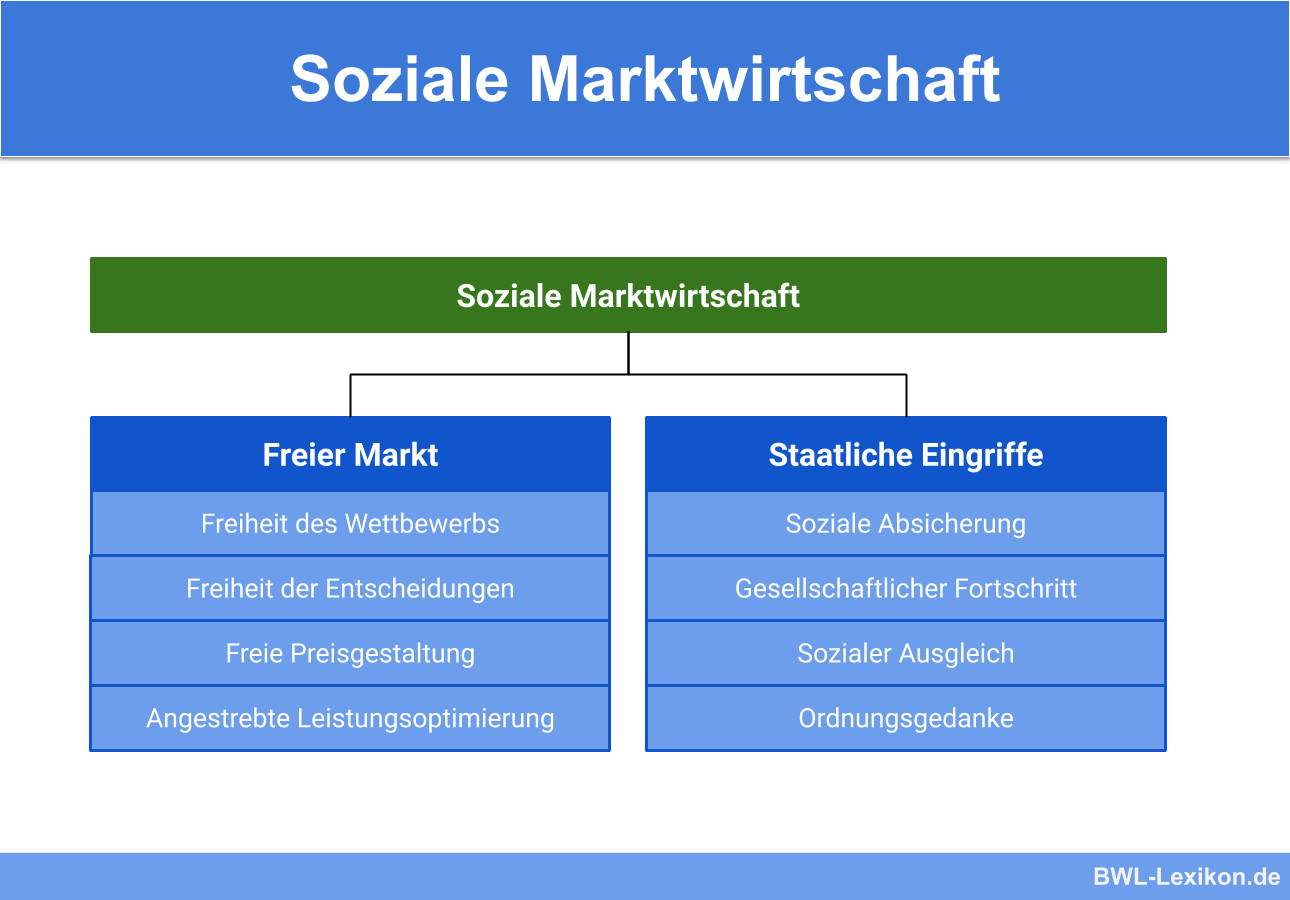
The soziale Marktwirtschaft, or social market economy, is a model that combines the principles of a free market with a strong social safety net and government regulation. It seeks to balance economic efficiency with social justice and security. This model is the foundation of the German economic system. Key characteristics include:
- Free Market Principles: Like the freie Marktwirtschaft, the soziale Marktwirtschaft emphasizes private property, free competition, and the price mechanism.
- Social Safety Net: The government provides a comprehensive social safety net, including unemployment benefits, healthcare, education, and social security. This is financed through taxes and contributions.
- Government Regulation: The government regulates businesses to protect workers, consumers, and the environment. This includes regulations on working conditions, product safety, and pollution.
- Co-determination: Workers have a voice in corporate governance through co-determination (Mitbestimmung). This gives them a say in decisions that affect their jobs and working conditions.
- Social Partnership: Employers, unions, and the government work together to address economic and social issues. This is known as social partnership (Sozialpartnerschaft).
The soziale Marktwirtschaft aims to harness the benefits of a free market while mitigating its negative consequences. It seeks to create a more equitable and sustainable economic system. The goals are:
- Economic Growth: To promote economic growth and create jobs.
- Full Employment: To achieve full employment and reduce unemployment.
- Price Stability: To maintain stable prices and prevent inflation.
- Social Justice: To reduce inequality and ensure that everyone has access to basic necessities.
- Environmental Protection: To protect the environment and promote sustainable development.
Critics of the soziale Marktwirtschaft argue that it can stifle innovation and economic growth due to high taxes, extensive regulations, and strong labor unions. They also claim that it can create dependency on the government and reduce individual initiative. However, proponents argue that it provides a more stable and equitable economic system that benefits everyone.
Key Differences Summarized
To clearly differentiate, consider these key points:
| Feature | Freie Marktwirtschaft (Free Market Economy) | Soziale Marktwirtschaft (Social Market Economy) |
|---|---|---|
| Government Intervention | Minimal; focuses on enforcing contracts and protecting property rights. | Significant; includes social safety net, regulation of businesses, and social partnership. |
| Social Welfare | Limited; relies on private charity and individual responsibility. | Extensive; provides universal access to healthcare, education, and social security. |
| Income Inequality | Potentially high; wealth tends to concentrate in the hands of a few. | Lower; government policies aim to reduce inequality and provide a social safety net. |
| Worker Rights | Limited; workers have little power to negotiate with employers. | Strong; workers have a voice in corporate governance through co-determination and strong unions. |
| Environmental Protection | Limited; businesses may prioritize profit over environmental concerns. | Significant; government regulations aim to protect the environment and promote sustainable development. |
| Focus | Economic efficiency and individual liberty. | Balancing economic efficiency with social justice and security. |
Germany's Implementation of the Soziale Marktwirtschaft
Germany's soziale Marktwirtschaft has evolved since its inception after World War II. It is not a static model but rather a dynamic system that adapts to changing economic and social conditions. Some key aspects of its implementation include:
- Healthcare System: Germany has a universal healthcare system funded by mandatory contributions from employers and employees.
- Education System: Education is free and compulsory for all children. The government provides funding for schools and universities.
- Social Security System: Germany has a comprehensive social security system that provides unemployment benefits, pensions, and other forms of social assistance.
- Labor Laws: Germany has strong labor laws that protect workers' rights, including minimum wage laws, regulations on working hours, and protections against unfair dismissal.
- Environmental Regulations: Germany has strict environmental regulations that aim to reduce pollution and promote sustainable development.
The German model is often cited as a successful example of balancing economic efficiency with social justice. However, it also faces challenges, such as an aging population, globalization, and technological change. The country continuously reforms its system to address these challenges and ensure its long-term sustainability.
Comparing to Other Systems
While many countries employ variations of market economies, the soziale Marktwirtschaft distinguishes itself. Compared to the more laissez-faire approach in the United States, Germany provides a much stronger social safety net and greater worker protections. In comparison to Scandinavian models, which also prioritize social welfare, the German system places a stronger emphasis on market competition and private enterprise, albeit within a regulated framework.
Conclusion
The freie Marktwirtschaft and soziale Marktwirtschaft represent fundamentally different approaches to economic organization. The former prioritizes individual freedom and economic efficiency with minimal government intervention, while the latter seeks to balance these goals with social justice and security through a robust social safety net and government regulation. Germany's soziale Marktwirtschaft demonstrates an attempt to reconcile the benefits of a free market with the need for a more equitable and sustainable society. Understanding the nuances of each model is crucial for navigating the German economic and social landscape.




![Unterschied Soziale Und Freie Marktwirtschaft Wirtschaftsordnung • Definition & Beispiele · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/WP_Wirtschaftsordnung_soziale-1024x576.jpg)
![Unterschied Soziale Und Freie Marktwirtschaft Wirtschaftsordnung • Definition & Beispiele · [mit Video]](https://blog.assets.studyflix.de/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/WP_Wirtschaftsordnung_freie-2-1024x576.jpg)