Was Macht Der Golgi Apparat

Willkommen! Have you ever wondered about the intricate inner workings of your cells? Perhaps not while planning your Berlin adventure, but curiosity knows no bounds! Today, we'll embark on a journey into the microscopic world to explore a fascinating cellular organelle: Der Golgi-Apparat. Don't worry, this isn't a biology exam! We'll keep it light, engaging, and explain why understanding this cellular powerhouse is actually quite… well, impressive!
Was Ist Der Golgi-Apparat? (What is the Golgi Apparatus?)
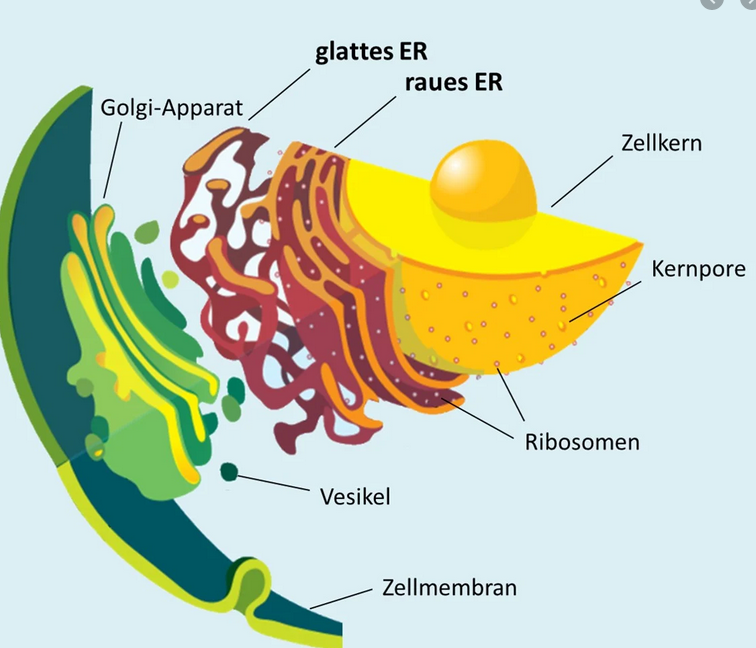
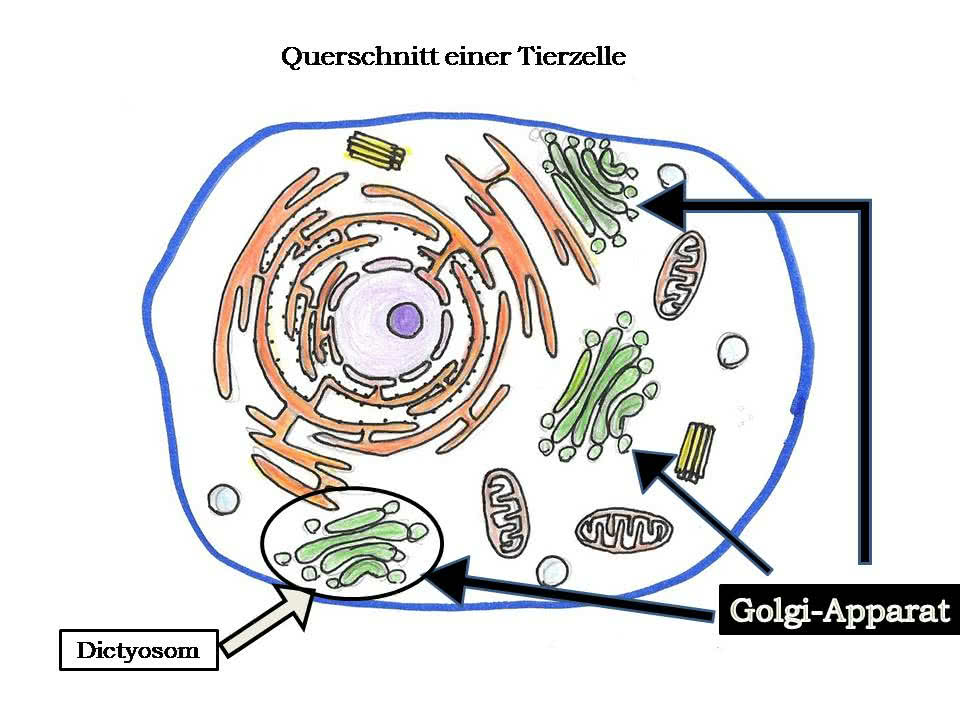
The Golgi-Apparat, sometimes called the Golgi-Körper or Golgi-Komplex, is essentially the cell's post office and packaging center. Imagine a highly efficient, multi-storied warehouse where proteins and lipids (fats) arrive, get sorted, modified, packaged, and then shipped off to their final destinations within the cell or even outside of it. Think of it as the Amazon distribution center, but for microscopic parcels!
In simple terms, the Golgi Apparatus:
- Processes and modifies proteins and lipids.
- Packages these molecules into vesicles.
- Sorts and directs these vesicles to their correct destinations.
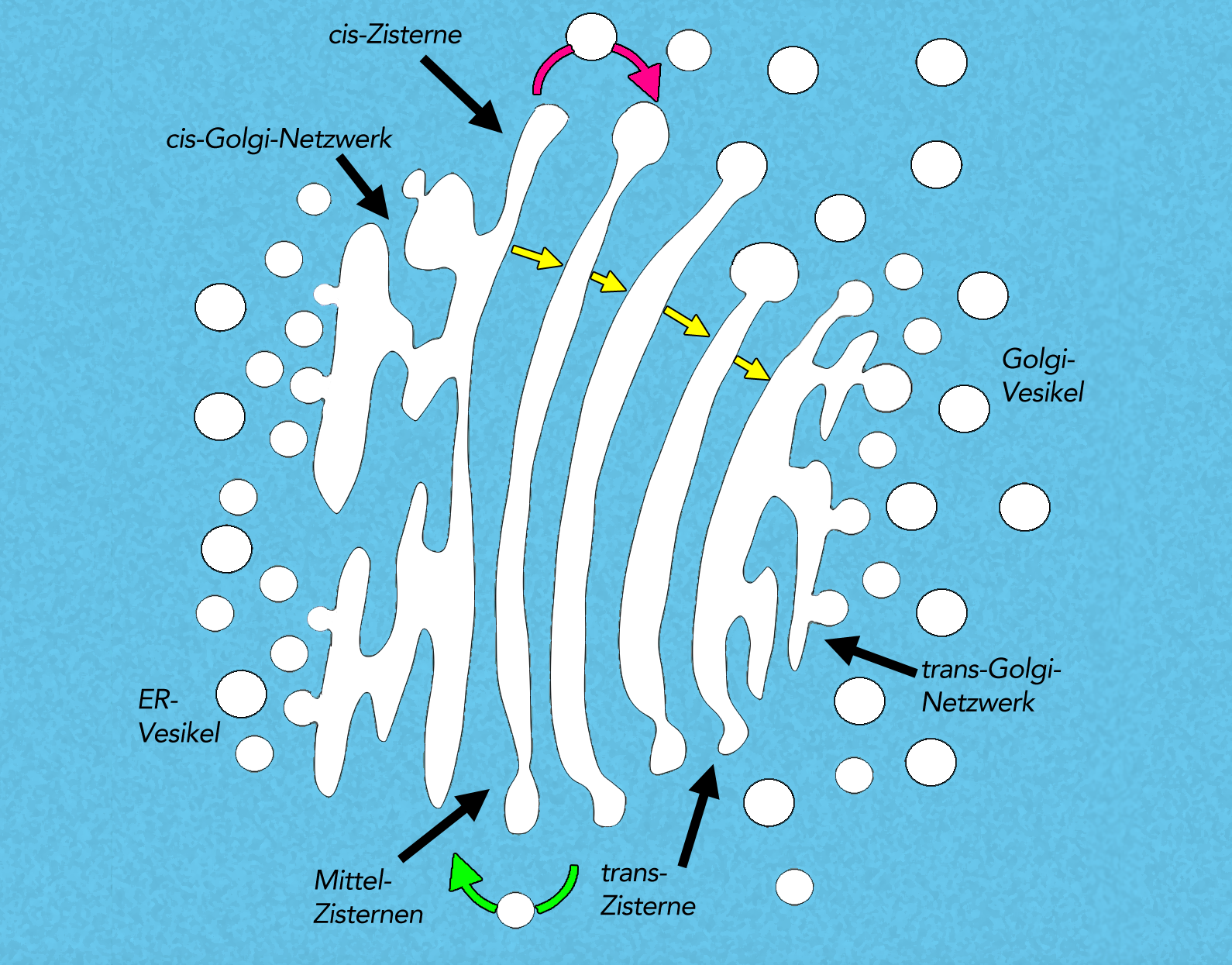
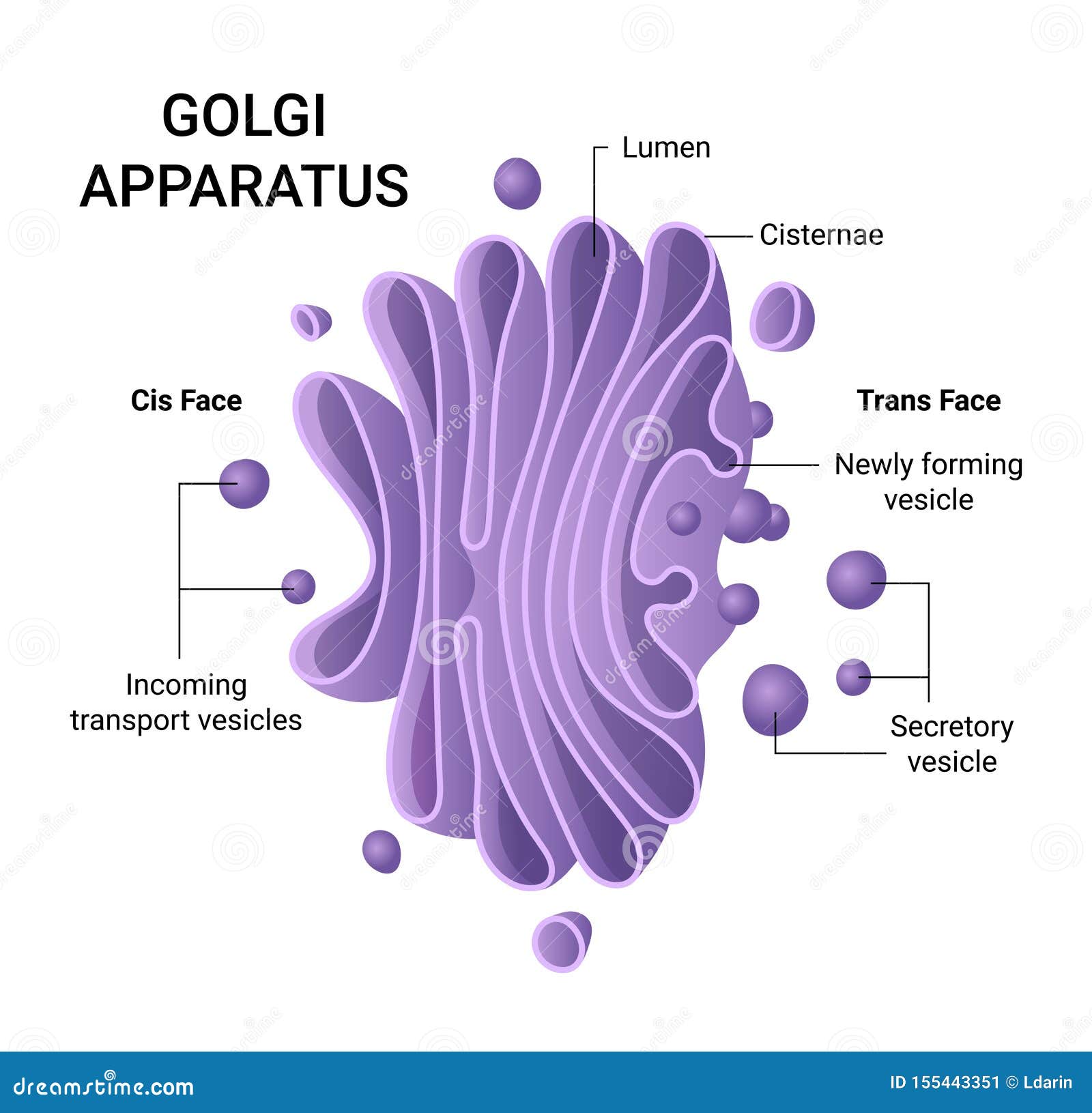
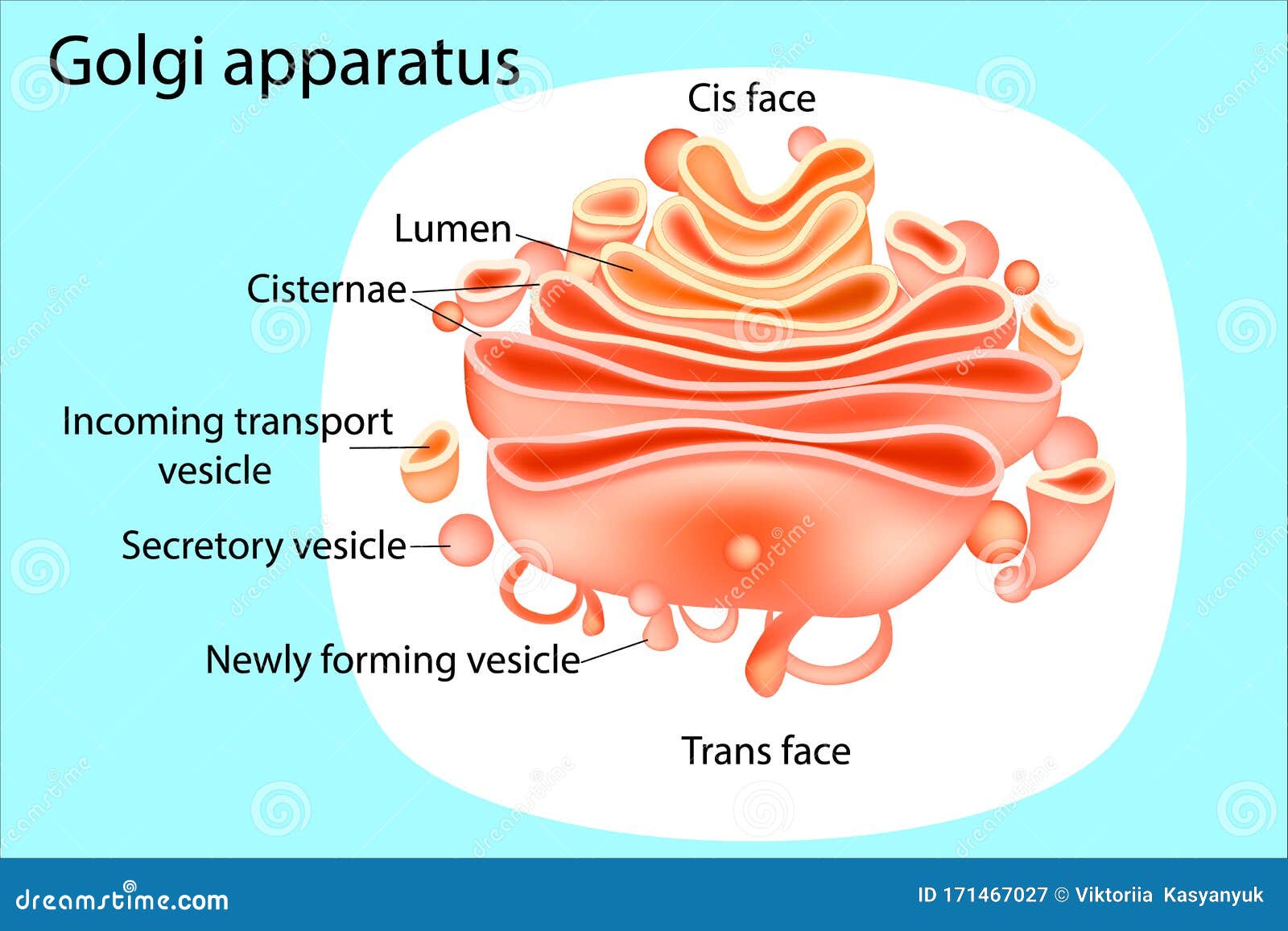
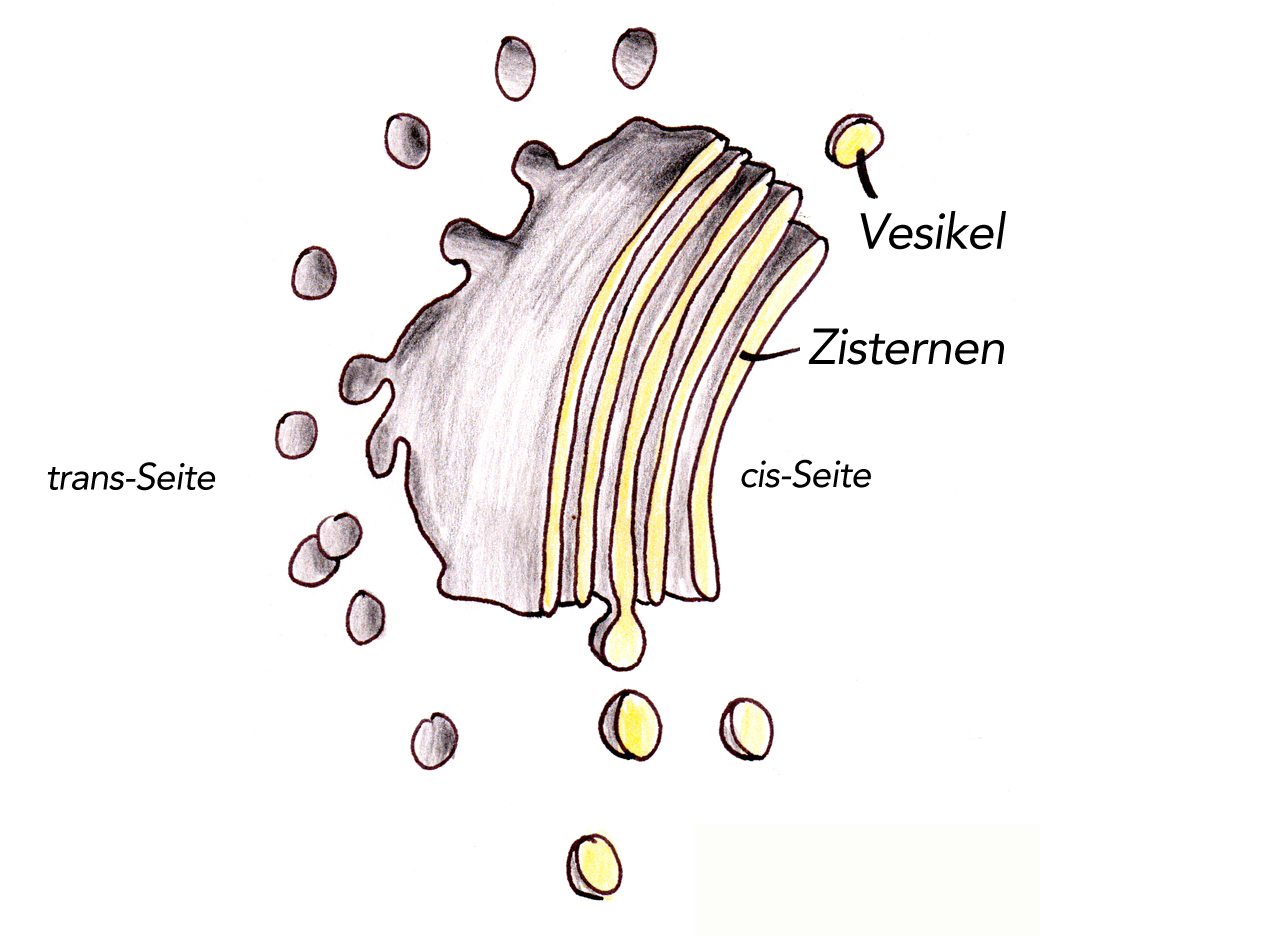
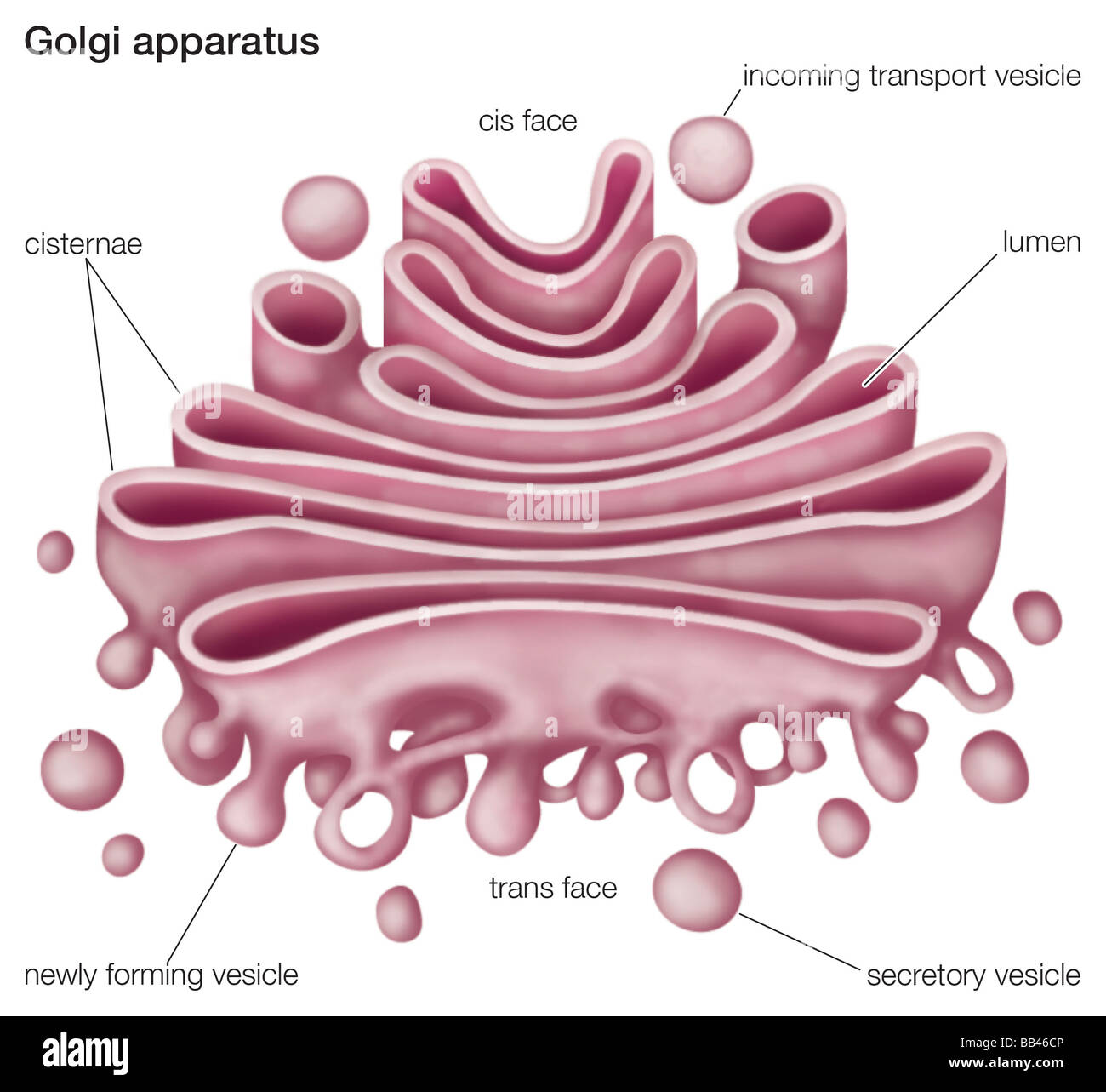
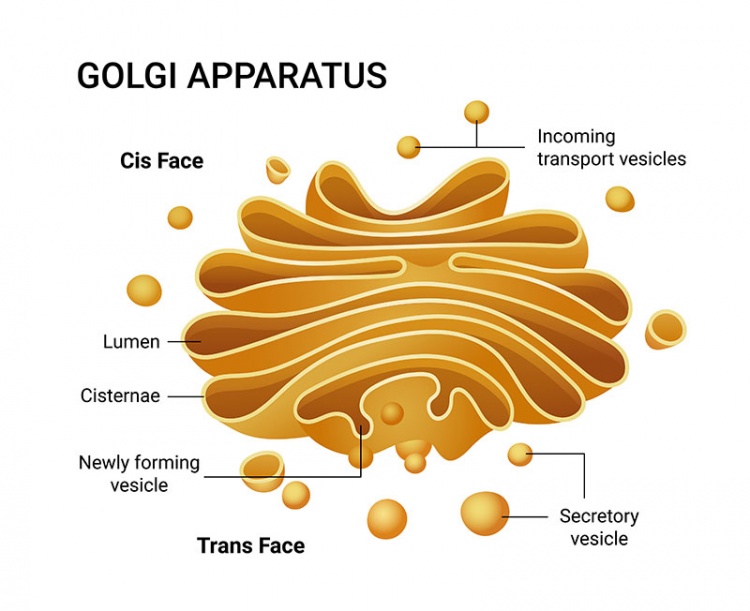
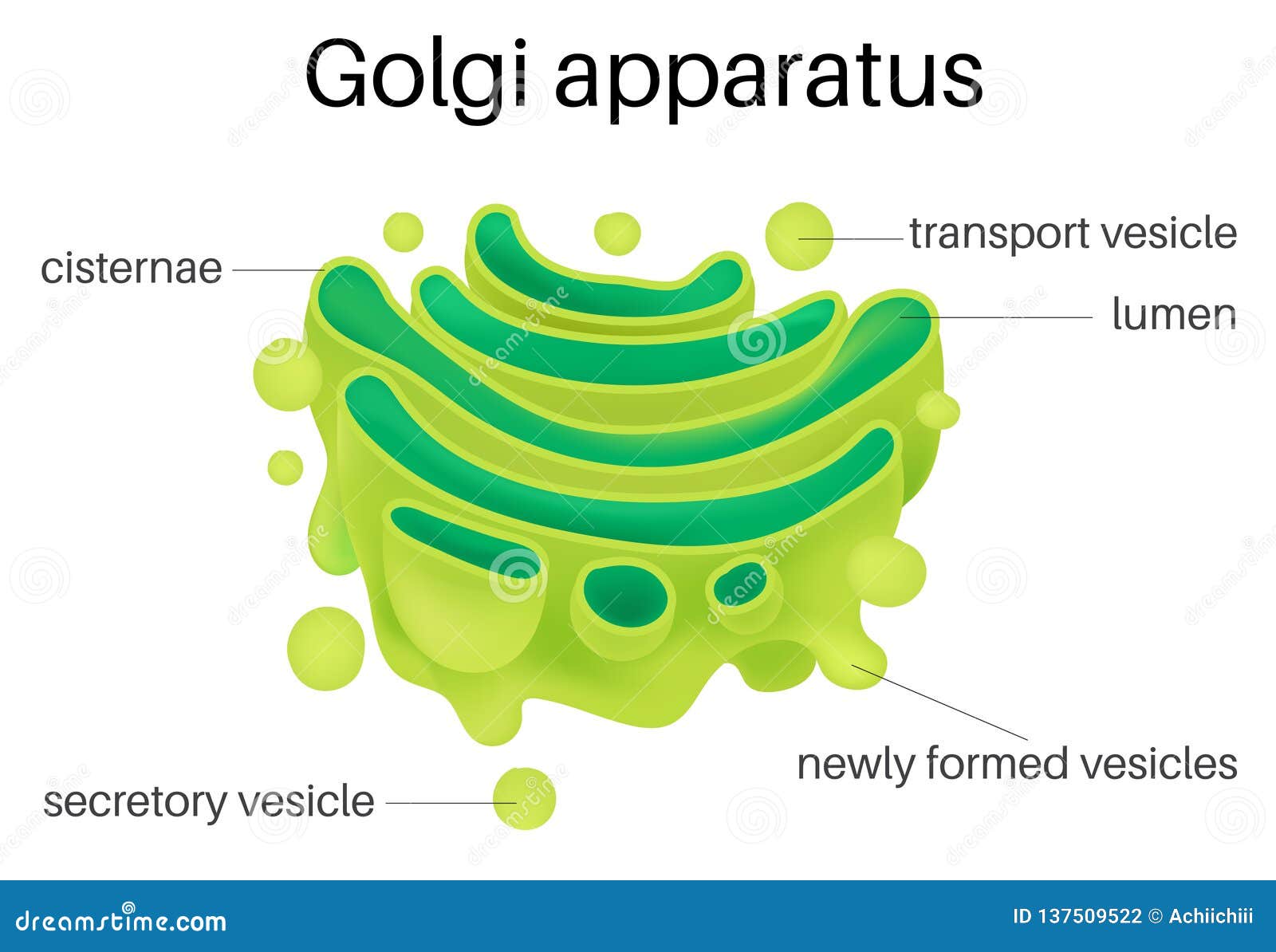
Structurally, the Golgi-Apparat resembles a stack of flattened, membrane-bound sacs called Zisternen (cisternae). These cisternae are arranged in a curved, polarized fashion. Think of them like a stack of slightly curved pita breads, all nestled together! This arrangement is key to its function.
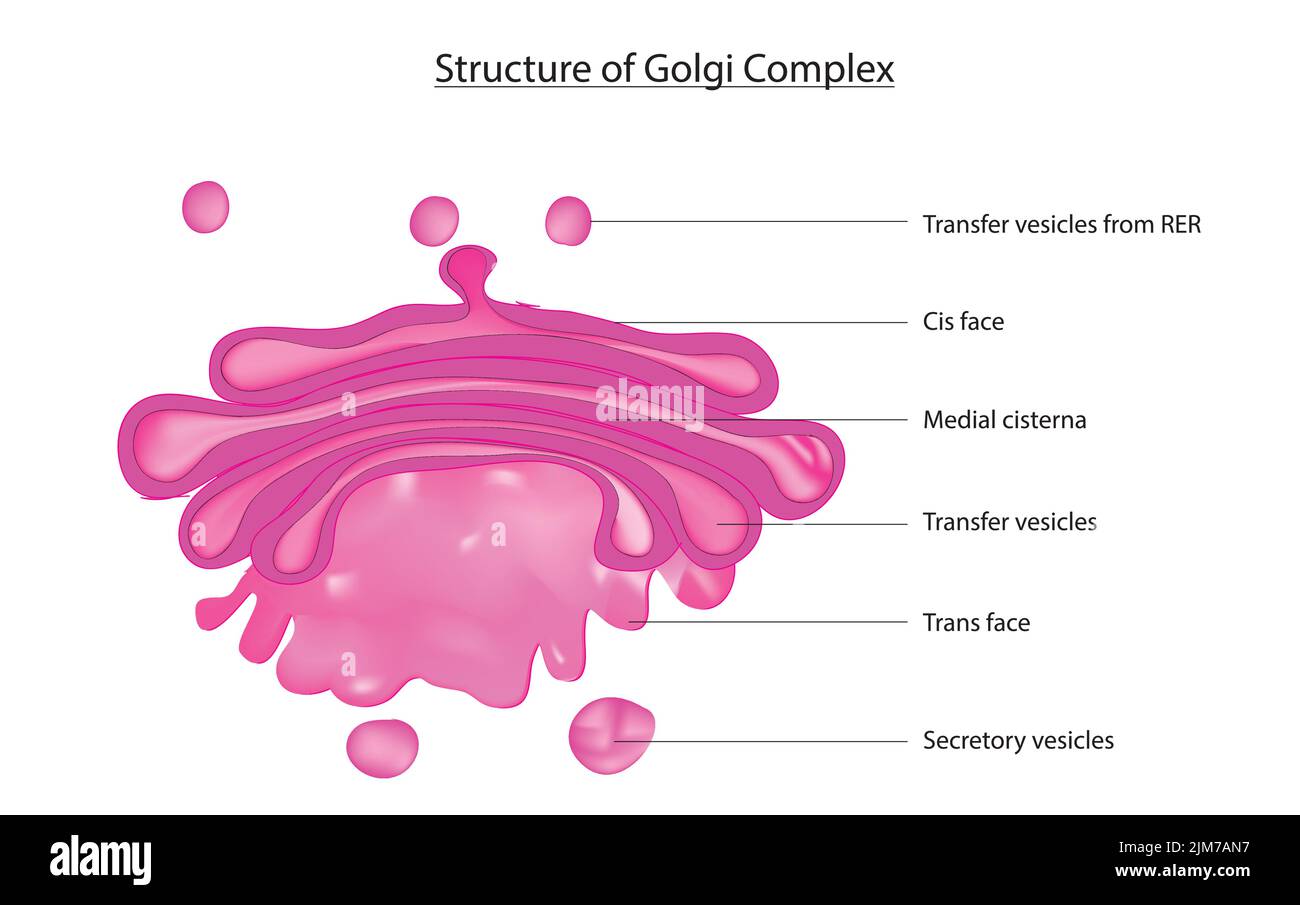
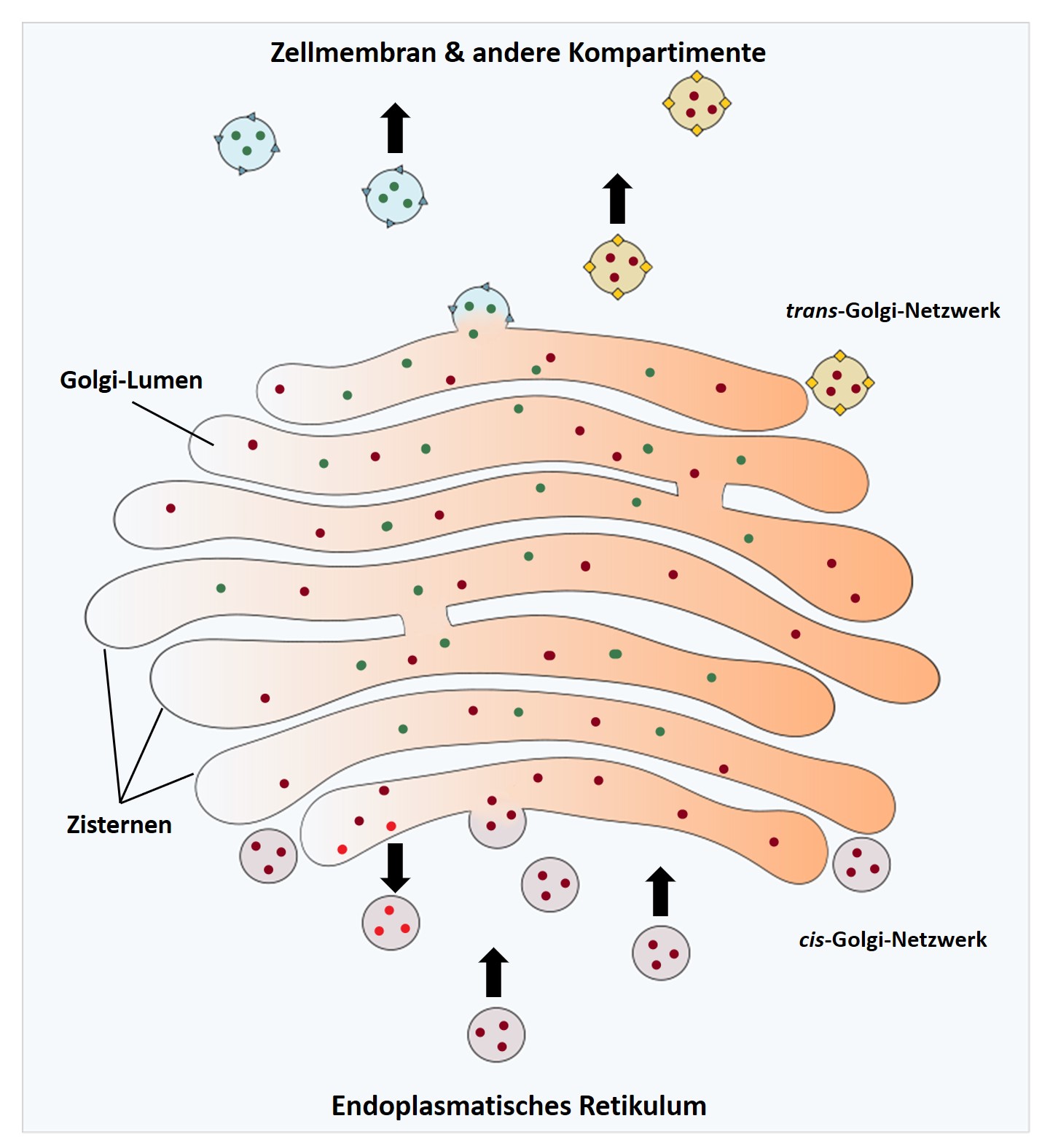
The Cis- and Trans- Sides: A Cellular Loading Dock
The Golgi-Apparat has two distinct faces: the cis face and the trans face. These represent the "receiving" and "shipping" ends of the organelle.
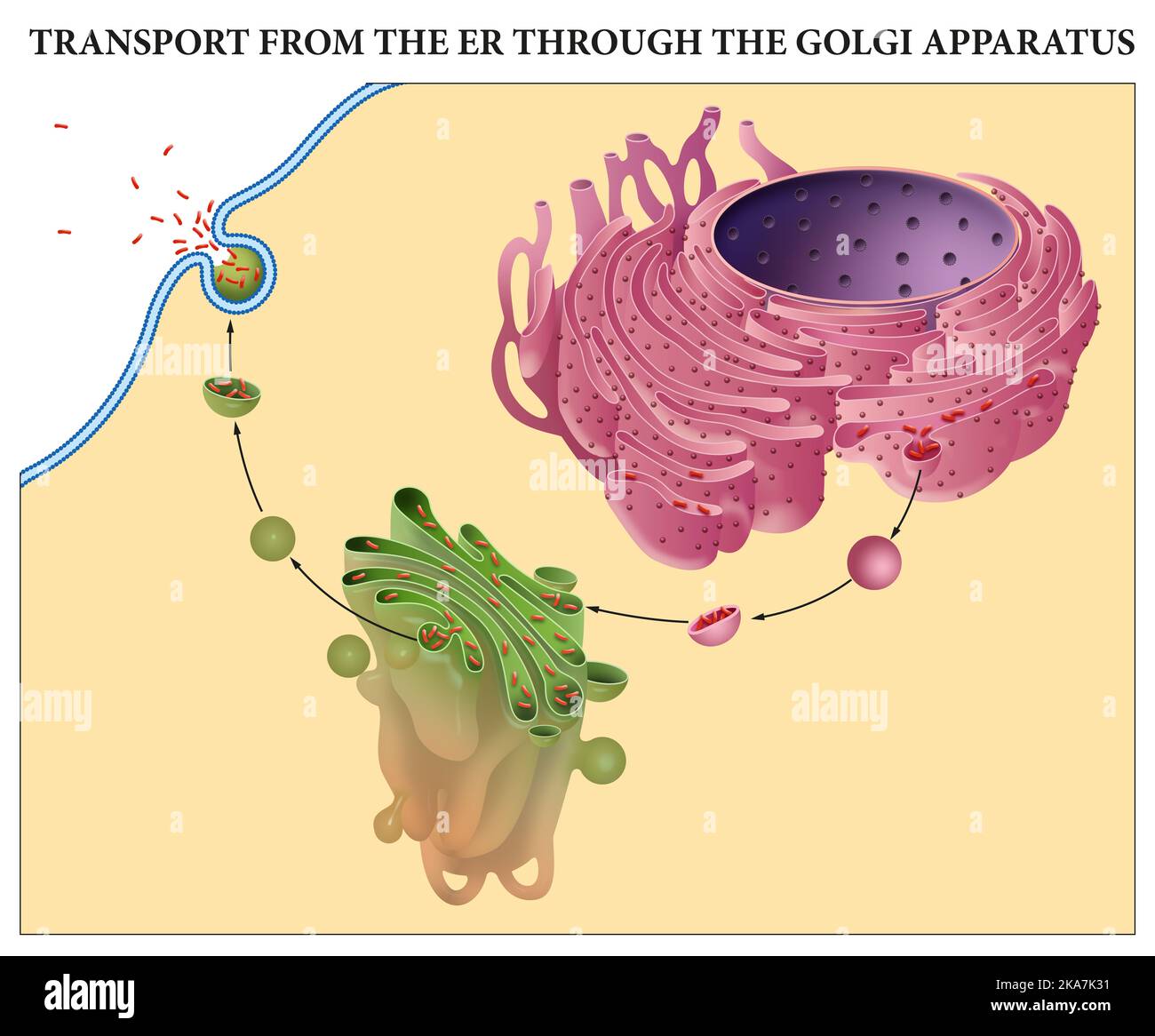
- The Cis-Face: This is the "receiving" side, closest to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), another key organelle involved in protein synthesis. Vesicles containing newly synthesized proteins and lipids bud off from the ER and fuse with the cis Golgi network. This is where the molecules enter the Golgi's processing pipeline.
- The Trans-Face: This is the "shipping" side, where molecules exit the Golgi. After being processed and modified as they travel through the Golgi stacks, the molecules are packaged into new vesicles at the trans Golgi network (TGN). These vesicles then bud off and are transported to their final destinations, which could be other organelles within the cell, the cell membrane, or even outside the cell.
Was Macht Der Golgi-Apparat? (What Does the Golgi Apparatus Do?)
Now for the important question: what exactly does this cellular post office *do*? The Golgi-Apparat plays a critical role in a variety of cellular processes, including:
1. Protein Modification: Adding the Finishing Touches
Proteins arriving from the ER are often incomplete. The Golgi acts like a master chef, adding the finishing touches. This includes:
- Glycosylation: This involves adding sugar molecules (glycans) to proteins. Glycosylation can affect protein folding, stability, and function. Think of it as adding decorative icing to a cake, making it both visually appealing and tastier (or, in this case, functionally optimized!).
- Phosphorylation: Adding phosphate groups to proteins can regulate their activity. It's like flipping a switch to turn a protein on or off.
- Sulfation: Adding sulfate groups to proteins can also affect their function and interactions.
These modifications are highly specific and carefully controlled, ensuring that each protein is properly equipped to perform its designated task.
2. Lipid Synthesis: Building the Cellular Foundation
While the ER is the primary site of lipid synthesis, the Golgi-Apparat also contributes to this process, particularly in modifying lipids and synthesizing specific types of lipids, such as sphingolipids and glycolipids. These lipids are essential components of cell membranes and play important roles in cell signaling and communication.
3. Packaging and Sorting: The Ultimate Organization
Perhaps the Golgi's most well-known function is packaging and sorting proteins and lipids into vesicles. These vesicles are like tiny delivery trucks, each carrying a specific cargo to a specific destination. The Golgi uses sophisticated sorting signals and mechanisms to ensure that the right molecules end up in the right vesicles.
The Golgi sorts molecules to various destinations, including:
- Lysosomes: These are the cell's recycling centers, containing enzymes that break down waste materials.
- The Cell Membrane: Proteins and lipids destined for the cell membrane are transported in vesicles that fuse with the membrane, delivering their cargo and expanding the cell's surface.
- Secretion: Some proteins are secreted outside the cell, such as hormones, enzymes, and antibodies. These are packaged into secretory vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the extracellular space.
4. Vesicle Transport: Delivering the Goods
Once the molecules are packaged into vesicles, they need to be transported to their final destinations. This is achieved by a complex network of motor proteins and cytoskeletal filaments (like microtubules and actin filaments). These motor proteins act like tiny truck drivers, pulling the vesicles along the filaments to their designated locations.
Why is the Golgi Apparatus Important?
The Golgi-Apparat is essential for the proper functioning of all eukaryotic cells (cells with a nucleus), including those in humans, animals, plants, and fungi. Without a functional Golgi, cells would be unable to process, modify, and sort proteins and lipids, leading to a variety of cellular dysfunctions. A malfunctioning Golgi can lead to diseases like:
- Certain genetic disorders (often rare)
- Some neurodegenerative diseases
- Even playing a role in some forms of cancer
In short, the Golgi is vital for:
- Maintaining cell structure and function
- Cell signaling and communication
- Proper protein and lipid metabolism
Der Golgi-Apparat: More Than Just a Cellular Post Office
While the analogy of a post office or packaging center is helpful, it's important to remember that the Golgi-Apparat is far more sophisticated. It's a dynamic and highly regulated organelle that plays a crucial role in cellular homeostasis. Its intricate processes ensure that the right molecules are delivered to the right places at the right time, allowing cells to perform their functions efficiently and effectively.
So, the next time you're enjoying a delicious Berliner or marveling at the architectural grandeur of the Brandenburg Gate, take a moment to appreciate the incredible complexity of the microscopic world within you – and the crucial role that the Golgi-Apparat plays in keeping it all running smoothly! Even on vacation, there's always something fascinating to learn!
Now you can impress your friends at the Biergarten with your newfound knowledge of cellular biology. Prost!
![Was Macht Der Golgi Apparat Golgi-Apparat einfach erklärt • Aufbau und Funktionen · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Folie1-4-1024x576.png)
![Was Macht Der Golgi Apparat Golgi-Apparat einfach erklärt • Aufbau und Funktionen · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Folie2-5-1024x576.png)