Welche Tiere Haben Kein Herz

Hallo zusammen! Welcome to a fascinating corner of the animal kingdom. You might be surprised to learn that not all creatures great and small possess a heart! While the heart is often considered a vital organ, some incredibly simple organisms have evolved to thrive without one. If you're curious about the natural world and enjoy uncovering unusual facts, then you're in for a treat. Let's dive into the world of animals without hearts!
Why No Heart? The Basics of Circulation
Before we meet our heartless stars, it's helpful to understand why a heart is important in the first place. A heart, quite simply, is a pump. Its primary job is to circulate fluids – usually blood – throughout an organism's body. This circulation is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products like carbon dioxide. Think of it as the body's intricate delivery and removal service.
However, this circulatory system becomes necessary when organisms become larger and more complex. Smaller, simpler creatures can rely on diffusion and other passive transport mechanisms to move essential substances around. Diffusion works by moving substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Imagine dropping a drop of food coloring into water – the color gradually spreads out. For very small animals, this is sufficient to meet their needs.
So, what kind of animals manage to survive without this essential pump? The answer lies in their simple body structures and lifestyles.
The Heartless Wonders: Meet the Candidates
Let's explore some specific animals that lack a heart:
1. Sponges (Porifera)
Sponges are among the simplest multicellular organisms on Earth. They are aquatic animals, mostly marine, and are often brightly colored. Think of them as living filters! They lack true tissues and organs, including, of course, a heart. Instead of a circulatory system, sponges rely on a network of pores and canals through which water flows. This water brings them food (tiny organic particles and plankton) and oxygen, while simultaneously carrying away waste.
The water flow is generated by specialized cells called choanocytes, which have flagella (whip-like structures) that beat in a coordinated manner. This movement creates a current that pulls water through the sponge's body. It’s an incredibly efficient system, especially considering its simplicity. When you see sponges during diving or snorkeling, you are actually witnessing a lifeform that completely bypasses the need for a heart!
Fun Fact: Sponges are capable of regenerating lost body parts! This ability showcases their remarkable simplicity and resilience.
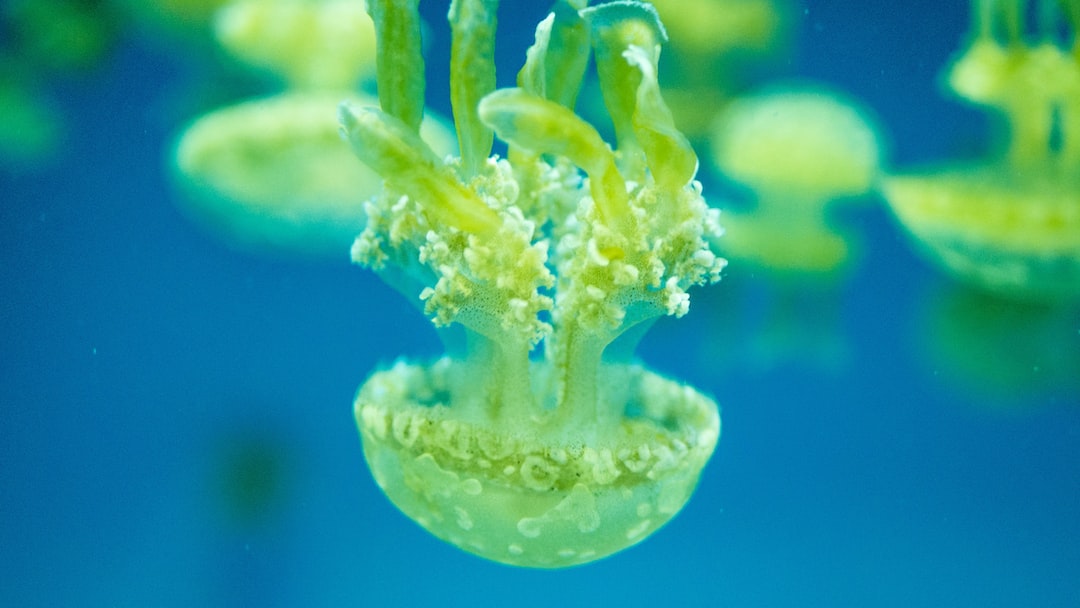
2. Jellyfish, Sea Anemones, and Corals (Cnidaria)
This group includes some of the most beautiful and mesmerizing creatures in the ocean. Jellyfish, with their graceful movements, and corals, with their vibrant colors, are both examples of Cnidarians. Like sponges, Cnidarians also lack a heart and a closed circulatory system. They possess a simple body plan characterized by radial symmetry and a sac-like body cavity called the gastrovascular cavity. This cavity serves as both a digestive system and a rudimentary circulatory system.
The gastrovascular cavity is lined with cells that secrete enzymes to break down food. Nutrients and oxygen are then distributed throughout the body via diffusion. Because Cnidarians are relatively thin-bodied, diffusion is sufficient to meet their metabolic needs. Waste products are also eliminated through the same cavity. Their entire body structure facilitates the distribution of resources, thereby making a dedicated heart unnecessary.
Jellyfish, in particular, exhibit a pulsating movement that helps to circulate fluids within their body cavity. This isn't a heart, but it helps to facilitate the movement of nutrients and waste. Important to remember: some jellyfish are venomous, so admire them from a safe distance!
3. Flatworms (Platyhelminthes)
Flatworms are a diverse group of invertebrates, including free-living species like planarians and parasitic species like tapeworms. While some flatworms have a more complex digestive system than sponges or Cnidarians, they still lack a heart and a circulatory system. Like their heartless counterparts, flatworms rely on diffusion to transport nutrients and oxygen throughout their body.
Flatworms are generally flat and thin, maximizing their surface area for diffusion. This allows them to efficiently exchange gases and nutrients with their environment. Some flatworms also possess a highly branched digestive system, which further enhances the distribution of nutrients throughout their body. However, their flat shape is crucial to their heartless existence.
While you might not encounter free-living flatworms as often as sponges or jellyfish during your travels, understanding their biology provides valuable insights into the diversity of life and the different ways organisms can adapt to their environments.
4. Nematodes (Roundworms)
Nematodes, or roundworms, are an incredibly abundant and diverse group of animals. They are found in virtually every habitat on Earth, from the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountain peaks. While they have a more complex body plan than sponges or Cnidarians, they still lack a heart and a circulatory system.
Nematodes have a pseudocoelom, a fluid-filled body cavity that surrounds their internal organs. This fluid helps to distribute nutrients and oxygen throughout their body. The movement of the worm also aids in the circulation of these fluids. However, diffusion remains the primary mechanism for nutrient and gas exchange.
Although you might not see them, nematodes play a crucial role in many ecosystems. They are important decomposers and nutrient recyclers, and some species are even used as biological control agents in agriculture. Their simple yet effective body plan allows them to thrive in a wide range of environments.
Why is this important for Tourists and Travelers?
You might be thinking: "Why should I care about animals without hearts on my vacation?" Well, understanding the diversity of life enhances your travel experiences! When you're snorkeling around coral reefs, appreciating the delicate beauty of jellyfish, or simply observing the natural world around you, knowing about these heartless wonders gives you a deeper appreciation for the complexity and adaptability of life on Earth.
Furthermore, learning about these creatures can inspire a sense of wonder and curiosity about the natural world. It encourages you to look beyond the familiar and to appreciate the incredible diversity of life forms that share our planet. This can lead to a more enriching and meaningful travel experience.
Practical Tip: When visiting marine ecosystems, be mindful of the delicate balance of these environments. Avoid touching corals or disturbing marine life. By being a responsible traveler, you can help to protect these incredible ecosystems for future generations to enjoy.
The Beauty of Simplicity
The animals without hearts may seem simple compared to more complex organisms like humans, but their existence highlights the ingenuity of evolution. They demonstrate that there are many different ways to thrive in the natural world, and that complexity is not always necessary for success.
So, next time you're exploring the world, remember the heartless wonders and appreciate the beauty of simplicity. You might be surprised at what you discover!
Final Thought: The absence of a heart doesn't make these animals any less fascinating or important. They are integral parts of their ecosystems and contribute to the biodiversity of our planet. So, embrace the unusual and explore the wonders of the natural world!