Vertrag über Die Arbeitsweise Der Europäischen Union

For those navigating the intricacies of the European Union, understanding its foundational treaties is crucial. Among these, the Vertrag über die Arbeitsweise der Europäischen Union (VWV, Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union - TFEU) stands out as a cornerstone. This treaty, often referred to alongside the Vertrag über die Europäische Union (EUV, Treaty on European Union), outlines the practical mechanisms and rules that govern the EU's day-to-day operations and policy-making processes. This article provides a clear and concise overview of the TFEU, helping expats, newcomers, and anyone seeking accurate information to grasp its essential elements.
What is the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU)?
The TFEU, formerly known as the Treaty Establishing the European Community (TEC) or the Treaty of Rome, is one of the two primary treaties forming the constitutional basis of the European Union. It details how the EU achieves the objectives set out in the EUV. While the EUV lays out the fundamental principles and objectives of the EU, the TFEU specifies the powers, procedures, and institutions responsible for enacting these principles and achieving these objectives.
Think of it this way: the EUV is the EU's constitution, outlining its goals and values, while the TFEU is its operational manual, describing how it functions in practice. Both treaties are legally binding on all EU member states.
Key Areas Covered by the TFEU
The TFEU is a comprehensive document covering a wide range of areas. Some of the most important aspects include:
1. The Internal Market:
The TFEU lays the groundwork for the EU's internal market, a single market where goods, services, capital, and people can move freely. Articles 26-117 detail the rules surrounding the establishment and functioning of this market, including:
- Customs Union: Eliminating tariffs and trade barriers between member states.
- Free Movement of Goods: Ensuring goods can be traded freely across borders, subject to certain exceptions.
- Freedom of Establishment and Freedom to Provide Services: Allowing businesses and individuals to establish themselves and offer services in any member state.
- Free Movement of Capital: Allowing capital to flow freely between member states.
- Competition Policy: Preventing anti-competitive practices like cartels and monopolies.
2. Economic and Monetary Policy:
The TFEU establishes the framework for the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), including the euro. Articles 119-144 address issues such as:
- Coordination of economic policies: Ensuring member states' economic policies are aligned to promote stability and growth.
- The European Central Bank (ECB): Defining the ECB's role in managing the euro and maintaining price stability.
- The Stability and Growth Pact: Setting rules for member states' budget deficits and national debt.
3. Policies in Specific Areas:
The TFEU dedicates considerable attention to specific policy areas where the EU has competence. These include:
- Agriculture (Articles 38-44): Establishing the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), which aims to support farmers and ensure food security.
- Fisheries (Articles 42-43): Managing fisheries resources and promoting sustainable fishing practices through the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP).
- Transport (Articles 90-100): Developing a common transport policy to promote efficient and sustainable transport across the EU.
- Environment (Articles 191-193): Protecting the environment and promoting sustainable development.
- Social Policy (Articles 151-161): Promoting employment, improving living and working conditions, and combating social exclusion.
- Consumer Protection (Article 169): Ensuring a high level of consumer protection.
- Public Health (Article 168): Contributing to a high level of human health protection.
- Research and Technological Development (Articles 179-190): Promoting research and innovation.
- Energy (Article 194): Ensuring the functioning of the energy market and promoting energy security.
- Tourism (Article 195): Supporting the tourism sector.
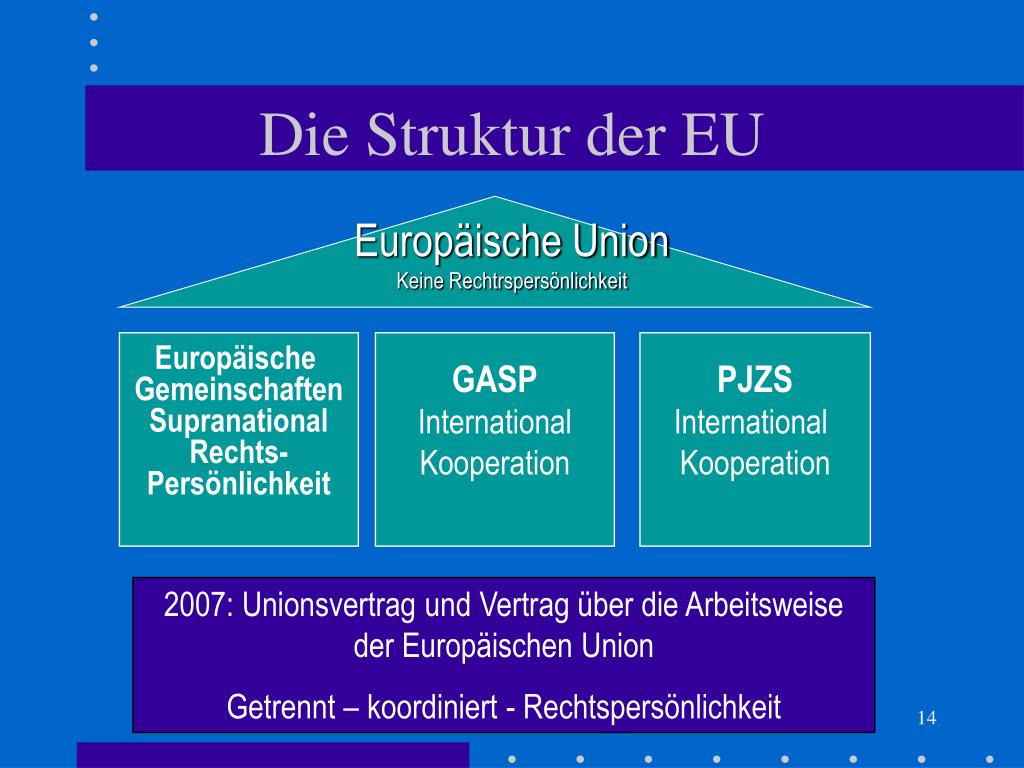
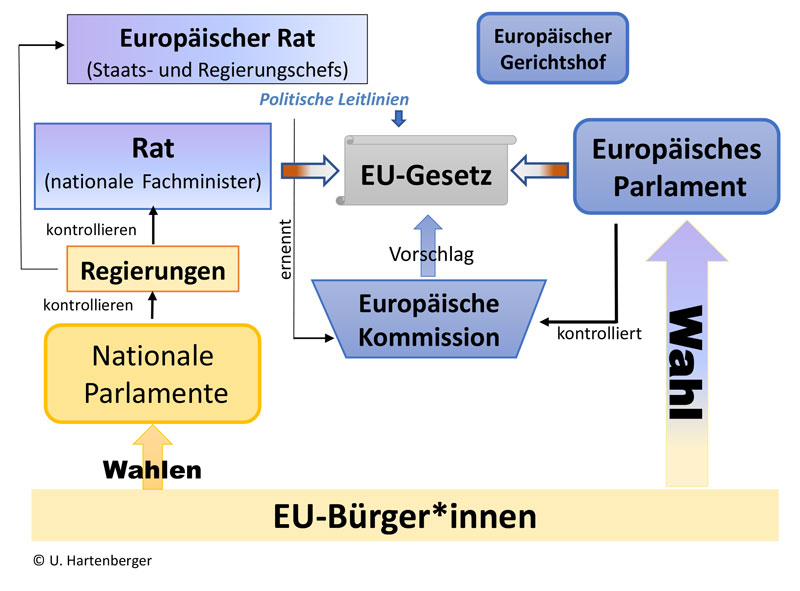
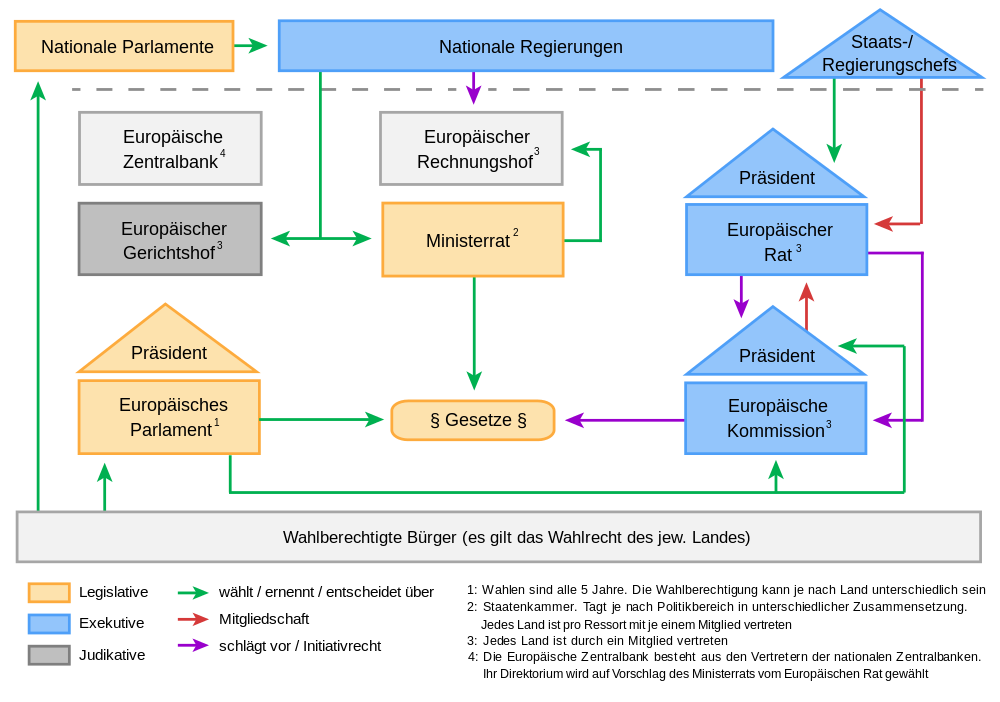
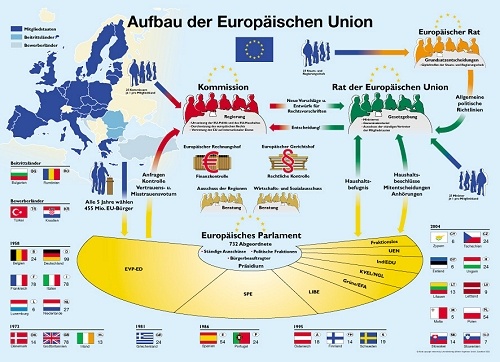
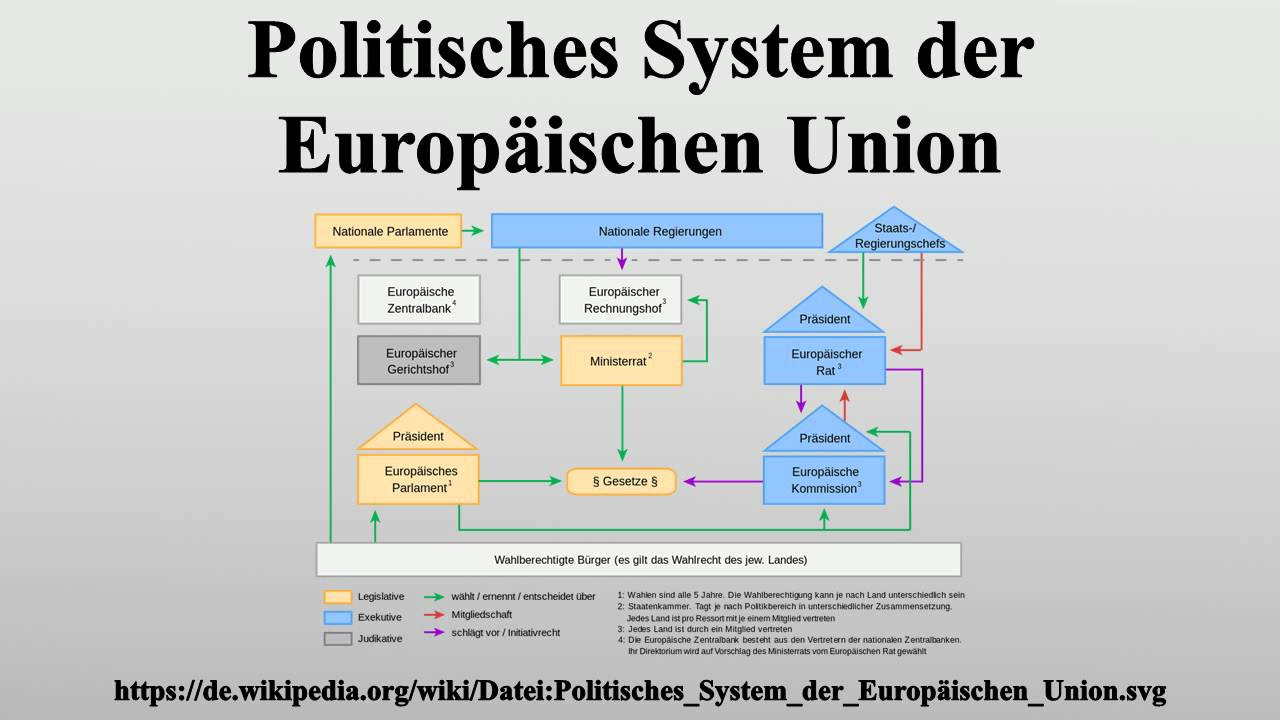
4. EU Institutions and Decision-Making:
The TFEU describes the roles and powers of the EU's main institutions, including:
- The European Parliament: Directly elected by EU citizens, the Parliament shares legislative and budgetary powers with the Council of the European Union.
- The Council of the European Union: Representing the governments of the member states, the Council shares legislative and budgetary powers with the Parliament.
- The European Commission: The EU's executive body, responsible for proposing legislation and implementing EU policies.
- The Court of Justice of the European Union: Ensuring EU law is interpreted and applied uniformly across the EU.
- The European Council: Setting the EU's overall political direction and priorities.
The treaty also outlines the different legislative procedures used by the EU, such as the ordinary legislative procedure (formerly known as co-decision), where the Parliament and the Council have equal powers, and the special legislative procedures, where the Council acts alone or after consulting the Parliament.
5. External Action:
The TFEU covers the EU's external relations, including its trade policy, development cooperation, and humanitarian aid. Articles 205-222 detail the framework for these activities, ensuring the EU acts as a unified force on the global stage.
Understanding Competences: Who Decides What?
A crucial aspect of the TFEU is the allocation of competences between the EU and its member states. This determines which level of government has the power to legislate in different areas. The TFEU distinguishes between three types of competences:
- Exclusive Competences (Article 3): Only the EU can legislate in these areas. Member states can only act if the EU authorizes them to do so. Examples include customs union, common commercial policy, and monetary policy for Eurozone countries.
- Shared Competences (Article 4): Both the EU and member states can legislate, but member states can only act if the EU has not already done so. This is the most common type of competence and covers areas such as the internal market, social policy, environment, consumer protection, and transport.
- Supporting Competences (Article 6): The EU can support, coordinate, or supplement member states' actions. The EU cannot legislate in these areas, but it can provide funding, share best practices, and promote cooperation. Examples include culture, tourism, education, and vocational training.
Understanding the distribution of competences is essential for understanding the limits of the EU's power and the role of member states in the EU system. The principle of subsidiarity, enshrined in the EUV, further clarifies this by stating that the EU should only act if action cannot be taken effectively at the national, regional, or local level.
Impact and Importance of the TFEU
The TFEU is a fundamental document that shapes the daily lives of EU citizens and businesses. Its impact is far-reaching, influencing everything from the prices of goods and services to environmental regulations and employment laws. The treaty ensures the free movement of goods, services, capital and people which provides significant benefits to EU citizens and economies. It also contributes to the development of common standards and regulations, which simplify cross-border trade and cooperation.
For expats and newcomers, understanding the TFEU can provide valuable insights into the legal and political framework of the EU. It can help them navigate the complexities of living and working in the EU, understand their rights and obligations, and participate more effectively in the EU political process.
Where to Find the Official Text
The official text of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, along with the Treaty on European Union, can be found on the EUR-Lex website, the official online access point to European Union law. It is available in all official EU languages.
Conclusion
The Vertrag über die Arbeitsweise der Europäischen Union is a complex but vital document for understanding how the European Union functions. By outlining the powers of the EU institutions, defining the scope of EU policies, and establishing the rules for the internal market, the TFEU plays a crucial role in shaping the EU's economic, social, and political landscape. While navigating its many articles can be challenging, understanding its key principles is essential for anyone seeking to engage with the EU effectively.