Wie Entsteht Der Saure Regen

Herzlich Willkommen! Planning a trip to Germany? Whether you're here to soak up the culture, explore the stunning landscapes, or delve into the rich history, you might hear whispers about "Saurer Regen" – Acid Rain. Don't worry, this isn't a weather phenomenon that will ruin your vacation! But understanding what it is and how it's formed is a fascinating piece of the environmental puzzle. So, let's dive into the world of acid rain in Germany and beyond, explained in a way that's easy to grasp and relevant to your stay.
What Exactly is Saurer Regen?
Saurer Regen, or Acid Rain, isn't just rain that's a little bit sour! It's a broader term referring to any form of precipitation – rain, snow, sleet, fog, or even dry deposition – that contains elevated levels of nitric and sulfuric acids. Normal rain is naturally slightly acidic, with a pH of around 5.6. Acid rain has a pH lower than that, often falling in the range of 4.2 to 4.4.
Think of it like this: imagine normal rain is a mild lemonade. Acid rain is like lemonade that's had way too much lemon juice squeezed into it – it's significantly more acidic than it should be.
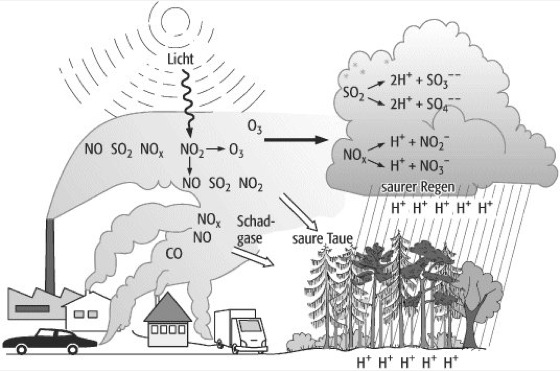
Wie Entsteht Der Saure Regen? (How is Acid Rain Formed?)
The formation of acid rain is a complex process involving atmospheric chemistry, but here’s a simplified breakdown:
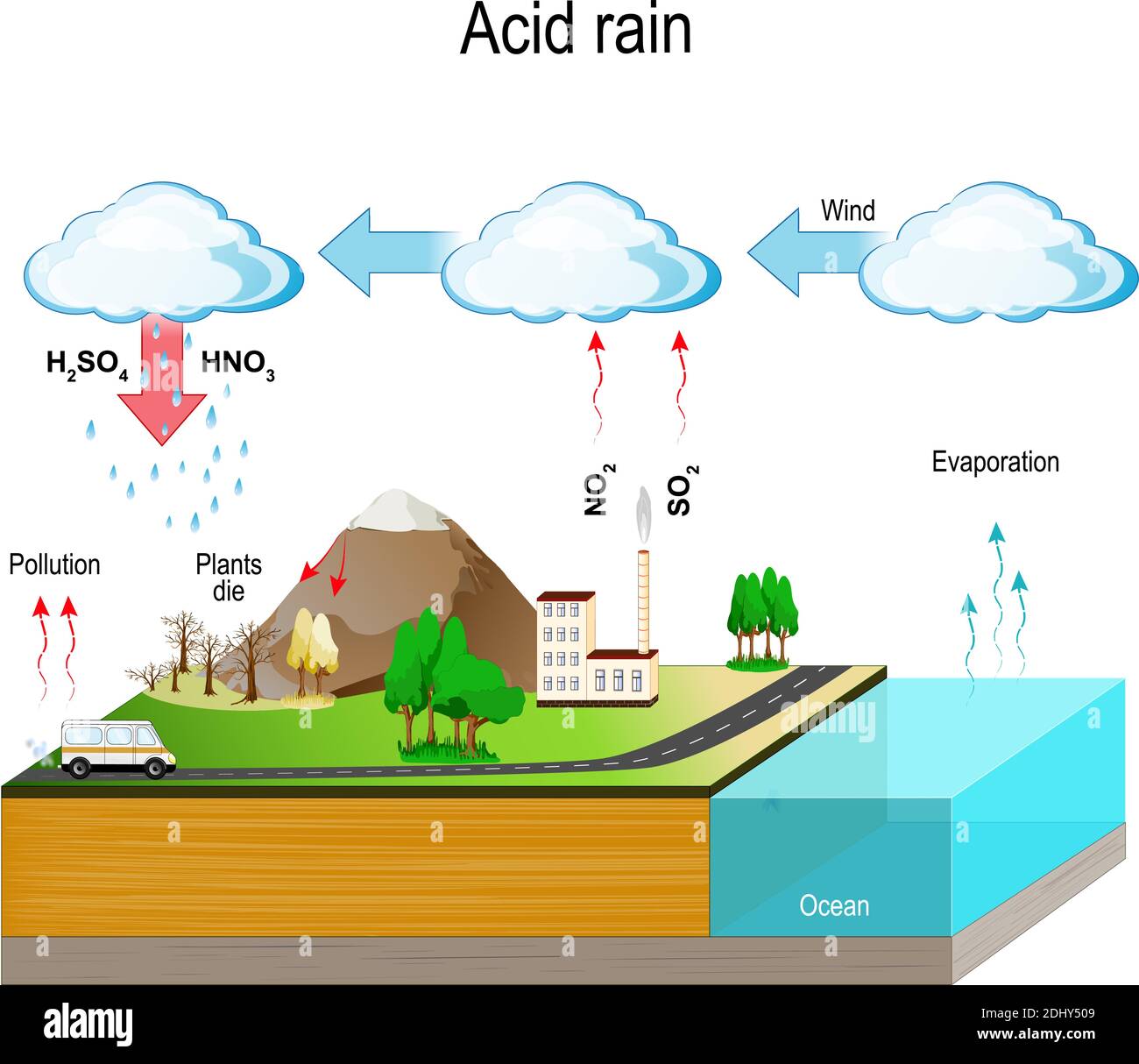
1. The Culprits: Pollutant Emissions
The main culprits behind acid rain are sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These gases are primarily released into the atmosphere through human activities, although some natural sources contribute too. The burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) in power plants, factories, and vehicles is the biggest offender. Other sources include:
- Industrial processes: Manufacturing processes, especially those involving smelting metals, can release significant amounts of SO2.
- Agricultural activities: Fertilizers and animal waste release ammonia (NH3), which can react in the atmosphere to form NOx.
- Transportation: Cars, trucks, and airplanes contribute to NOx emissions.
- Natural sources: Volcanic eruptions and lightning strikes can release SO2 and NOx, but these are generally less significant than human-caused emissions.
2. Atmospheric Transformation: Chemical Reactions
Once SO2 and NOx are in the atmosphere, they undergo a series of chemical reactions. These reactions involve oxidants like ozone (O3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals (OH•). Here's the gist:
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): SO2 reacts with oxidants to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This reaction can occur in the gas phase or within cloud droplets.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): NOx reacts with oxidants to form nitric acid (HNO3). Similar to SO2, this reaction can happen in both gas and liquid phases.
Essentially, the pollutant gases get transformed into strong acids in the atmosphere.
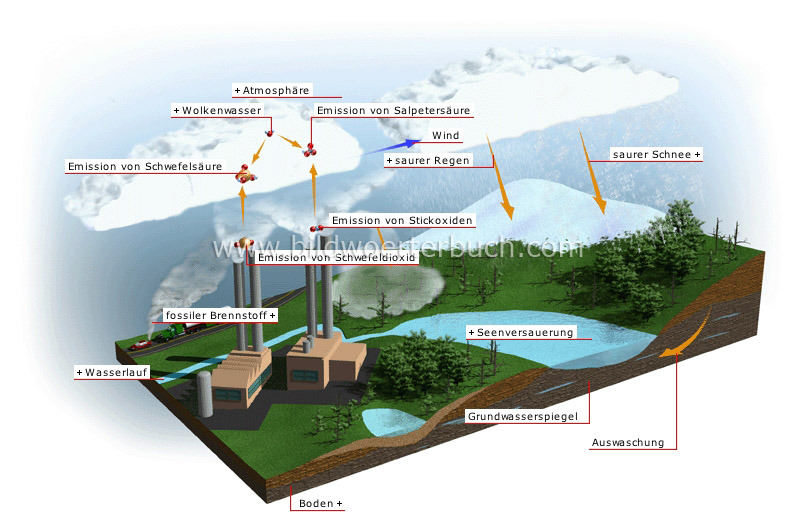
3. Deposition: Acid Falls to Earth
The sulfuric and nitric acids formed in the atmosphere eventually fall back to Earth through a process called deposition. There are two main types of deposition:
- Wet Deposition: This occurs when the acids are dissolved in rain, snow, sleet, or fog. This acidic precipitation then falls to the ground. This is what we typically think of as "acid rain."
- Dry Deposition: This happens when acidic particles and gases directly deposit onto surfaces like buildings, cars, trees, and soil. These dry deposits can then be washed away by subsequent rainfall, contributing to acid rain in the long run.
The distance that pollutants travel before being deposited can vary significantly. They can travel hundreds or even thousands of kilometers, meaning that acid rain can affect areas far away from the original source of pollution. This is often referred to as transboundary pollution.
The Effects of Acid Rain: A Wider Perspective
Acid rain has a wide range of negative effects on the environment and even human infrastructure. Here are some key impacts:
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Acid rain can acidify lakes, rivers, and streams, making it difficult for fish and other aquatic organisms to survive. Some species are more sensitive to acidity than others, leading to a disruption of the food chain. In extreme cases, entire lakes can become virtually lifeless.
- Forests: Acid rain damages tree leaves and needles, making them more vulnerable to diseases, pests, and harsh weather conditions. It also leaches essential nutrients from the soil, weakening trees and hindering their growth.
- Soil: Acid rain can alter the chemical composition of the soil, mobilizing toxic metals like aluminum, which can damage plant roots.
- Buildings and Monuments: Acid rain corrodes stone and metal structures, including buildings, statues, and monuments. Limestone and marble are particularly vulnerable to damage. Think of the majestic cathedrals and historical buildings across Europe – acid rain is a constant threat to their preservation.
- Human Health: While acid rain itself isn't directly harmful to humans, the pollutants that cause it (SO2 and NOx) can contribute to respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis.
Acid Rain in Germany: A Success Story of Reduction
Germany, like many other industrialized nations, has faced significant challenges related to acid rain. In the past, the industrial heartlands of the Ruhrgebiet and the former East Germany were particularly affected due to heavy reliance on coal-fired power plants and industrial activities.
However, Germany has made significant progress in reducing acid rain through a combination of policies and technological advancements. These include:
- Emission Controls: Strict regulations on industrial emissions and power plants have been implemented, requiring the use of technologies like scrubbers to remove SO2 from exhaust gases.
- Shift to Cleaner Energy Sources: Germany has been actively transitioning to renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and biomass, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy Efficiency Measures: Promoting energy efficiency in buildings and industries has helped to reduce overall energy consumption and emissions.
- Vehicle Emission Standards: Stricter emission standards for vehicles have been introduced, leading to a reduction in NOx emissions.
As a result of these efforts, acid rain is no longer as severe of a problem in Germany as it once was. The pH of rainfall has improved, and forests are showing signs of recovery in some areas. However, ongoing monitoring and continued efforts are still needed to ensure that the problem doesn't resurface.
What Can You Do During Your Stay?
While acid rain isn't likely to ruin your vacation in Germany, being aware of the issue and making environmentally conscious choices can contribute to a more sustainable future. Here are a few simple things you can do:
- Choose public transportation: Opt for trains, buses, or trams instead of renting a car whenever possible.
- Support eco-friendly businesses: Look for hotels, restaurants, and tour operators that prioritize sustainability.
- Conserve energy: Turn off lights and appliances when you leave your hotel room.
- Reduce your consumption: Avoid single-use plastics and other disposable items.
- Educate yourself: Learn more about environmental issues affecting Germany and other parts of the world.
By making small changes in your behavior, you can help to reduce your environmental impact and contribute to a healthier planet. Enjoy your stay in Germany! Knowing about Saurer Regen gives you an extra layer of appreciation for the efforts made and those still required to keep this beautiful country green and vibrant.
Remember: Even though acid rain is less of a problem in Germany now than in the past, continued vigilance and action are crucial to protecting our environment for future generations.