Was Entsteht Bei Der Photosynthese
Willkommen! Germany is known for many things: its vibrant cities, stunning landscapes, and rich culture. But have you ever stopped to think about the unseen processes happening all around you that make all this possible? One of the most fundamental is photosynthesis, or, auf Deutsch, die Photosynthese. Let’s delve into what happens during this vital process, especially as you enjoy the beautiful German outdoors.
Die Photosynthese: The Basics
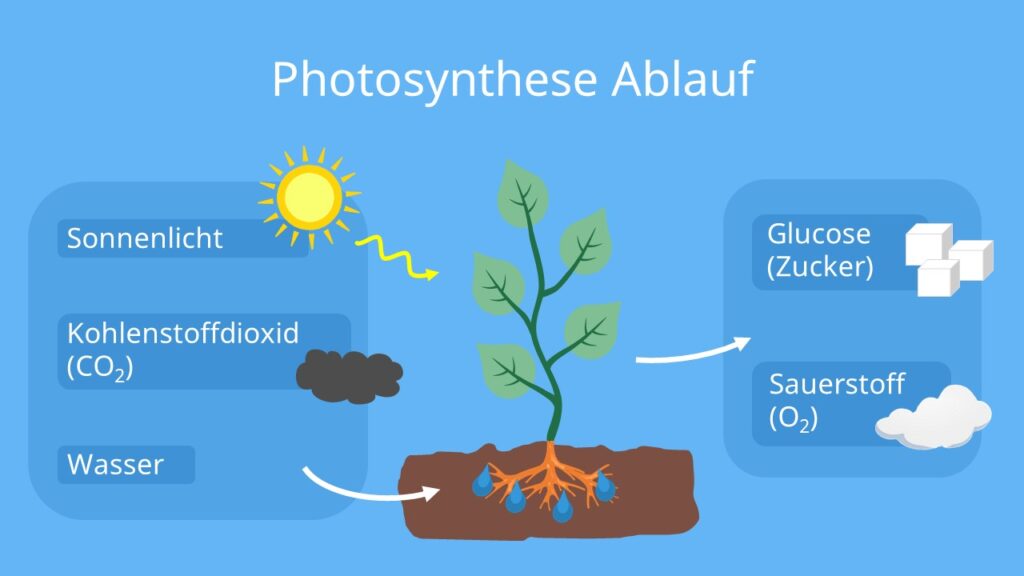
Photosynthesis is, at its core, the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of sugars. Think of it as the engine that powers the entire green world, and by extension, much of the life on Earth. Without it, there would be no plants, no food for animals (including us!), and a drastically different atmosphere.
To understand what's created during photosynthesis, we need to look at the ingredients and the end results.
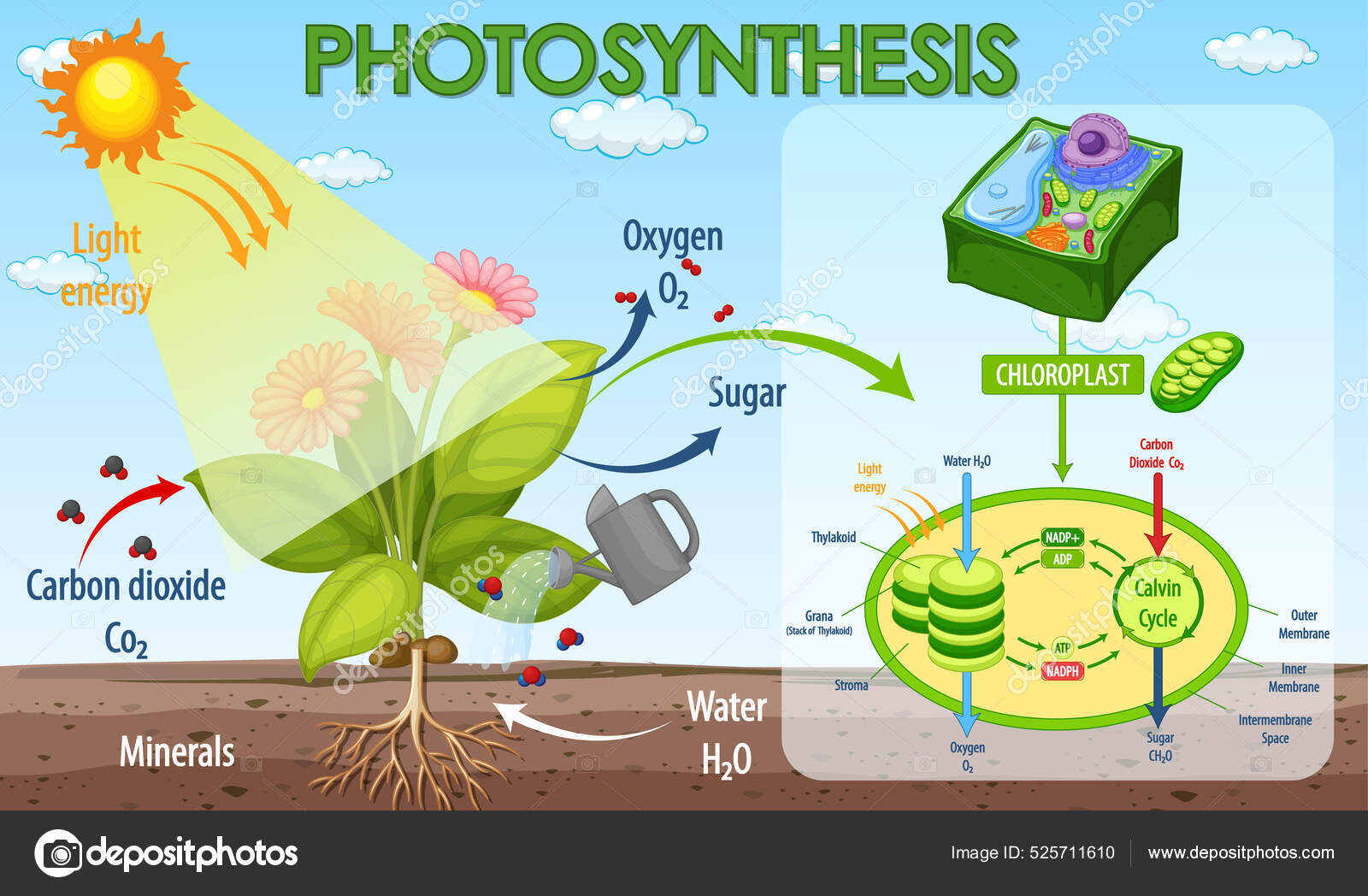
What Goes In? The Ingredients
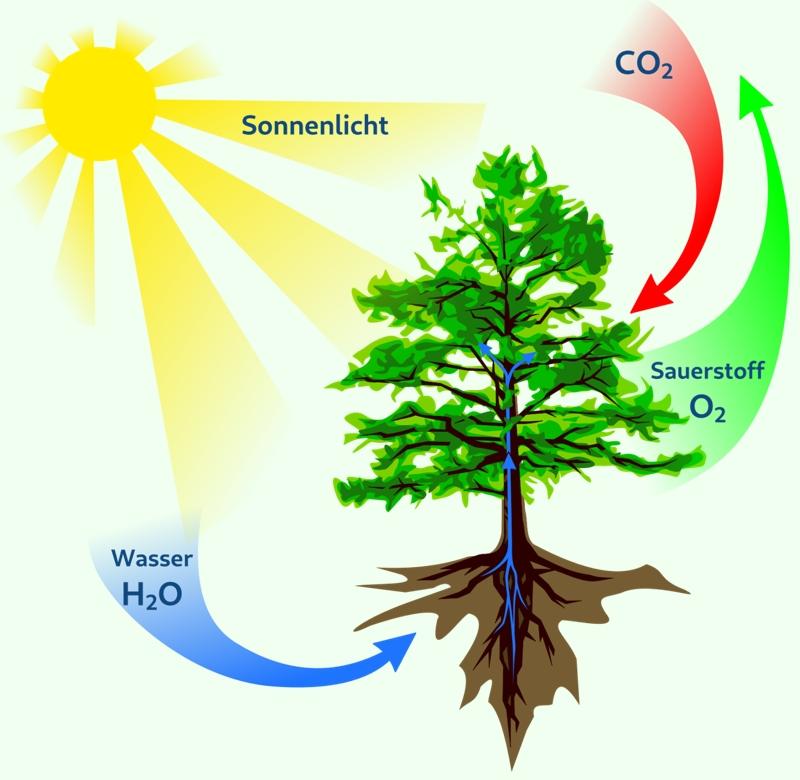
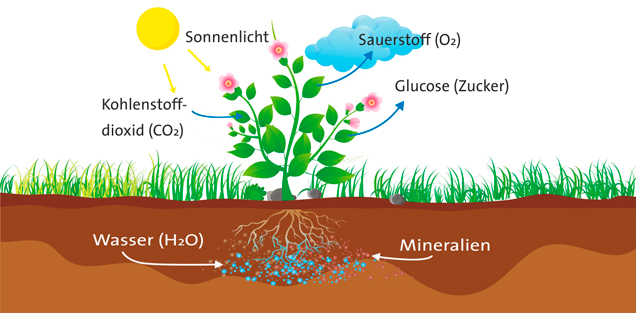
Photosynthesis requires a few key ingredients:
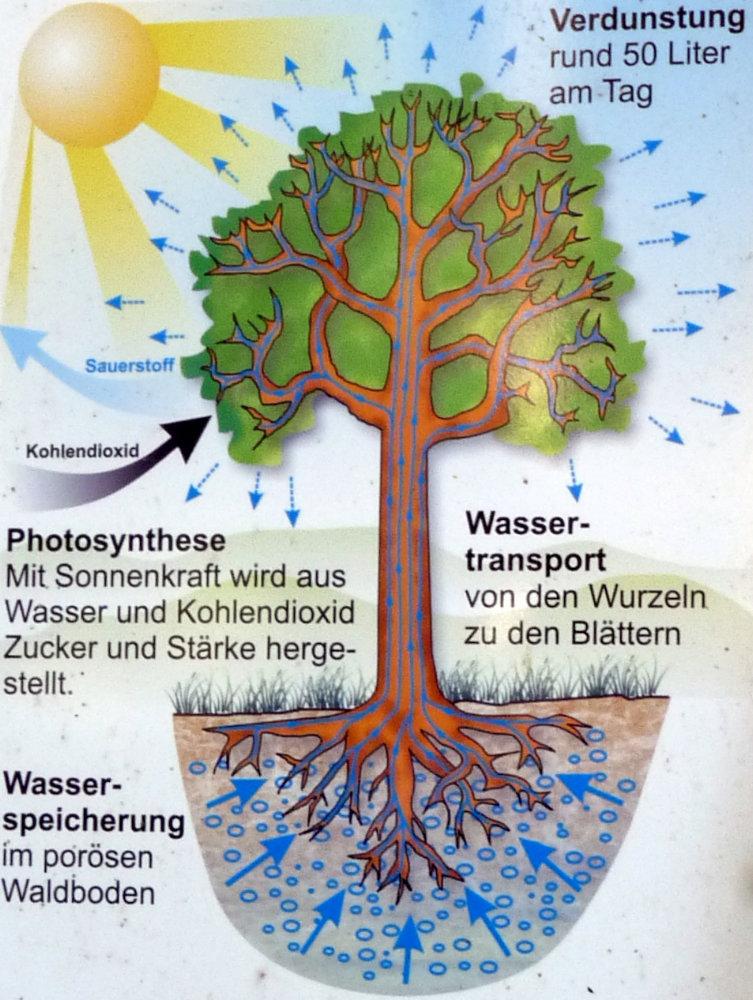
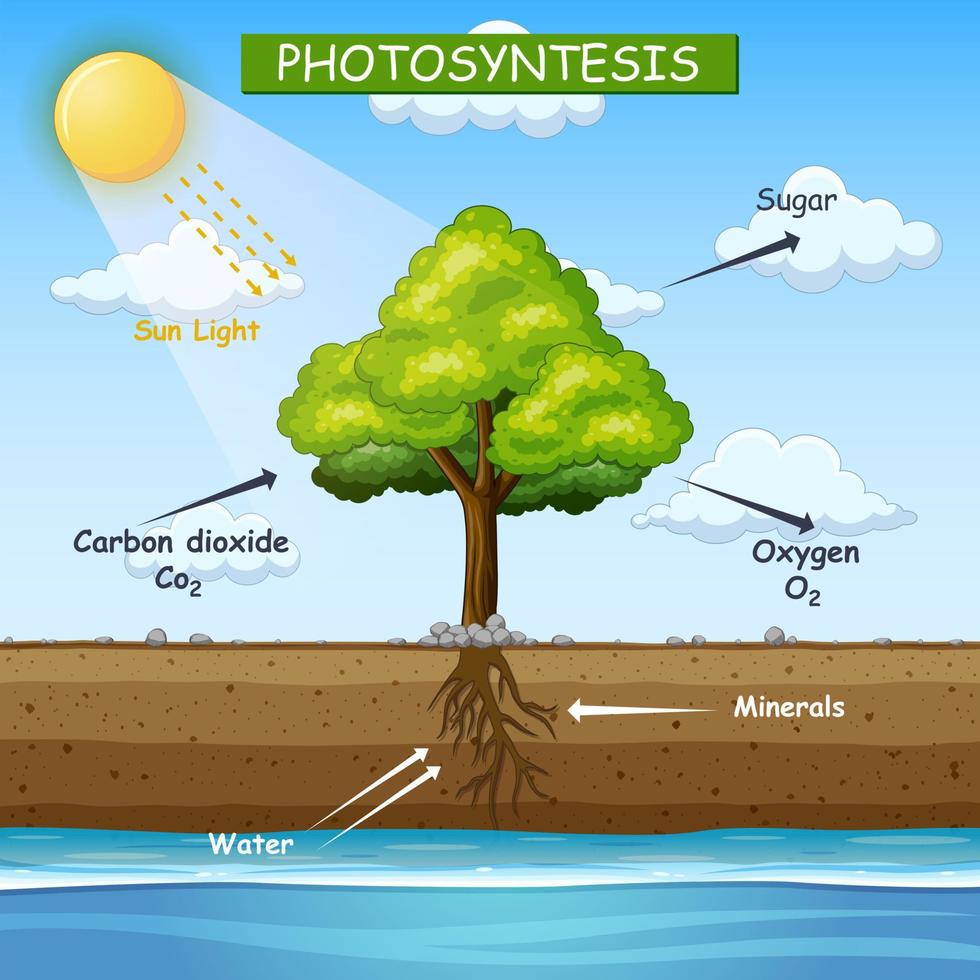
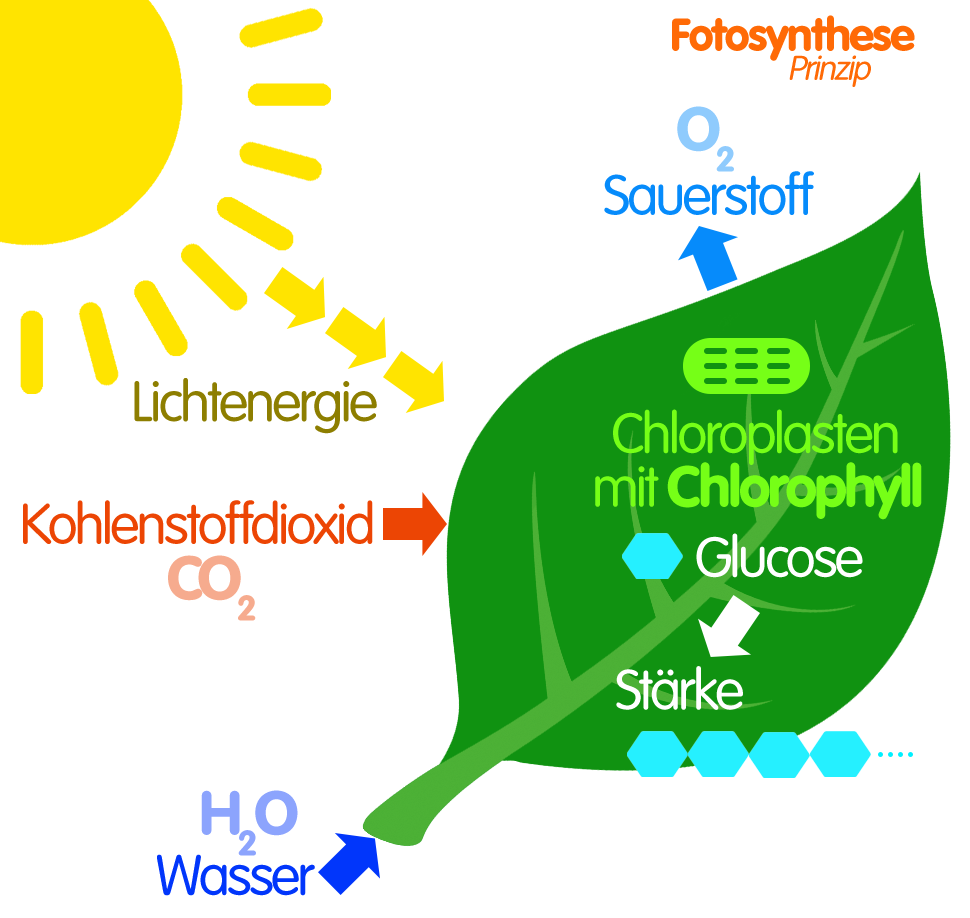
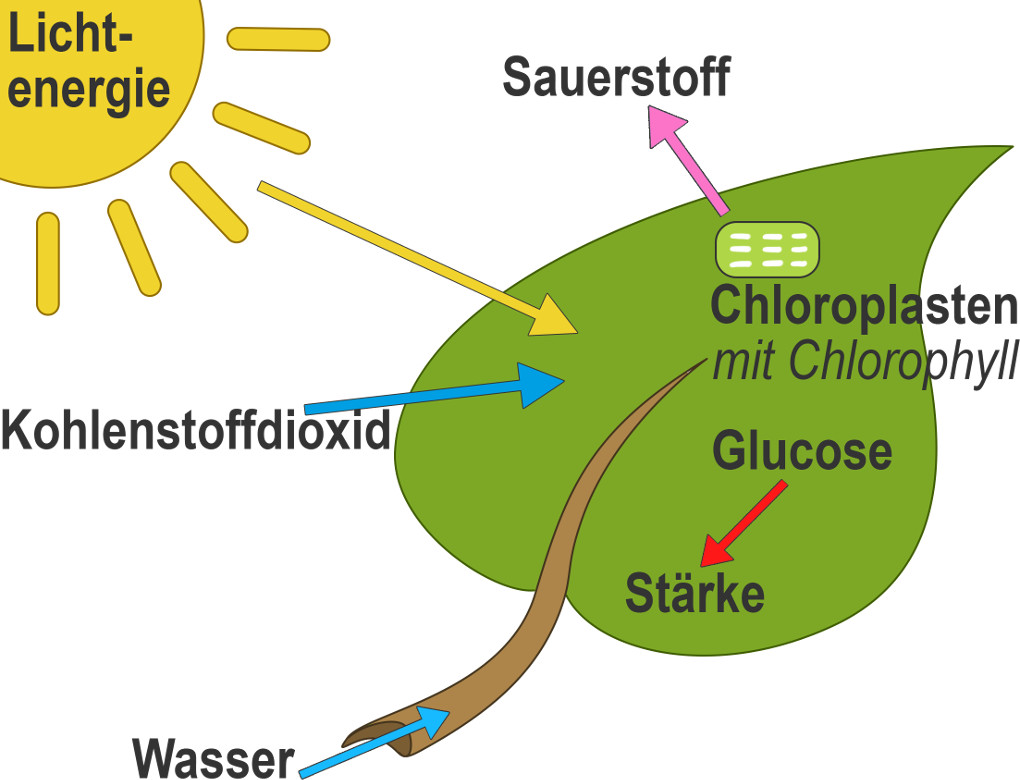
- Kohlendioxid (Carbon Dioxide): Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata, mostly located on their leaves. You’ll find this CO2 readily available in the air, regardless of whether you’re in a bustling city like Berlin or a serene forest in Bavaria.
- Wasser (Water): Water is absorbed from the soil through the plant's roots. Germany’s diverse landscapes, from the Black Forest with its abundant rainfall to the drier regions of Brandenburg, influence how easily plants can access water.
- Sonnenlicht (Sunlight): Sunlight provides the energy to power the entire process. While Germany may not be known for constant sunshine, even on cloudy days, enough light penetrates to fuel photosynthesis. Consider the lush vegetation even in areas with frequent rainfall – a testament to the efficiency of this process.
- Chlorophyll: This is the green pigment found in plant cells (specifically in organelles called chloroplasts). Chlorophyll captures the light energy from the sun. It's what gives plants their characteristic green color and is absolutely essential for photosynthesis.
What Comes Out? The Products
Now for the exciting part: what does the plant *make* using those ingredients? The primary products of photosynthesis are:
- Glukose (Glucose): This is a type of sugar, a simple carbohydrate, and the plant's primary source of energy. It's the plant's "food." The plant uses glucose immediately for energy or converts it into other forms for storage. Imagine a tree in the German forest using glucose to grow taller and stronger, adding new branches and leaves each year.
- Sauerstoff (Oxygen): This is a byproduct of photosynthesis, but it's absolutely crucial for us! Plants release oxygen (O2) into the atmosphere through those same stomata they use to absorb carbon dioxide. It’s the air we breathe! Think about the importance of the Black Forest as a "green lung" contributing to clean air, thanks to the oxygen produced through photosynthesis.
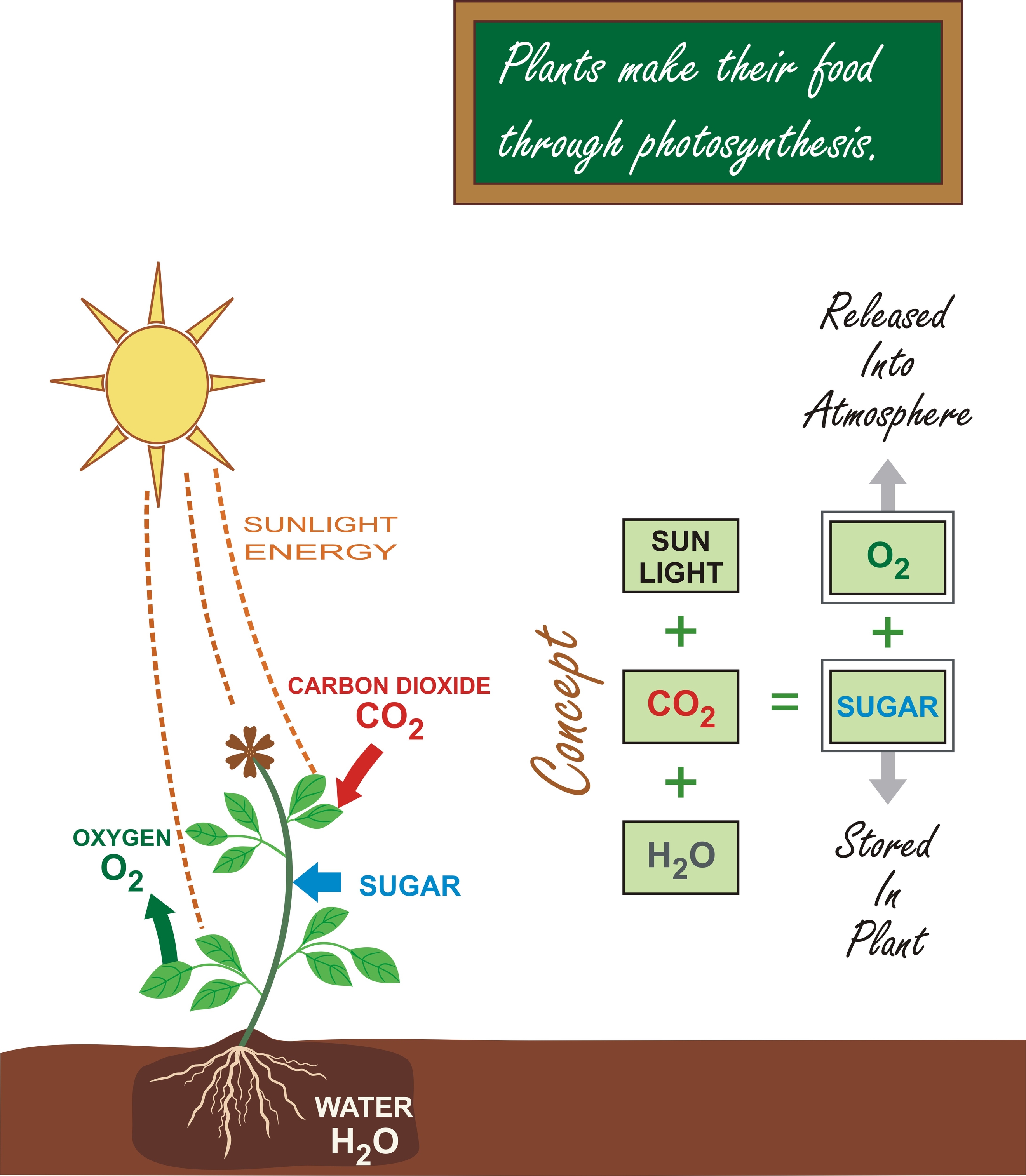
In short: carbon dioxide + water + sunlight -> glucose + oxygen.
The Chemical Equation
For the scientifically inclined, here's the simplified chemical equation for photosynthesis:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where:
- 6CO2 represents six molecules of carbon dioxide.
- 6H2O represents six molecules of water.
- C6H12O6 represents one molecule of glucose.
- 6O2 represents six molecules of oxygen.
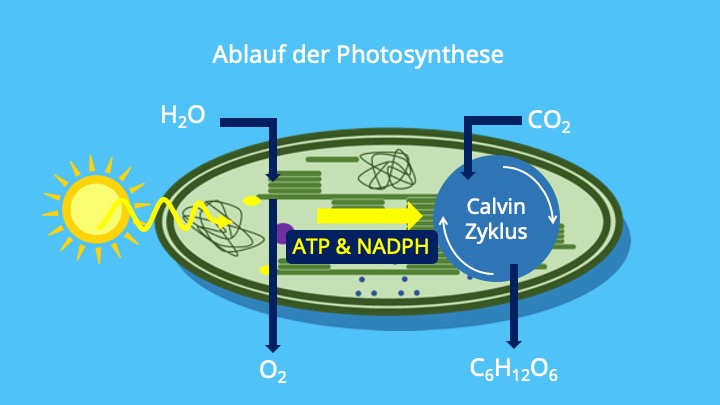
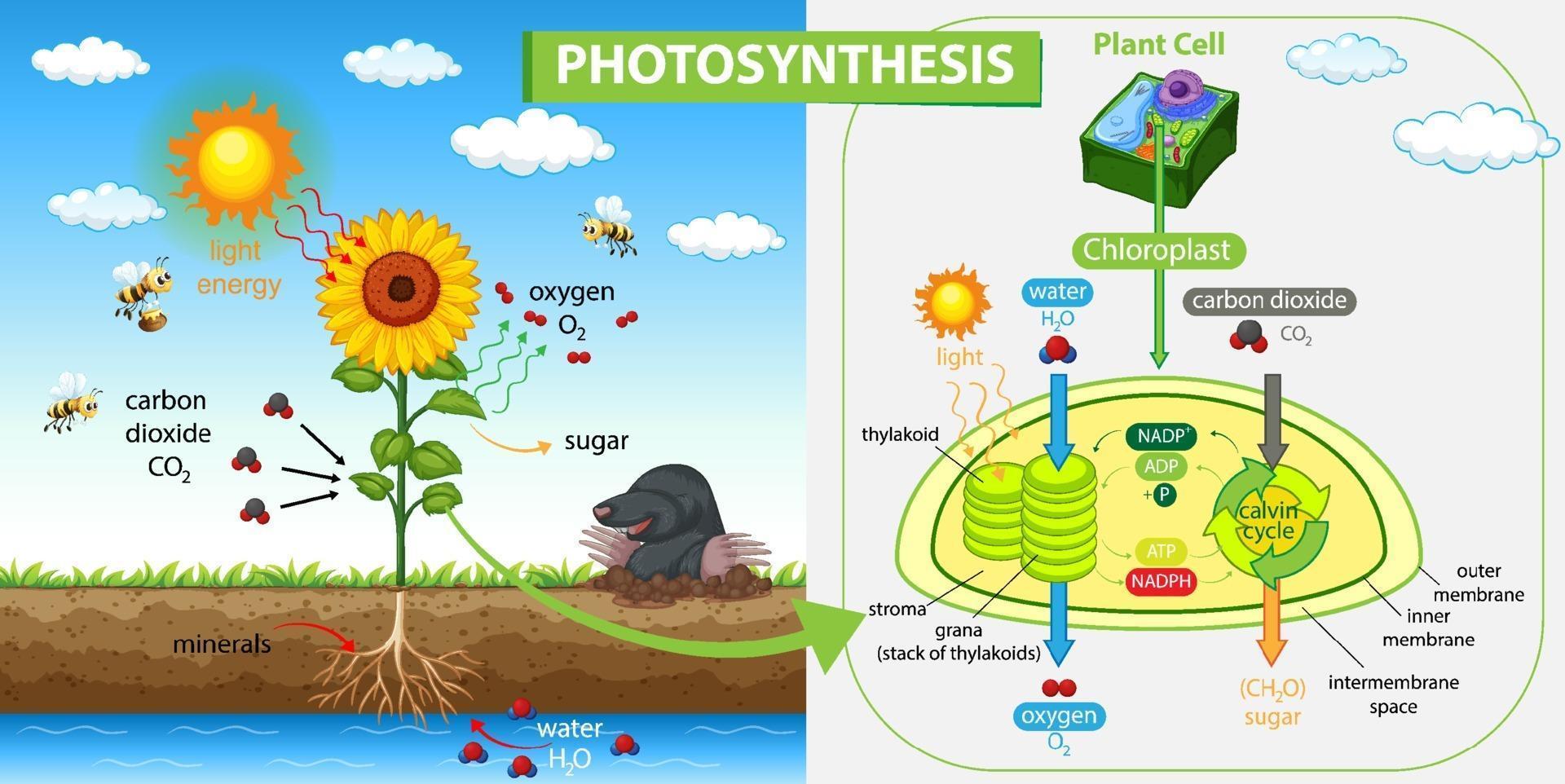
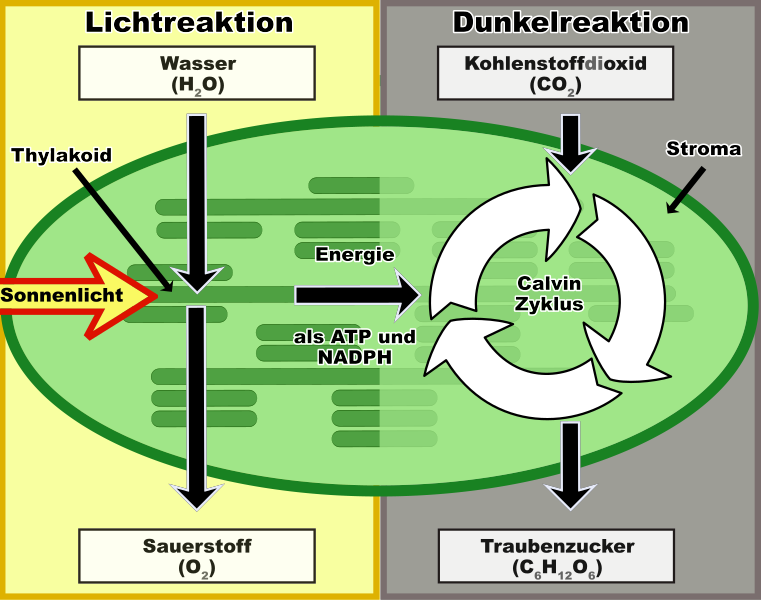
The Two Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis isn't a single step process; it's actually divided into two main stages:
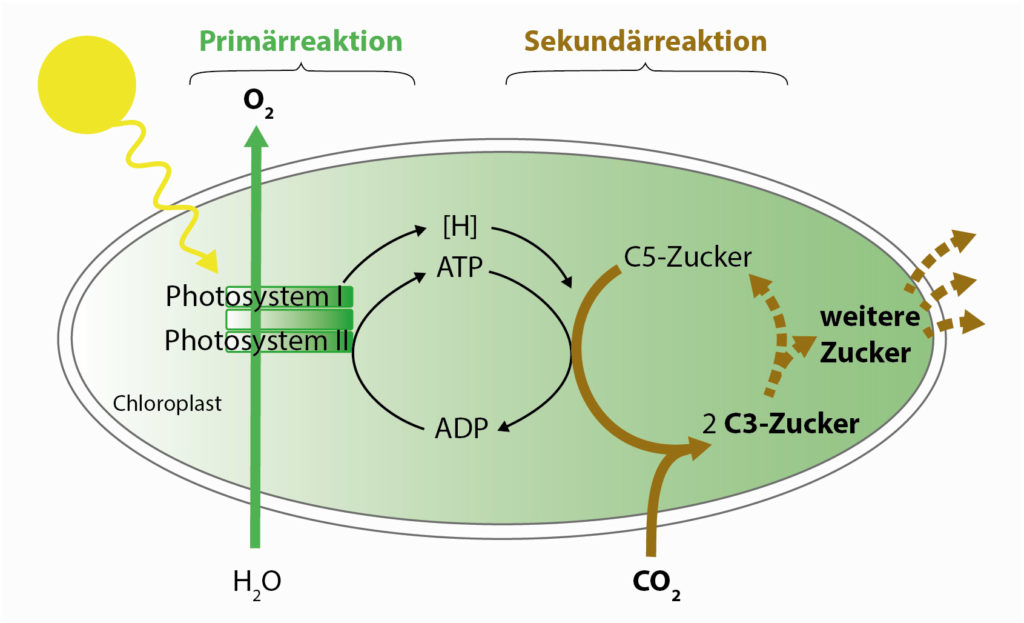
1. Lichtabhängige Reaktionen (Light-Dependent Reactions)
These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes inside the chloroplasts and *require* light. Here's what happens:
- Light Absorption: Chlorophyll absorbs light energy.
- Water Splitting: Water molecules are split into hydrogen ions (H+), electrons, and oxygen.
- ATP and NADPH Production: The light energy is used to create ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH, which are energy-carrying molecules that will power the next stage.
- Oxygen Release: Oxygen is released as a byproduct.
Think of it like this: the light-dependent reactions are like charging a battery. They capture the solar energy and convert it into a usable form.
2. Lichtunabhängige Reaktionen (Light-Independent Reactions) / Calvin Cycle
Also known as the Calvin cycle, these reactions occur in the stroma (the fluid-filled space) of the chloroplasts and do *not* directly require light. However, they rely on the ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions.
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is "fixed" or incorporated into an organic molecule.
- Sugar Production: Using the energy from ATP and NADPH, the fixed carbon is converted into glucose.
- Regeneration: The molecules needed for the process to continue are regenerated.
The Calvin cycle is like using the charged battery to power a machine that produces something valuable – in this case, glucose.
Why Photosynthesis Matters (Especially in Germany!)
Understanding photosynthesis is crucial for appreciating the world around you. Here's why it's so important, particularly as you explore Germany:
- Food Production: All the food we eat, directly or indirectly, comes from plants that perform photosynthesis. From the wheat used to make German bread (Brot) to the apples (Äpfel) grown in orchards, photosynthesis is the foundation.
- Oxygen Production: Photosynthesis is the primary source of oxygen in our atmosphere. Imagine hiking through the Alps – the fresh air you're breathing is largely thanks to photosynthesis! The dense forests of Germany, like the Bavarian Forest, are especially important for oxygen production.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Plants absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, from the atmosphere. This helps regulate the Earth's climate. Preserving and expanding Germany's forests and green spaces is vital for mitigating climate change.
- Ecosystem Support: Photosynthesis supports entire ecosystems by providing food and energy for all living organisms. The diverse flora and fauna you encounter in Germany’s national parks, like the Jasmund National Park on Rügen Island, are all dependent on photosynthesis.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Understanding photosynthesis can help us develop more sustainable agricultural practices. By optimizing conditions for plant growth, we can increase food production while minimizing environmental impact. Germany is increasingly focused on sustainable agriculture and organic farming (ökologischer Landbau), recognizing the importance of working with nature rather than against it.
Experiencing Photosynthesis in Germany
While you might not see the process happening directly, you can certainly appreciate its effects all around you during your visit to Germany:
- Visit a Botanical Garden (Botanischer Garten): Explore the diverse plant life and learn more about the different species that rely on photosynthesis. Many German cities have impressive botanical gardens, such as the Berlin-Dahlem Botanical Garden and Museum.
- Hike in a Forest (Wald): Immerse yourself in the lush greenery and breathe in the fresh, oxygen-rich air. The Black Forest (Schwarzwald), the Bavarian Forest (Bayerischer Wald), and the Harz Mountains offer incredible hiking opportunities.
- Explore a Vineyard (Weinberg): Many of Germany's famous wines are produced in beautiful vineyard regions, like the Mosel Valley. Observe the grapevines and appreciate the role of photosynthesis in producing the grapes that are used to make wine.
- Visit a Farm (Bauernhof): Learn about sustainable agriculture and see firsthand how food is produced. Many farms offer tours and educational programs.
- Simply Observe Nature: Take a walk in a park, sit by a river, or enjoy a picnic in a field. Pay attention to the plants around you and appreciate the vital role they play in our ecosystem.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is a truly remarkable process that underpins life as we know it. As you explore the beautiful landscapes and enjoy the vibrant culture of Germany, take a moment to appreciate the unseen power of photosynthesis at work, creating the food we eat, the air we breathe, and the stunning environment we all enjoy. Understanding this fundamental process will deepen your appreciation for the natural world and enhance your travel experience. Have a wonderful time discovering Germany!


![Was Entsteht Bei Der Photosynthese Adenosintriphosphat (ATP) • Funktion einfach erklärt · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/ATP-Verbrauch_bei_der_Photosynthese_WP-1024x576.jpg)