Was Ist Eine Harmonische Schwingung
Willkommen! Planning a trip to Germany? Perhaps you're already here, enjoying the *Gemütlichkeit* and hoping to dive a little deeper into the language and culture? Then let's talk about something you might encounter, perhaps surprisingly often: the world of physics! Don't worry, we'll keep it light and applicable to your everyday experience. Today's topic is: Was ist eine Harmonische Schwingung? (What is a Harmonic Oscillation?)
Now, "Harmonische Schwingung" might sound intimidating, like something straight out of a university textbook. But fear not! It's simply a very regular, predictable back-and-forth motion. Think of it as a pendulum swinging, a child on a swing set, or even the regular pulsing of a metronome. The key is that this motion repeats itself consistently over time.
The Basics of a Harmonic Oscillation
To truly understand a "Harmonische Schwingung," let's break down the key elements:
- Schwingung (Oscillation): This is the fundamental movement. It's the back-and-forth, up-and-down, or side-to-side action. Think of a tuning fork vibrating after you strike it – that's an oscillation.
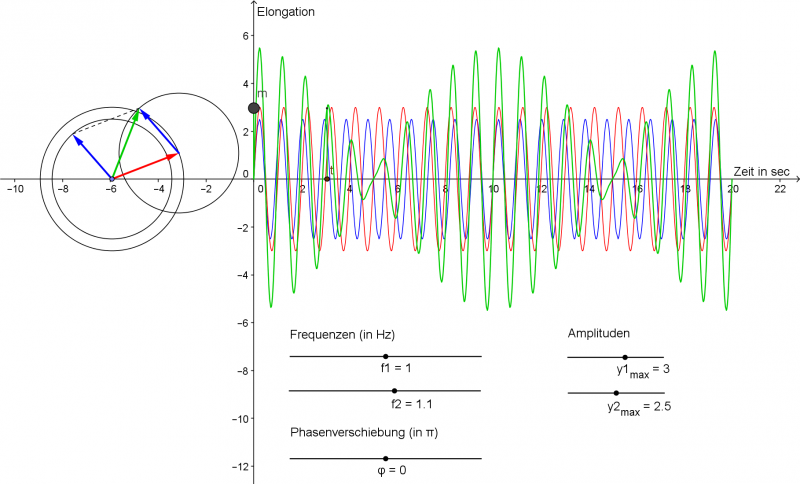
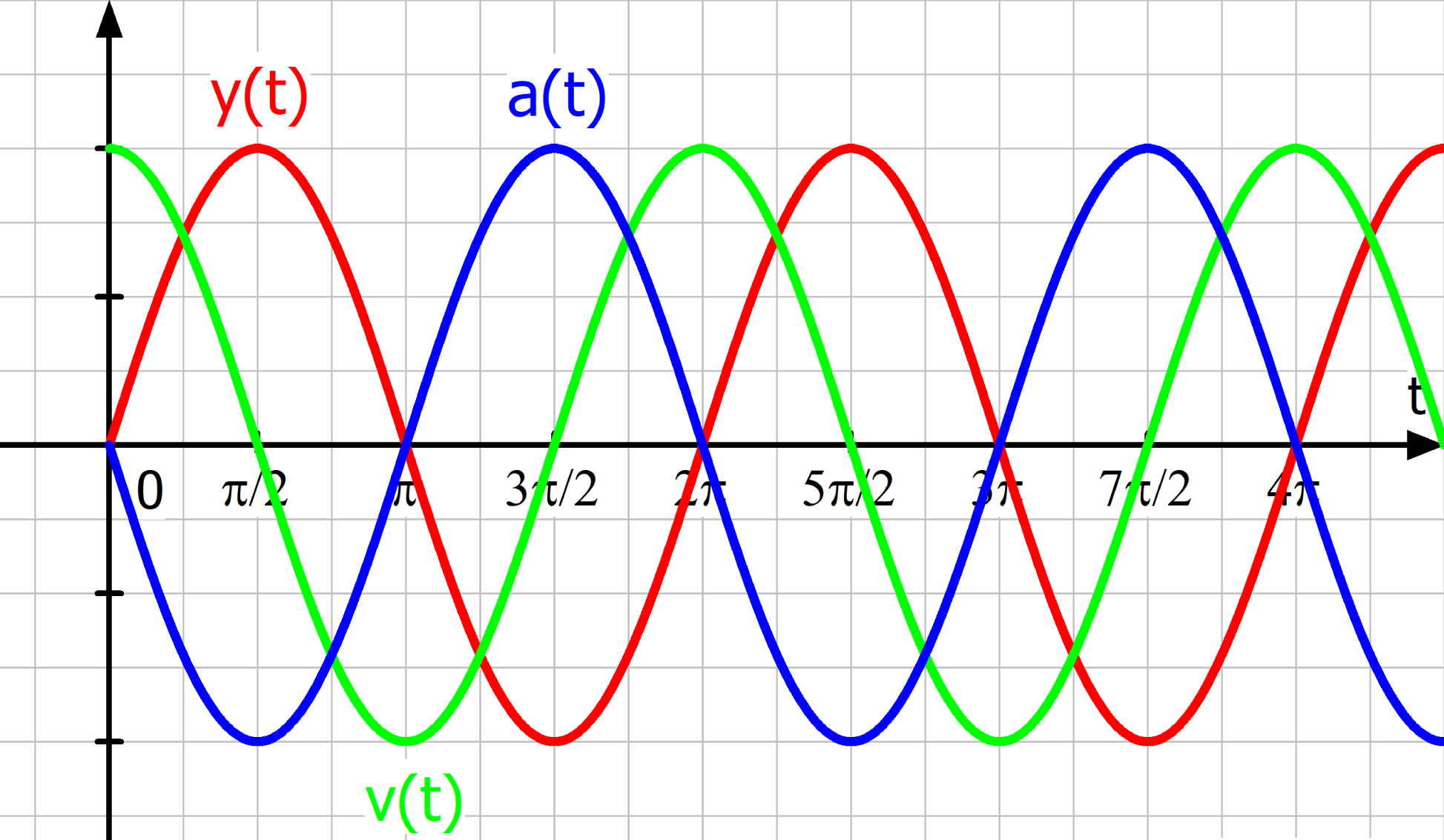
- Harmonisch (Harmonic): This is where the 'magic' happens. "Harmonisch" means that the oscillation is *smooth* and *repeating*. It follows a specific mathematical pattern called a sine wave (or a cosine wave – they're essentially the same, just shifted). This pattern dictates how the object moves over time.
In other words, a harmonic oscillation is a repeating, predictable movement that follows a smooth, wave-like pattern.
Visualizing the Harmonic Oscillation
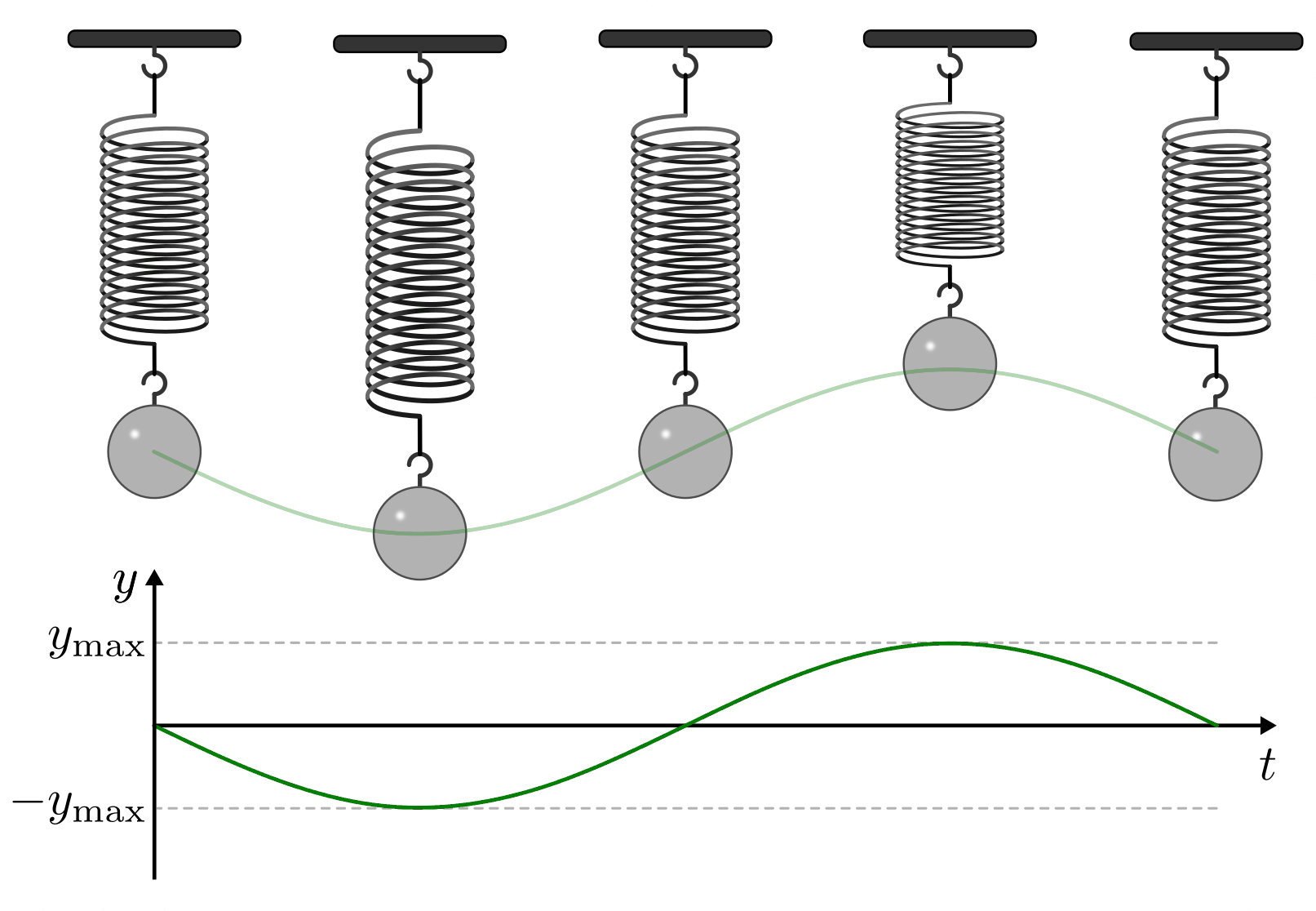
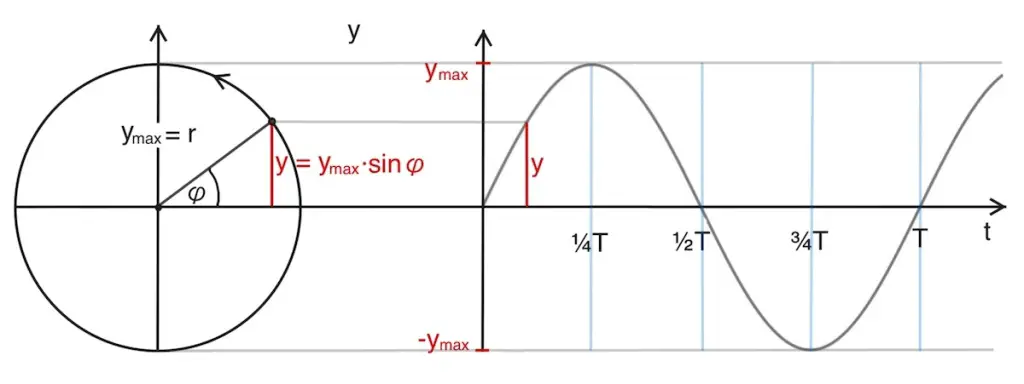
Imagine a simple pendulum. When you pull it to one side and release it, it swings back and forth. Now, picture graphing the pendulum's position over time. You'd get a beautiful, undulating curve – a sine wave! This curve represents the pendulum's displacement (how far it is from its resting position) at any given moment.
Think about these characteristics of the sine wave in relation to the pendulum:
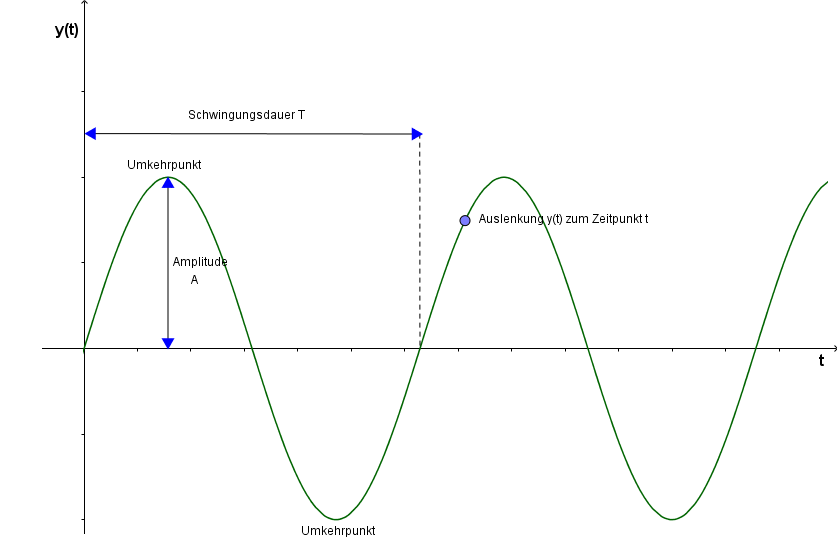
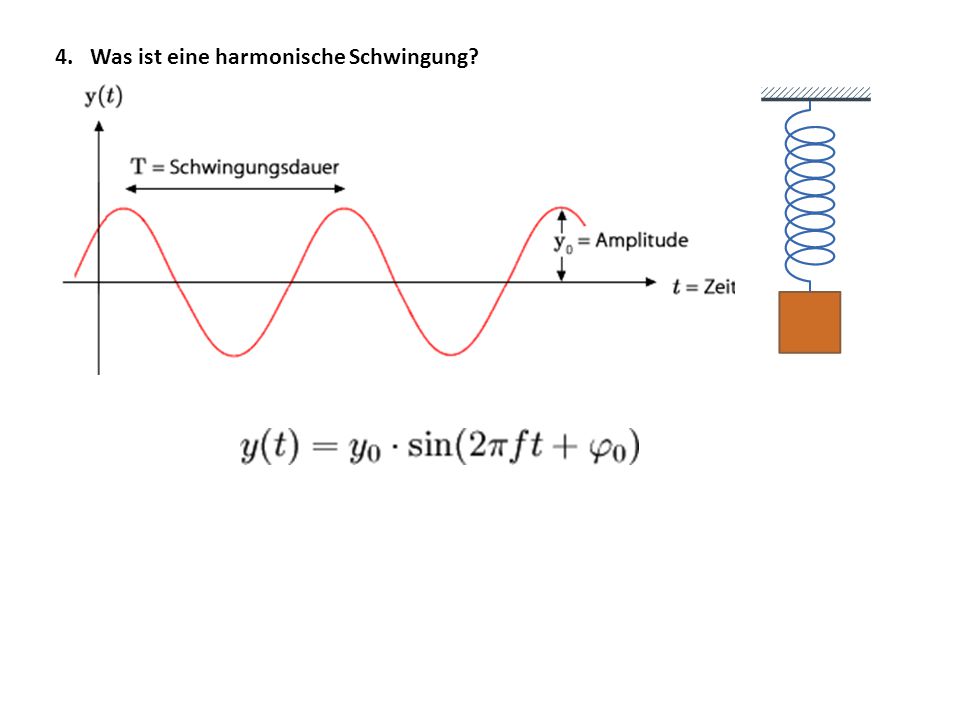
- Amplitude: The *amplitude* is the maximum displacement of the pendulum from its resting position. It's how far the pendulum swings to either side. A larger amplitude means a bigger swing!
- Period: The *period* is the time it takes for the pendulum to complete one full swing – from one extreme, to the other, and back again. A longer period means a slower swing.
- Frequency: The *frequency* is the number of complete swings the pendulum makes per second (or any other unit of time). It's the inverse of the period. A higher frequency means a faster swing.
These three elements – amplitude, period, and frequency – completely define a harmonic oscillation.
Why is it Important?
You might be wondering, "Okay, so it's a predictable back-and-forth motion. Why should I, as a tourist or expat, care about harmonic oscillations?" Well, the concept is far more pervasive than you might think! It underlies many technologies and phenomena you'll encounter in Germany and beyond:
- Music: Musical instruments, from guitars to pianos to flutes, rely on harmonic oscillations to produce sound. The strings vibrate, creating sound waves that follow a harmonic pattern. The specific frequency of these vibrations determines the pitch of the note. Germany, with its rich musical heritage, is brimming with examples!
- Clocks and Watches: Many timekeeping devices, especially older mechanical ones, use a pendulum or balance wheel that oscillates harmonically to keep time. You'll see many beautiful examples of these in museums and antique shops.
- Radio and Electronics: Radio waves, which carry information for communication, are a type of electromagnetic wave that oscillates harmonically. Your smartphone, radio, and television all rely on this principle.
- Buildings and Bridges: Even buildings and bridges can oscillate! Engineers carefully consider the natural frequencies of these structures to ensure they can withstand external forces like wind or earthquakes. Resonance (when the frequency of the external force matches the structure's natural frequency) can be dangerous, so it's carefully avoided.
Consider these examples during your stay:
- Listen to the church bells ringing. Their sound is created by a complex system, but the initial vibration of the bell follows oscillatory principles.
- Admire the intricate mechanisms of a cuckoo clock in the Black Forest. The pendulum is a classic example of harmonic motion.
- Notice the smooth swaying of boats in a harbor. This is a more complex type of oscillation, but the underlying principles are similar.
Harmonische Schwingung in Action: Examples You Might See
Let's make this even more concrete. Here are a few scenarios where you might encounter harmonic oscillations during your travels in Germany:
* The Metronome in a Music School: If you happen to visit a music school or attend a concert, you'll likely see a metronome. This device uses a pendulum to keep time and provides a visual representation of a harmonic oscillation. The adjustable weight changes the period and frequency of the swing. * Swinging on a Playground: Take a stroll through a park and watch children on swings. A swing is a perfect example of a damped harmonic oscillation (we'll get to damping in a moment!). * Tuning Forks in a Science Museum: Many science museums have exhibits showcasing sound waves. You might see tuning forks that vibrate when struck, producing a pure tone. This is a direct manifestation of a harmonic oscillation.Beyond the Ideal: Damped and Forced Oscillations
So far, we've talked about ideal harmonic oscillations, where the motion continues indefinitely without losing energy. However, in the real world, things aren't so perfect. Two important deviations from the ideal are:
Damped Oscillations (Gedämpfte Schwingungen)
In reality, friction and air resistance will eventually slow down and stop any oscillation. This is called damping. Think of a pendulum that gradually swings less and less until it comes to a complete stop. The energy is being dissipated as heat due to friction. A Gedämpfte Schwingung is a harmonic oscillation where the amplitude gradually decreases over time.
Forced Oscillations (Erzwungene Schwingungen)
Sometimes, an external force can keep an oscillation going. This is called a forced oscillation. Think of pushing a child on a swing. You're applying a force at the right time to counteract the damping and keep the swing moving. If the frequency of the applied force is close to the natural frequency of the system, you get resonance, where the amplitude of the oscillation becomes very large. This can be a good thing (like in musical instruments) or a bad thing (like when a bridge vibrates too much). An Erzwungene Schwingung occurs when an external force drives an oscillatory system.
The German Vocabulary: A Quick Guide
Here are some key German words related to harmonic oscillations that might be useful during your stay:
* Harmonische Schwingung: Harmonic oscillation * Schwingung: Oscillation * Amplitude: Amplitude * Periode: Period * Frequenz: Frequency * Auslenkung: Displacement * Gedämpfte Schwingung: Damped oscillation * Erzwungene Schwingung: Forced oscillation * Resonanz: Resonance * Pendel: PendulumKnowing these terms, even superficially, will enhance your understanding of the German language and culture.
Conclusion: Embrace the Oscillations!
Hopefully, this has demystified the concept of "Harmonische Schwingung" and shown you how it's relevant to your experience in Germany. From the musical traditions to the engineering marvels, oscillations are everywhere. So, the next time you hear a church bell, see a child on a swing, or admire a clock, take a moment to appreciate the physics behind the motion. Enjoy your travels and Auf Wiedersehen!
Remember, learning a little bit about the science behind the everyday things you see can add a whole new layer of appreciation to your travels. Don't be afraid to ask questions, explore, and discover the fascinating world around you!
This is just a basic introduction. If you're interested in learning more, there are many resources available online and in libraries. Have fun exploring!
![Was Ist Eine Harmonische Schwingung Schwingungsdauer und Amplitude: Berechnen Pendel · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Amplitude-1024x576.jpg)





![Was Ist Eine Harmonische Schwingung Was ist eine harmonische Schwingung? [Formel]](https://images.cdn.sofatutor.net/videos/pictures/5339/normal/Vorschaubild_Die_harmonische_mechanische_Schwingung.jpg?1581427449)
![Was Ist Eine Harmonische Schwingung Schwingungsdauer und Amplitude: Berechnen Pendel · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Schwingungsdauer-1024x576.jpg)